|
Asynchronous System
The primary focus of this article is asynchronous control in digital electronic systems. In a synchronous system, operations ( instructions, calculations, logic, etc.) are coordinated by one, or more, centralized clock signals. An asynchronous system, in contrast, has no global clock. Asynchronous systems do not depend on strict arrival times of signals or messages for reliable operation. Coordination is achieved using event-driven architecture triggered by network packet arrival, changes (transitions) of signals, handshake protocols, and other methods. Modularity Asynchronous systems – much like object-oriented software – are typically constructed out of modular 'hardware objects', each with well-defined communication interfaces. These modules may operate at variable speeds, whether due to data-dependent processing, dynamic voltage scaling, or process variation. The modules can then be combined to form a correct working system, without reference to a global ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Synchronous System
In digital electronics, a synchronous circuit is a digital circuit in which the changes in the state of memory elements are synchronized by a clock signal. In a sequential digital logic circuit, data is stored in memory devices called flip-flops or latches. The output of a flip-flop is constant until a pulse is applied to its "clock" input, upon which the input of the flip-flop is latched into its output. In a synchronous logic circuit, an electronic oscillator called the ''clock'' generates a string (sequence) of pulses, the "clock signal". This clock signal is applied to every storage element, so in an ideal synchronous circuit, every change in the logical levels of its storage components is simultaneous. Ideally, the input to each storage element has reached its final value before the next clock occurs, so the behaviour of the whole circuit can be predicted exactly. Practically, some delay is required for each logical operation, resulting in a maximum speed limitations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quasi-delay-insensitive Circuit
A quasi-delay-insensitive circuit (QDI circuit) is an asynchronous circuit design methodology employed in digital logic design. Developed in response to the performance challenges of building sub-micron, multi-core architectures with conventional synchronous designs, QDI circuits exhibit lower power consumption, extremely fine-grain pipelining, high circuit robustness against process–voltage–temperature variations, on-demand (event-driven) operation, and data-dependent completion time. Overview Advantages * Robust against process variation, temperature fluctuation, circuit redesign, and FPGA remapping. * Natural event sequencing facilitates complex control circuitry. * Automatic clock gating and compute-dependent cycle time can save dynamic power and increase throughput by optimizing for average-case workload characteristics instead of worst-case. Disadvantages * Delay insensitive encodings generally require twice as many wires for the same data. * Communication protoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Worst-case
In computer science, best, worst, and average cases of a given algorithm express what the resource usage is ''at least'', ''at most'' and ''on average'', respectively. Usually the resource being considered is running time, i.e. time complexity, but could also be memory or some other resource. Best case is the function which performs the minimum number of steps on input data of n elements. Worst case is the function which performs the maximum number of steps on input data of size n. Average case is the function which performs an average number of steps on input data of n elements. In real-time computing, the worst-case execution time is often of particular concern since it is important to know how much time might be needed ''in the worst case'' to guarantee that the algorithm will always finish on time. Average performance and worst-case performance are the most used in algorithm analysis. Less widely found is best-case performance, but it does have uses: for example, where the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rail (electronics)
Rail or rails may refer to: Rail transport *Rail transport and related matters *Railway track or railway lines, the running surface of a railway Arts and media Film * ''Rails'' (film), a 1929 Italian film by Mario Camerini * ''Rail'' (1967 film), a film by Geoffrey Jones for British Transport Films * ''Rail'' (2024 film), a Tamil-language film Magazines * ''Rail'' (magazine), a British rail transport periodical * ''Rails'' (magazine), a former New Zealand based rail transport periodical Other arts *The Rails, a British folk-rock band * Rail (theater) or batten, a pipe from which lighting, scenery, or curtains are hung Technology *Rails framework or Ruby on Rails, a web application framework *Rail system (firearms), a mounting system for firearm attachments *Front engine dragster *Runway alignment indicator lights, a configuration of an approach lighting system *Rule Augmented Interconnect Layout, a specification for expressing guidelines for printed circuit boards; companion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
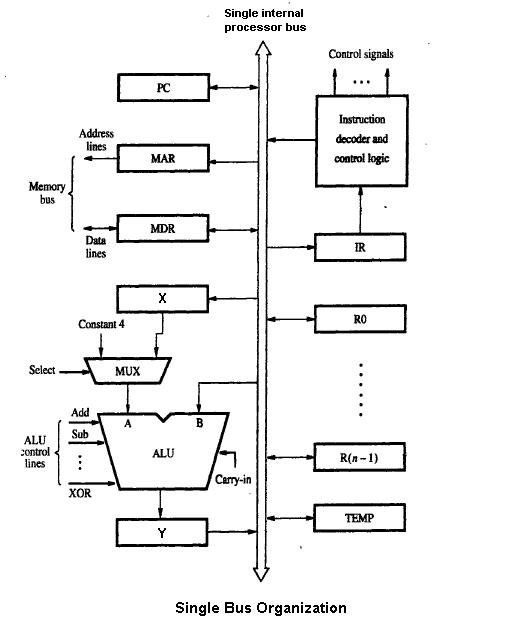
Datapath
A data path is a collection of functional units such as arithmetic logic units (ALUs) or multipliers that perform data processing operations, registers, and buses. Along with the control unit it composes the central processing unit (CPU). A larger data path can be made by joining more than one data paths using multiplexers. A data path is the ALU, the set of registers, and the CPU's internal bus(es) that allow data to flow between them. The simplest design for a CPU uses one common internal bus. Efficient addition requires a slightly more complicated three-internal-bus structure. Many relatively simple CPUs have a 2-read, 1-write register file connected to the 2 inputs and 1 output of the ALU. During the late 1990s, there was growing research in the area of reconfigurable data paths—data paths that may be re-purposed at run-time using programmable fabric—as such designs may allow for more efficient processing as well as substantial power savings. Finite-state machi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Protocol (computing)
A communication protocol is a system of rules that allows two or more entities of a communications system to transmit information via any variation of a physical quantity. The protocol defines the rules, syntax, semantics, and synchronization of communication and possible error recovery methods. Protocols may be implemented by hardware, software, or a combination of both. Communicating systems use well-defined formats for exchanging various messages. Each message has an exact meaning intended to elicit a response from a range of possible responses predetermined for that particular situation. The specified behavior is typically independent of how it is to be implemented. Communication protocols have to be agreed upon by the parties involved. To reach an agreement, a protocol may be developed into a technical standard. A programming language describes the same for computations, so there is a close analogy between protocols and programming languages: ''protocols are to communica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Handshake (computing)
In computing, a handshake is a signal between two devices or programs, used to, e.g., authenticate, coordinate. An example is the handshaking between a hypervisor and an application in a guest virtual machine. In telecommunications, a handshake is an automated process of negotiation between two participants (example "Alice and Bob") through the exchange of information that establishes the protocols of a communication link at the start of the communication, before full communication begins. The handshaking process usually takes place in order to establish rules for communication when a computer attempts to communicate with another device. Signals are usually exchanged between two devices to establish a communication link. For example, when a computer communicates with another device such as a modem, the two devices will signal each other that they are switched on and ready to work, as well as to agree to which protocols are being used. Handshaking can negotiate parameters tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Synchronize
Synchronization is the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. For example, the conductor of an orchestra keeps the orchestra synchronized or ''in time''. Systems that operate with all parts in synchrony are said to be synchronous or ''in sync''—and those that are not are ''asynchronous''. Today, time synchronization can occur between systems around the world through satellite navigation signals and other time and frequency transfer techniques. Navigation and railways Time-keeping and synchronization of clocks is a critical problem in long-distance ocean navigation. Before radio navigation and satellite-based navigation, navigators required accurate time in conjunction with astronomical observations to determine how far east or west their vessel traveled. The invention of an accurate marine chronometer revolutionized marine navigation. By the end of the 19th century, important ports provided time signals in the form of a signal gun, flag, or dropping tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Communication Channel
A communication channel refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel in telecommunications and computer networking. A channel is used for information transfer of, for example, a digital bit stream, from one or several '' senders'' to one or several '' receivers''. A channel has a certain capacity for transmitting information, often measured by its bandwidth in Hz or its data rate in bits per second. Communicating an information signal across distance requires some form of pathway or medium. These pathways, called communication channels, use two types of media: Transmission line-based telecommunications cable (e.g. twisted-pair, coaxial, and fiber-optic cable) and broadcast (e.g. microwave, satellite, radio, and infrared). In information theory, a channel refers to a theoretical ''channel model'' with certain error characteristics. In this more general view, a storag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Asynchronous Communication
In telecommunications, asynchronous communication is transmission of data, generally without the use of an external clock signal, where data can be transmitted intermittently rather than in a steady stream. Any timing required to recover data from the communication symbols is encoded within the symbols. The most significant aspect of asynchronous communications is that data is not transmitted at regular intervals, thus making possible variable bit rate, and that the transmitter and receiver clock generators do not have to be exactly synchronized all the time. In asynchronous transmission, data is sent one byte at a time and each byte is preceded by start and stop bits. Physical layer In asynchronous serial communication in the physical protocol layer, the data blocks are code words of a certain word length, for example octets ( bytes) or ASCII characters, delimited by start bits and stop bits. A variable length space can be inserted between the code words. No bit syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pipeline (computing)
In computing, a pipeline, also known as a data pipeline, is a set of data processing elements connected in series, where the output of one element is the input of the next one. The elements of a pipeline are often executed in parallel or in time-sliced fashion. Some amount of buffer storage is often inserted between elements. Concept and motivation Pipelining is a commonly used concept in everyday life. For example, in the assembly line of a car factory, each specific task—such as installing the engine, installing the hood, and installing the wheels—is often done by a separate work station. The stations carry out their tasks in parallel, each on a different car. Once a car has had one task performed, it moves to the next station. Variations in the time needed to complete the tasks can be accommodated by "buffering" (holding one or more cars in a space between the stations) and/or by "stalling" (temporarily halting the upstream stations), until the next station becomes avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Microcontroller
A microcontroller (MC, uC, or μC) or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Program memory in the form of NOR flash, OTP ROM, or ferroelectric RAM is also often included on the chip, as well as a small amount of RAM. Microcontrollers are designed for embedded applications, in contrast to the microprocessors used in personal computers or other general-purpose applications consisting of various discrete chips. In modern terminology, a microcontroller is similar to, but less sophisticated than, a system on a chip (SoC). A SoC may include a microcontroller as one of its components but usually integrates it with advanced peripherals like a graphics processing unit (GPU), a Wi-Fi module, or one or more coprocessors. Microcontrollers are used in automatically controlled products and devices, such as automobile engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |