|
Askim
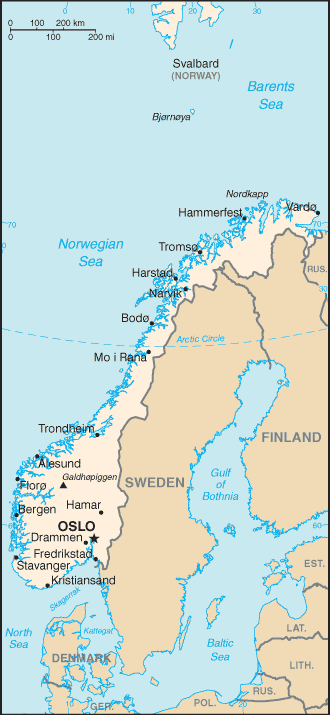
Askim () is a town and a former municipality in (from January 1, 2020) Indre Østfold Kommune in the former county of Østfold county (from January 1, 2020 a part of Viken county), Norway. The administrative centre of the Askim municipality was the town of Askim. Askim was established as a municipality on 1 January 1838 (see formannskapsdistrikt). Askim is the largest population centre in the Indre Østfold region, with 15,315 inhabitants as of 2012, and serves as a regional center for nine municipalities in the Indre Østfold region. It lies next to the longest river in Norway, Glomma, which forms the border with the former Spydeberg municipality to the north and west, and Skiptvet municipality to the south. Askim also borders to the former Trøgstad municipality to the northeast and the former Eidsberg municipality to the southeast. Askim produces large amounts of hydroelectricity at three dams / hydroelectric power plants in the river Glomma The Glomma, or Glåma, is N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solbergfoss
Solbergfoss is a small village in Askim municipality, Norway. Located a few miles north of the town Askim on the east bank of the Glomma The Glomma, or Glåma, is Norway's longest and most voluminous river. With a total length of , it has a drainage basin that covers fully 13% of Norway's surface area, all in the southern part of the country. Geography At its fullest length, the ... river, Solbergfoss has a power plant which was built in 1924. In 1918 a railway line, Askim–Solbergfosslinjen, from Askim to Solbergfoss was built. ReferencesSolbergfoss Spydeberg-Askim Villages in Østfold Askim Populated places on the Glomma River {{østfold-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Østfold
Østfold is a traditional region, a former county and a current electoral district in southeastern Norway. It borders Akershus and southwestern Sweden (Västra Götaland County and Värmland), while Buskerud and Vestfold are on the other side of Oslofjord. The county's administrative seat was Sarpsborg. The county controversially became part of the newly established Viken County on 1 January 2020. Many manufacturing facilities are situated here, such as the world's most advanced biorefinery, Borregaard in Sarpsborg. Fredrikstad has shipyards. There are granite mines in Østfold and stone from these were used by Gustav Vigeland. The county slogan is "The heartland of Scandinavia". The local dialects are characterized by their geographical proximity to Sweden. The name The old name of the Oslofjord was ''Fold''; ''Østfold'' means 'the region east of the Fold' (see also Vestfold). The name was first recorded in 1543; in the Middle Ages the name of the county was ''Borga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kykkelsrud
Kykkelsrud is a village in Askim municipality, Norway. Located a few kilometres west of the town Askim, it is a part of the urban area of the same name, which has a population of 12,570. Kykkelsrud, located on the east bank of the Glomma river, has a power plant which harnesses the Kykkelsrud waterfall. Immediately north of the village is the four-lane Smaalenene Bridge, opened in 2010 and carrying the European Route E18 European route E18 runs from Craigavon in Northern Ireland to Saint Petersburg in Russia, passing through Scotland, England, Norway, Sweden and Finland. It is about in length. Although the designation implies the possibility of a through jo ... over the Glomma. References Kykkelsrud hydroelectric plant- Hafslund Energi Villages in Østfold Askim Populated places on the Glomma River {{østfold-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glava
Glava AS is a Norwegian industrial company with headquarters in Askim. The name is a portmanteau of the Norwegian word ''glassvatt'', meaning glass wool. Glass wool used as insulation material is the company's main product. Production takes place at the company's production facilities in Askim and Stjørdal. Glava employs around 500 people, and in 2007 had a revenue just short of NOK 1,500 million. The company's history goes back to 1935, when industrialist Jens Bull was offered licensed production in Norway of glass wool, originally a German invention. The company was originally called "Glassvatt". During the post-war reconstruction of Norway, Glava grew dramatically, as the need for insulation of buildings became clear. The product is today made on a licence from the French company Saint-Gobain. It is produced from borosilicate glass, which is heated to around 1,400 °C before being stretched into fibres. In 1959, the company was responsible for the so-called " ice block e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Towns And Cities In Norway
Below is a list of towns and cities in Norway. The Norwegian word for town or city is ''by''. Cities were formerly categorized as ''kjøpstad'' (market town) or '' ladested'' (small seaport), each with special rights. The special trading rights for cities were abolished in 1857, and the classification was entirely rescinded in 1952 and replaced by the simple classification ''by''. Overview From 1 January 1965 the focus was moved from the individual cities to their corresponding municipalities. Norwegian municipalities were classified as ''bykommune'' (urban municipality) or ''herredskommune'' (rural municipality). The distinction was rescinded by The Local Government Act of 1992. The municipalities were ordered by so-called municipality numbers, four-digit codes based on ISO 3166-2:NO which in 1946 were assigned to each municipality. Urban municipalities got a municipality number in which the third digit was a zero. Between 1960 and 1965 many Norwegian municipalities were merged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vamma Hydroelectric Power Station
Vamma Power Station (''Vamma kraftstasjon'') is a hydroelectric power station located on the river Glomma approximately 4.5 km south of Askim, Østfold, Norway. Sam Eyde formed Vamma Fossekompagnie in 1902 to build a power plant for a fertilizer factory. The factory plans were canceled in 1912 and Vamma Fossekompagnie was sold to Hafslund (company). Construction of the power station started in 1907 and in 1915 the first two turbines were completed. Another six turbines were built between 1915 and 1927. In 1944 the final two were complete. The installed capacity at that point was from ten horizontal Francis turbines with dual runners. Between 1967 and 1971 a Kaplan turbine was built, adding another , and it now operates at an installed capacity of , with an average annual production of 1,275 GWh. In 2015 the construction of a twelfth turbine began on the south side of the dam. This is also a Kaplan turbine rated at . The new turbine will allow the ten old turbines to only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spydeberg
Spydeberg was a municipality in former Østfold county, Norway, until December 31. 2019. At January 1. 2020 it became a part of the new and greater municipality named " Indre Østfold Kommune" after the region, together with Askim and Trøgstad and Eidsberg and Hobøl kommuner (Municipalities). The administrative centre of the Spydeberg municipality was the village of Spydeberg. Spydeberg Kommune (municipality) was divided into the parishes of Spydeberg, Heli, and Hovin and was established as a municipality on 1 January 1838 (see formannskapsdistrikt). The village of Spydeberg has approximately 5,500 inhabitants. It is located southeast of Oslo and is easily reached by both car and bus and train. At the most there used to be 16 daily buses to Oslo (the capital of Norway), and about 21 train departures. Like the rest of the Indre Østfold region, many of the citizens of Spydeberg commute daily to Oslo for work. General information Name The municipality (originally the par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indre Østfold
Indre Østfold is a mostly rural countryside region north in the former county of Østfold county in Norway, noted for its mostly unspoilt nature and for its agriculture. At January 1. 2020 five of the municipalities of Indre Østfold merged into the new Indre Østfold municipality at the same date as the Østfold fylke and neighbouring Akershus fylke merged with Buskerud fylke and became regions in the new Viken fylke (county). Today the region consists of these five municipalities: * Indre Østfold * Marker Kommune (Marker, Norway) * Skiptvet * Rakkestad * Aremark * Former municipality of Rømskog, now a part of the municipality of Aurskog-Høland. Location It is located around 30 kilometers from Norway's capital Oslo, with the Europavei ("Europe Way" / European route) E18 as the main arterial road through the region, and several Riksvei national roads running through the area. Indre Østfold also has its own rail route, the Eastern Østfold Line of the Østfold Line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formannskapsdistrikt
() is the name for Norwegian local self-government districts that were legally enacted on 1 January 1838. This system of municipalities was created in a bill approved by the Parliament of Norway and signed into law by King Carl Johan on 14 January 1837. The ''formannskaps'' law, which fulfilled an express requirement of the Constitution of Norway, required that every parish ( no, prestegjeld) form a ''formannsskapsdistrikt'' (municipality) on 1 January 1838. In this way, the parishes of the state Church of Norway became worldly, administrative districts as well. (Although some parishes were divided into two or three municipalities.) In total, 396 ''formannsskapsdistrikts'' were created under this law, and different types of ''formannskapsdistrikts'' were created, also: History The introduction of self government in rural districts was a major political change. The Norwegian farm culture (''bondekultur'') that emerged came to serve as a symbol of nationalistic resistance to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia are three of the leading rubber producers. Types of polyisoprene that are used as natural rubbers are classified as elastomers. Currently, rubber is harvested mainly in the form of the latex from the rubber tree (''Hevea brasiliensis'') or others. The latex is a sticky, milky and white colloid drawn off by making incisions in the bark and collecting the fluid in vessels in a process called "tapping". The latex then is refined into the rubber that is ready for commercial processing. In major areas, latex is allowed to coagulate in the collection cup. The coagulated lumps are collected and processed into dry forms for sale. Natural rubber is used extensively in many applications and products, either alone or in combination wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Tyres
Continental AG, commonly known as Continental or colloquially as Conti, is a German multinational automotive parts manufacturing company specializing in tires, brake systems, interior electronics, automotive safety, powertrain and chassis components, tachographs, and other parts for the automotive and transportation industries. Continental is structured into six divisions: Chassis and Safety, Powertrain, Interior, Tires, ContiTech, ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems). It is headquartered in Hanover, Lower Saxony. Continental is the world's fourth-largest tire manufacturer. Continental sells tires for automobiles, motorcycles, and bicycles worldwide under the Continental brand. It also produces and sells other brands with more select distribution such as Viking (limited global presence), General (US/Canada), Gislaved (Canada, Spain, Nordic Markets), Semperit Tyres, Barum to serve EU & Russia. Other brands are ''Uniroyal'' (Europe), Sportiva, Mabor and Matador and formerl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking Gummi
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden), who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9–22. They also voyaged as far as the Mediterranean, North Africa, Volga Bulgaria, the Middle East, and North America. In some of the countries they raided and settled in, this period is popularly known as the Viking Age, and the term "Viking" also commonly includes the inhabitants of the Scandinavian homelands as a collective whole. The Vikings had a profound impact on the early medieval history of Scandinavia, the British Isles, France, Estonia, and Kievan Rus'. Expert sailors and navigators aboard their characteristic longships, Vikings established Norse settlements and governments in the British Isles, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Greenland, Normandy, and the Baltic coast, as well as alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |