|
Atlaua
In Aztec mythology, Atlahua, Ahtlahua, Atlahoa, Atlavâ or Atlaua was a water God (the blue version of Tlaloc, the Tlaloc from the South), fisherman and archer. There were said to be at least four ancient Aztec temples at which he was worshiped, the tallest supposedly being over 200 feet tall (61 metres) . The Aztecs prayed to him when there were deaths in water, such as when Hernando Cortez conquered Tenochtitlan (the Ancient Aztec capital on a lake, now Mexico City), and the lake was said to be "floating with heads and corpses". The original image appears in General History of the Things of New Spain by Fray Bernardino de Sahagún Bernardino de Sahagún, OFM (; – 5 February 1590) was a Franciscan friar, missionary priest and pioneering ethnographer who participated in the Catholic evangelization of colonial New Spain (now Mexico). Born in Sahagún, Spain, in 1499, he ...: The Florentine Codex. Book II: The Ceremonies References Aztec mythology and religion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlaua - Project Gutenberg EText 14993
In Aztec mythology, Atlahua, Ahtlahua, Atlahoa, Atlavâ or Atlaua was a water God (the blue version of Tlaloc, the Tlaloc from the South), fisherman and archer. There were said to be at least four ancient Aztec temples at which he was worshiped, the tallest supposedly being over 200 feet tall (61 metres) . The Aztecs prayed to him when there were deaths in water, such as when Hernando Cortez conquered Tenochtitlan (the Ancient Aztec capital on a lake, now Mexico City), and the lake was said to be "floating with heads and corpses". The original image appears in General History of the Things of New Spain by Fray Bernardino de Sahagún Bernardino de Sahagún, OFM (; – 5 February 1590) was a Franciscan friar, missionary priest and pioneering ethnographer who participated in the Catholic evangelization of colonial New Spain (now Mexico). Born in Sahagún, Spain, in 1499, he ...: The Florentine Codex. Book II: The Ceremonies References Aztec mythology and religion W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Mythology
Aztec mythology is the body or collection of myths of the Aztec civilization of Central Mexico. The Aztecs were Nahuatl-speaking groups living in central Mexico and much of their mythology is similar to that of other Mesoamerican cultures. According to legend, the various groups who were to become the Aztecs arrived from the north into the Anahuac valley around Lake Texcoco. The location of this valley and lake of destination is clear – it is the heart of modern Mexico City – but little can be known with certainty about the origin of the Aztec. There are different accounts of their origin. In the myth the ancestors of the Mexica/Aztec came from a place in the north called Aztlan, the last of seven ''nahuatlacas'' (Nahuatl-speaking tribes, from ''tlaca'', "man") to make the journey southward, hence their name "Azteca." Other accounts cite their origin in Chicomoztoc, "the place of the seven caves," or at Tamoanchan (the legendary origin of all civilizations). The Mexic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hernando Cortez
Hernando is a common Spanish given name, equivalent to Fernando and the English Ferdinand. It may refer to: Places ;Canada * Hernando Island, British Columbia ;United States * Hernando, Florida * Hernando County, Florida * Hernando, Mississippi ;Argentina * Hernando, Córdoba * Hernandos Hideaway long jetty Australia People * Hernando de Soto (economist) * Hernando de Soto (explorer) * Hernando Cortes, alternate spelling of Hernán Cortés * Mila Hernando (1957–2017), Spanish diplomat Horse * Hernando (horse) (1990-2013), French-trained racehorse, winner of the 1993 Prix du Jockey Club {{Disambiguation, geo, given name, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
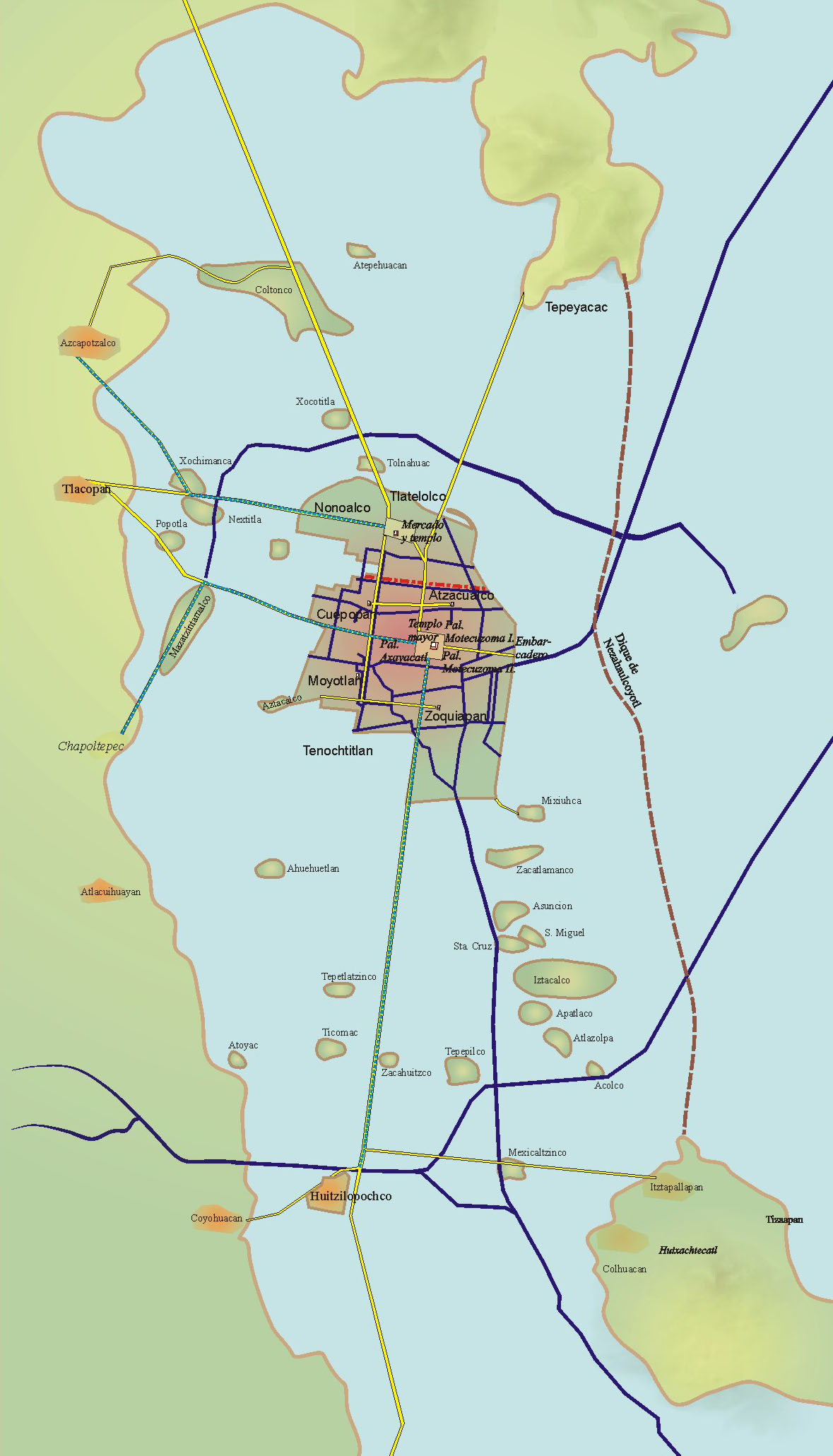
Tenochtitlan
, ; es, Tenochtitlan also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, ; es, México-Tenochtitlan was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear. The date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th anniversary of the city. The city was built on an island in what was then Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. The city was the capital of the expanding Aztec Empire in the 15th century until it was captured by the Spanish in 1521. At its peak, it was the largest city in the pre-Columbian Americas. It subsequently became a '' cabecera'' of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Today, the ruins of are in the historic center of the Mexican capital. The World Heritage Site of contains what remains of the geography (water, boats, floating gardens) of the Mexica capital. was one of two Mexica (city-states or polities) on the island, the other being . The city is located in modern-day Mexico City. Etymolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernardino De Sahagún
Bernardino de Sahagún, OFM (; – 5 February 1590) was a Franciscan friar, missionary priest and pioneering ethnographer who participated in the Catholic evangelization of colonial New Spain (now Mexico). Born in Sahagún, Spain, in 1499, he journeyed to New Spain in 1529. He learned Nahuatl and spent more than 50 years in the study of Aztec beliefs, culture and history. Though he was primarily devoted to his missionary task, his extraordinary work documenting indigenous worldview and culture has earned him the title as “the first anthropologist."Arthur J.O. Anderson, "Sahagún: Career and Character" in Bernardino de Sahagún, ''Florentine Codex: The General History of the Things of New Spain, Introductions and Indices'', Arthur J.O. Anderson and Charles Dibble, translators. Salt Lake City: University of Utah Press 1982, p. 40.M. León-Portilla, ''Bernardino de Sahagún: The First Anthropologist'' (University of Oklahoma Press, Norman, 2002), pp. He also contributed to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Mythology And Religion
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl language and who dominated large parts of Mesoamerica from the 14th to the 16th centuries. Aztec culture was organized into city-states (''altepetl''), some of which joined to form alliances, political confederations, or empires. The Aztec Empire was a confederation of three city-states established in 1427: Tenochtitlan, city-state of the Mexica or Tenochca; Texcoco; and Tlacopan, previously part of the Tepanec empire, whose dominant power was Azcapotzalco. Although the term Aztecs is often narrowly restricted to the Mexica of Tenochtitlan, it is also broadly used to refer to Nahua polities or peoples of central Mexico in the prehispanic era, as well as the Spanish colonial era (1521–1821). The definitions of Aztec and Aztecs have long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |