|
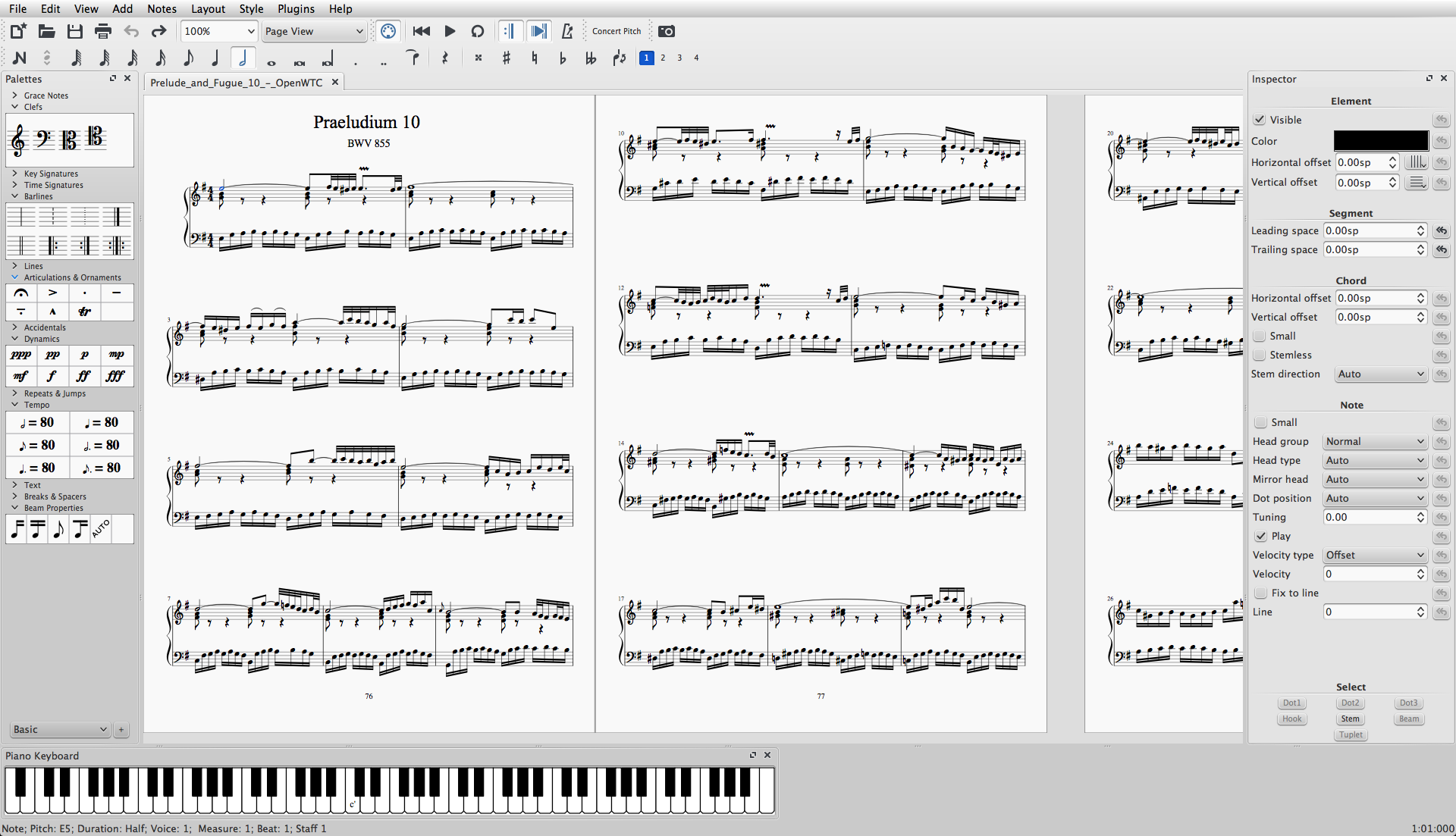
Audiveris
Audiveris is an open source tool for optical music recognition (OMR). It allows a user to import scanned music scores and export them to MusicXML format for use in other applications, e.g. music notation programs or page turning software for digital sheet music. Thanks to Tesseract it can also recognize text in scores. Audiveris is written in Java and published as free software. Audiveris V4 was published 26 November 2013 on the basis of Java Web Start under the terms of the GNU General Public License (GNU GPLv2). The source code of legacy versions as well as current development has moved to GitHub and is available under the terms of the GNU Affero General Public License The GNU Affero General Public License (GNU AGPL) is a free, copyleft license published by the Free Software Foundation in November 2007, and based on the GNU General Public License, version 3 and the Affero General Public License. The Free So ... (GNU AGPLv3). References External links * {{Official, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Music Recognition
Optical music recognition (OMR) is a field of research that investigates how to computationally read musical notation in documents. The goal of OMR is to teach the computer to read and interpret sheet music and produce a machine-readable version of the written music score. Once captured digitally, the music can be saved in commonly used file formats, e.g. MIDI (for playback) and MusicXML (for page layout). In the past it has, misleadingly, also been called "music optical character recognition". Due to significant differences, this term should no longer be used. History Optical music recognition of printed sheet music started in the late 1960s at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology when the first image scanners became affordable for research institutes. Due to the limited memory of early computers, the first attempts were limited to only a few measures of music. In 1984, a Japanese research group from Waseda University developed a specialized robot, called WABOT (WAseda roBOT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Music Recognition
Optical music recognition (OMR) is a field of research that investigates how to computationally read musical notation in documents. The goal of OMR is to teach the computer to read and interpret sheet music and produce a machine-readable version of the written music score. Once captured digitally, the music can be saved in commonly used file formats, e.g. MIDI (for playback) and MusicXML (for page layout). In the past it has, misleadingly, also been called "music optical character recognition". Due to significant differences, this term should no longer be used. History Optical music recognition of printed sheet music started in the late 1960s at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology when the first image scanners became affordable for research institutes. Due to the limited memory of early computers, the first attempts were limited to only a few measures of music. In 1984, a Japanese research group from Waseda University developed a specialized robot, called WABOT (WAseda roBOT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MusicXML
MusicXML is an XML-based file format for representing Western musical notation. The format iopen fully documented, and can be freely used under the W3C Community Final Specification Agreement. History MusicXML was invented by Michael Good and initially developed by Recordare LLC. It derived several key concepts from existing academic formats (such as Walter Hewlett's ASCII-based MuseData and David Huron's Humdrum). It is designed for the interchange of scores, particularly between different scorewriters. MusicXML development was managed by MakeMusic following the company's acquisition of Recordare in 2011. MusicXML development was transferred to the W3C Music Notation Community Group in July 2015. Version 1.0 was released in January 2004. Version 1.1 was released in May 2005 with improved formatting support. Version 2.0 was released in June 2007 and included a standard compressed format. All of these versions were defined by a series of document type definitions (DTDs). An XML Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Sheet Music
Digital sheet music is technology for representing and displaying sheet music in a computer-readable format. With the emergence of several technological innovations, sheet music evolved in several stages into what was to be termed digital sheet music. Music Notation Software With the increased use of professional and personal computers during the 1980s, different programmers started working on desktop publishing music notation software. Various boxed music notation software applications appeared on the market, allowing users to input and edit sheet music digitally. In the beginning, the software only permitted printing on paper. It took some time before other virtual formats became possible (e.g. standard MIDI file, audio (wav, mp3) and MusicXML export). These files allowed manipulation such as instrument changes, transposition and even MIDI playback. In particular, software projects Finale and Sibelius grew to become successful commercial products and to define certain standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-platform Free Software
In computing, cross-platform software (also called multi-platform software, platform-agnostic software, or platform-independent software) is computer software that is designed to work in several computing platforms. Some cross-platform software requires a separate build for each platform, but some can be directly run on any platform without special preparation, being written in an interpreted language or compiled to portable bytecode for which the interpreters or run-time packages are common or standard components of all supported platforms. For example, a cross-platform application may run on Microsoft Windows, Linux, and macOS. Cross-platform software may run on many platforms, or as few as two. Some frameworks for cross-platform development are Codename One, Kivy, Qt, Flutter, NativeScript, Xamarin, Phonegap, Ionic, and React Native. Platforms ''Platform'' can refer to the type of processor (CPU) or other hardware on which an operating system (OS) or application runs, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music OCR Software
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect of all human societies, a cultural universal. While scholars agree that music is defined by a few specific elements, there is no consensus on their precise definitions. The creation of music is commonly divided into musical composition, musical improvisation, and musical performance, though the topic itself extends into academic disciplines, criticism, philosophy, and psychology. Music may be performed or improvised using a vast range of instruments, including the human voice. In some musical contexts, a performance or composition may be to some extent improvised. For instance, in Hindustani classical music, the performer plays spontaneously while following a partially defined structure and using characteristic motifs. In modal jazz the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GitHub
GitHub, Inc. () is an Internet hosting service for software development and version control using Git. It provides the distributed version control of Git plus access control, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, continuous integration, and wikis for every project. Headquartered in California, it has been a subsidiary of Microsoft since 2018. It is commonly used to host open source software development projects. As of June 2022, GitHub reported having over 83 million developers and more than 200 million repositories, including at least 28 million public repositories. It is the largest source code host . History GitHub.com Development of the GitHub.com platform began on October 19, 2007. The site was launched in April 2008 by Tom Preston-Werner, Chris Wanstrath, P. J. Hyett and Scott Chacon after it had been made available for a few months prior as a beta release. GitHub has an annual keynote called GitHub Universe. Organizational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public License (GNU GPL or simply GPL) is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the Four Freedoms (Free software), four freedoms to run, study, share, and modify the software. The license was the first copyleft for general use and was originally written by the founder of the Free Software Foundation (FSF), Richard Stallman, for the GNU Project. The license grants the recipients of a computer program the rights of the Free Software Definition. These GPL series are all copyleft licenses, which means that any derivative work must be distributed under the same or equivalent license terms. It is more restrictive than the GNU Lesser General Public License, Lesser General Public License and even further distinct from the more widely used permissive software licenses BSD licenses, BSD, MIT License, MIT, and Apache License, Apache. Historically, the GPL license family has been one of the most popular software licenses in the free and open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java Web Start
In computing, Java Web Start (also known as JavaWS, javaws or JAWS) is a deprecated framework developed by Sun Microsystems (now Oracle) that allows users to start application software for the Java Platform directly from the Internet using a web browser. The technology enables seamless version updating for globally distributed applications and greater control of memory allocation to the Java virtual machine. Java Web Start was distributed as part of the Java Platform until being removed in Java SE 11, following its deprecation in Java SE 9. The code for Java Web Start was not released by Oracle as part of OpenJDK, and thus OpenJDK originally did not support it. IcedTea-Web provides an independent open source implementation of Java Web Start that is currently developed by the AdoptOpenJDK community, RedHat and Karakun AG, and which is bundled in the official OpenJDK installer. Next to this OpenWebStart provides an open source based implementation that is based on IcedTea-Web but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
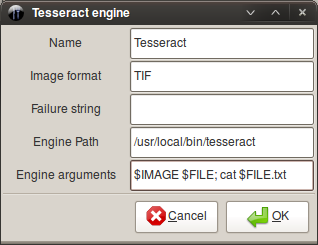
Tesseract (software)
Tesseract is an optical character recognition engine for various operating systems. It is free software, released under the Apache License. Originally developed by Hewlett-Packard as proprietary software in the 1980s, it was released as open source in 2005 and development has been sponsored by Google since 2006.Announcing Tesseract OCR - The official Google blog In 2006, Tesseract was considered one of the most accurate open-source OCR engines available. History The Tesseract engine was originally developed as proprietary software at Hewlett Packard labs in Bristol, England and Greeley, Colorado between 1985 and 1994, with more changes made in 1996 to port to Windows, and some migration from C (programming lan ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy. Popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, and Ubuntu, the latter of which itself consists of many different distributions and modifications, including Lubuntu and Xubuntu. Commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux Enterprise. Desktop Linux distributions include a windowing system such as X11 or Wayland, and a desktop environment such as GNOME or KDE Plasma. Distributions intended for ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scorewriter
A scorewriter, or music notation program is software for creating, editing and printing sheet music. A scorewriter is to music notation what a word processor is to text, in that they typically provide flexible editing and automatic layout, and produce high-quality printed results. Most scorewriters, especially those from the 2000s, can record notes played on a MIDI keyboard (or other MIDI instruments), and play music back via MIDI or virtual instruments. Playback is especially useful for novice composers and music students, and when musicians are not available or affordable. Several free programs are widely used, such as MuseScore. The three main professional-level programs are Finale, Sibelius and Dorico. Comparison with multitrack sequencer software Multitrack sequencer software and scorewriters typically employ different methods for notation input and display. Scorewriters are based on traditional music notation, using staff lines and round note heads, which originates f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)