|
Assembly Theory
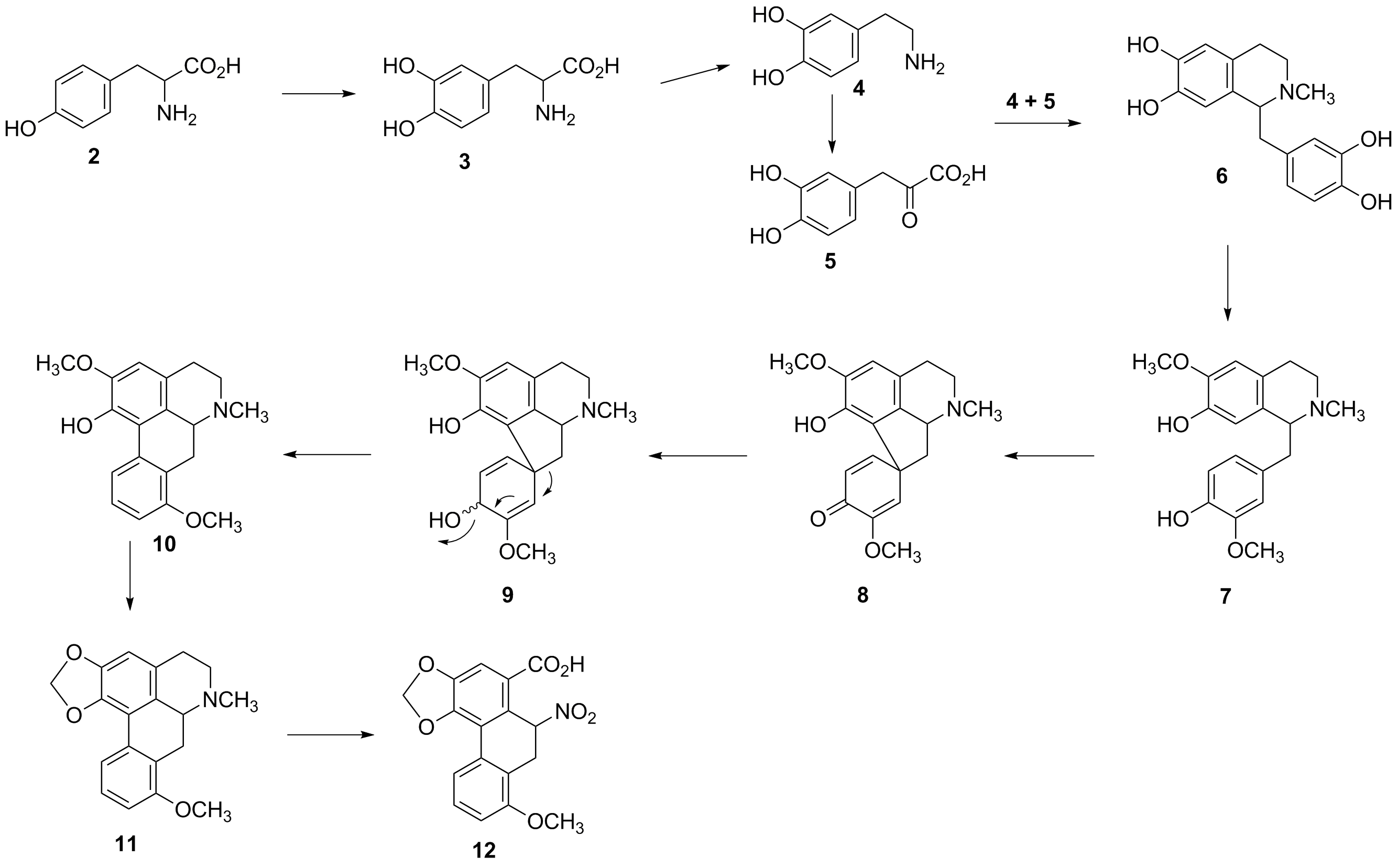
Assembly theory is a theory that characterizes object complexity. When applied to molecule complexity, its authors claim it to be the first technique that is experimentally verifiable, unlike other molecular complexity algorithms that lack experimental measure. The theory was developed as a means to detect evidence of extraterrestrial life from data gathered by astronomical observations or probes. Background The theory was invented by Leroy Cronin and developed by the team he leads at the University of Glasgow, then extended in collaboration with a team at Arizona State University led by Sara Imari Walker. It is difficult to identify chemical signatures that are unique to life. For example, the Viking lander biological experiments detected molecules that could be explained by either living or natural non-living processes. Assembly theory outputs how complex a given object is as a function of the number of independent parts and their abundances. To calculate how complex an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking Lander Biological Experiments
In 1976 two identical Viking program landers each carried four types of biological experiments to the surface of Mars. The first successful Mars landers, ''Viking 1'' and ''Viking 2'', then carried out experiments to look for biosignatures of microbial life on Mars. The landers each used a robotic arm to pick up and place soil samples into sealed test containers on the craft. The two landers carried out the same tests at two places on Mars' surface, ''Viking 1'' near the equator and ''Viking 2'' further north. The experiments The four experiments below are presented in the order in which they were carried out by the two Viking landers. The biology team leader for the Viking program was Harold P. Klein (NASA Ames). Gas chromatograph — mass spectrometer A gas chromatograph — mass spectrometer (GCMS) is a device that separates vapor components chemically via a gas chromatograph and then feeds the result into a mass spectrometer, which measures the molecular weight of each c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lex Fridman Podcast
Lex Fridman ( /'lɛks 'friːdmæn/; , Russian: ) is a Russian-American computer scientist, podcaster, and an artificial intelligence researcher. He is a research scientist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, and he hosts the ''Lex Fridman Podcast'', a podcast and YouTube series. Early life Fridman was born in Chkalovsk on 15 August 1983, and grew up in Moscow. He is primarily of Ukrainian-Jewish descent. His father, plasma physicist Alexander Fridman, was born in Kyiv and serves as the John A. Nyheim Chair Professor and Director of the C.J. Nyheim Plasma Institute at Drexel University's College of Engineering. His maternal grandmother was born and raised in Kharkiv, and his maternal grandfather was a machine gunner in the Ukrainian branch of the Red Army against the Nazis during World War II. In 1994, Fridman moved to the U.S. with his family at the age of 11. He attended Neuqua Valley High School in Naperville, Illinois, graduating in 2001. He then went on to obta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Problem For Groups
In mathematics, especially in the area of abstract algebra known as combinatorial group theory, the word problem for a finitely generated group ''G'' is the algorithmic problem of deciding whether two words in the generators represent the same element. More precisely, if ''A'' is a finite set of generators for ''G'' then the word problem is the membership problem for the formal language of all words in ''A'' and a formal set of inverses that map to the identity under the natural map from the free monoid with involution on ''A'' to the group ''G''. If ''B'' is another finite generating set for ''G'', then the word problem over the generating set ''B'' is equivalent to the word problem over the generating set ''A''. Thus one can speak unambiguously of the decidability of the word problem for the finitely generated group ''G''. The related but different uniform word problem for a class ''K'' of recursively presented groups is the algorithmic problem of deciding, given as input a pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Interstellar And Circumstellar Molecules
This is a list of molecules that have been detected in the interstellar medium and circumstellar envelopes, grouped by the number of component atoms. The chemical formula is listed for each detected compound, along with any ionized form that has also been observed. Background The molecules listed below were detected through astronomical spectroscopy. Their spectral features arise because molecules either absorb or emit a photon of light when they transition between two molecular energy levels. The energy (and thus the wavelength) of the photon matches the energy difference between the levels involved. Molecular electronic transitions occur when one of the molecule's electrons moves between molecular orbitals, producing a spectral line in the ultraviolet, optical or near-infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. Alternatively, a vibrational transition transfers quanta of energy to (or from) vibrations of molecular bonds, producing signatures in the mid- or far-infrared. Ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosignatures
A biosignature (sometimes called chemical fossil or molecular fossil) is any substance – such as an element, isotope, or molecule – or phenomenon that provides scientific evidence of past or present life. Measurable attributes of life include its complex physical or chemical structures and its use of free energy and the production of biomass and wastes. A biosignature can provide evidence for living organisms outside the Earth and can be directly or indirectly detected by searching for their unique byproducts. Types In general, biosignatures can be grouped into ten broad categories:NASA Astrobiology Strategy 2015 .(PDF), NASA # |
Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Tandem mass spectrometry, also known as MS/MS or MS2, is a technique in instrumental analysis where two or more mass analyzers are coupled together using an additional reaction step to increase their abilities to analyse chemical samples. A common use of tandem MS is the analysis of biomolecules, such as proteins and peptides. The molecules of a given sample are ionized and the first spectrometer (designated MS1) separates these ions by their mass-to-charge ratio (often given as m/z or m/Q). Ions of a particular m/z-ratio coming from MS1 are selected and then made to split into smaller fragment ions, e.g. by collision-induced dissociation, ion-molecule reaction, or photodissociation. These fragments are then introduced into the second mass spectrometer (MS2), which in turn separates the fragments by their m/z-ratio and detects them. The fragmentation step makes it possible to identify and separate ions that have very similar m/z-ratios in regular mass spectrometers. Struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recursively
Recursion (adjective: ''recursive'') occurs when a thing is defined in terms of itself or of its type. Recursion is used in a variety of disciplines ranging from linguistics to logic. The most common application of recursion is in mathematics and computer science, where a function being defined is applied within its own definition. While this apparently defines an infinite number of instances (function values), it is often done in such a way that no infinite loop or infinite chain of references ("crock recursion") can occur. Formal definitions In mathematics and computer science, a class of objects or methods exhibits recursive behavior when it can be defined by two properties: * A simple ''base case'' (or cases) — a terminating scenario that does not use recursion to produce an answer * A ''recursive step'' — a set of rules that reduces all successive cases toward the base case. For example, the following is a recursive definition of a person's ''ancestor''. One's ances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
YouTube
YouTube is a global online video platform, online video sharing and social media, social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by Google, and is the List of most visited websites, second most visited website, after Google Search. YouTube has more than 2.5 billion monthly users who collectively watch more than one billion hours of videos each day. , videos were being uploaded at a rate of more than 500 hours of content per minute. In October 2006, YouTube was bought by Google for $1.65 billion. Google's ownership of YouTube expanded the site's business model, expanding from generating revenue from advertisements alone, to offering paid content such as movies and exclusive content produced by YouTube. It also offers YouTube Premium, a paid subscription option for watching content without ads. YouTube also approved creators to participate in Google's Google AdSens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sara Imari Walker
Sara Imari Walker is an American Theoretical physics, theoretical physicist and Astrobiology, astrobiologist with research interests in the origins of life, astrobiology, physics of life, emergence, complex and dynamical systems, and artificial life. Walker is currently Deputy Director of the Beyond Center for Fundamental Concepts in Science at Arizona State University, Associate Director of the ASU-SFI Center for Biosocial Complex Systems and an associate professor at Arizona State University (ASU). She is a co-founder of the astrobiology social network S.A.G.A.N., SAGANet.org, and on the board of directors for Blue Marble Space a nonprofit education and science organization. She has appeared on multiple media sources, such as Through the Wormhole, "Through the Wormhole with Morgan Freeman", to communicate science to the public. Education and background Walker was born and raised in Connecticut. She studied at the Florida Institute of Technology where she graduated cum laude ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complexity
Complexity characterises the behaviour of a system or model whose components interaction, interact in multiple ways and follow local rules, leading to nonlinearity, randomness, collective dynamics, hierarchy, and emergence. The term is generally used to characterize something with many parts where those parts interact with each other in multiple ways, culminating in a higher order of emergence greater than the sum of its parts. The study of these complex linkages at various scales is the main goal of complex systems theory. The intuitive criterion of complexity can be formulated as follows: a system would be more complex if more parts could be distinguished, and if more connections between them existed. Science takes a number of approaches to characterizing complexity; Zayed ''et al.'' reflect many of these. Neil F. Johnson, Neil Johnson states that "even among scientists, there is no unique definition of complexity – and the scientific notion has traditionally been conveyed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
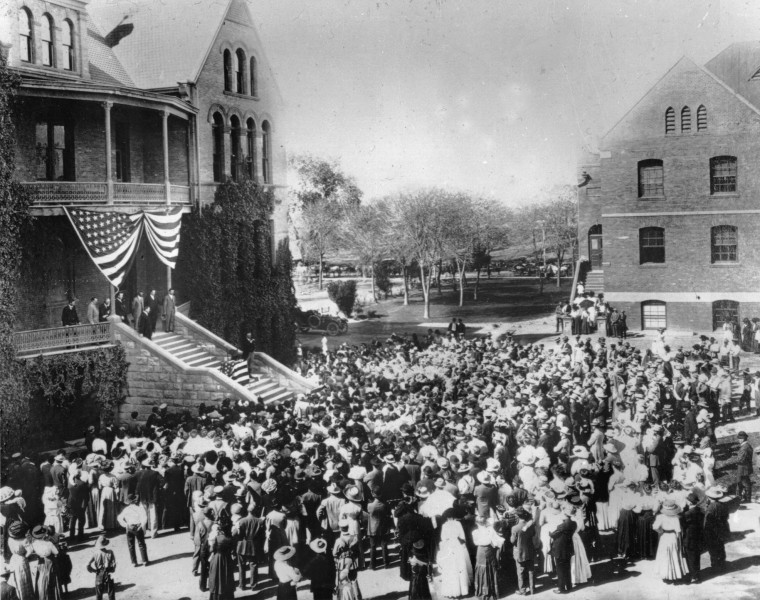
Arizona State University
Arizona State University (Arizona State or ASU) is a public research university in the Phoenix metropolitan area. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, ASU is one of the largest public universities by enrollment in the U.S. One of three universities governed by the Arizona Board of Regents, ASU is a member of the Universities Research Association and classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very High Research Activity". ASU has nearly 150,000 students attending classes, with more than 38,000 students attending online, and 90,000 undergraduates and nearly 20,000 postgraduates across its five campuses and four regional learning centers throughout Arizona. ASU offers 350 degree options from its 17 colleges and more than 170 cross-discipline centers and institutes for undergraduates students, as well as more than 400 graduate degree and certificate programs. The Arizona State Sun Devils compete in 26 varsity-level sports in the NCAA Division I Pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |