|
Ashoka's Hell
Ashoka's Hell was, according to legend, an elaborate torture chamber disguised as a beautiful palace full of amenities such as exclusive baths and decorated with flowers, fruit trees and ornaments. It was built by Emperor Ashoka (304–232 BCE) in Pataliputra (modern-day Patna, India), the capital city of the Maurya Empire. The torture palace's legend is detailed in the ''Ashokavadana'', the text that describes Emperor Ashoka's life through both legendary and historical accounts. According to legend, the palatial torture chamber was artfully designed to make its exterior visually pleasing, and was referred to as the "beautiful gaol". Beneath the veneer of beauty and deep inside the exclusive mansion, however, chambers were constructed filled with sadistic and cruel instruments of torture—including furnaces used to melt the metals that were to be poured on prisoners. The narrative states the chamber's architect drew inspiration from the five tortures of the Buddhist hell. The ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torture Chamber
A torture chamber is a room where torture is inflicted.Princeton Wordnet definition of Torture chamber Wordnetweb.princeton.edu. Retrieved on 2011-08-30. The medieval torture chamber was windowless and often built underground, was lit by a few candles and was specifically designed to induce "horror, dread and despair" to anyone but those possessing a strong mind and "nerves of steel". Historically, torture chambers were located in royal palaces, in castles of the nobility and even buildings belonging to the church. They featured secret trap-doors which could be activated to throw victims into dark |
Nelumbo
''Nelumbo'' is a genus of aquatic plants with large, showy flowers. Members are commonly called lotus, though the name is also applied to various other plants and plant groups, including the unrelated genus '' Lotus''. Members outwardly resemble those in the family Nymphaeaceae ("water lilies"), but ''Nelumbo'' is actually very distant to that family. There are only two known living species of lotus; ''Nelumbo nucifera'' is native to East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia and probably Australia, and is better-known. It is commonly cultivated; it is eaten and used in traditional Chinese medicine. The other lotus is ''Nelumbo lutea'', which is native to North America and the Caribbean. Horticultural hybrids have been produced between these two allopatric species. Description Ultrahydrophobicity The leaves of ''Nelumbo'' are highly water-repellent (i.e. they exhibit ultrahydrophobicity) and have given the name to what is called the lotus effect. Ultrahydrophobicity involves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Patna
Patna, the capital of Bihar state, India, is one of the oldest continuously inhabited places in the world and the history of Patna spans at least three millennia. Patna has the distinction of being associated with the two most ancient religions of the world, namely, Buddhism and Jainism. The ancient city of Pataliputra (predecessor of modern Patna) was the capital of the Mauryan, Shunga, and Gupta Empires. It has been a part of the Delhi Sultanate and the Mughal Empire and has seen the rule of the Nawabs of Bengal, the East India Company and the British Raj. During British rule, the Patna University, as well as several other educational institutions, were established. Patna was one of the nerve centers of First War of Independence, participated actively in India's Independence movement, and emerged in the post-independent India as the most populous city of East India after Kolkata. Prehistory and Origin The first accepted references to the place are observed m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd-century BC Establishments In India
The 3rd century was the period from 201 ( CCI) to 300 (CCC) Anno Domini (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar.. In this century, the Roman Empire saw a crisis, starting with the assassination of the Roman Emperor Severus Alexander in 235, plunging the empire into a period of economic troubles, barbarian incursions, political upheavals, civil wars, and the split of the Roman Empire through the Gallic Empire in the west and the Palmyrene Empire in the east, which all together threatened to destroy the Roman Empire in its entirety, but the reconquests of the seceded territories by Emperor Aurelian and the stabilization period under Emperor Diocletian due to the administrative strengthening of the empire caused an end to the crisis by 284. This crisis would also mark the beginning of Late Antiquity. In Persia, the Parthian Empire was succeeded by the Sassanid Empire in 224 after Ardashir I defeated and killed Artabanus V during the Battle of Hormozdgan. The Sassanids the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferno (Dante)
''Inferno'' (; Italian language, Italian for "Hell") is the first part of Italian writer Dante Alighieri's 14th-century Epic poetry, epic poem ''Divine Comedy''. It is followed by ''Purgatorio'' and ''Paradiso (Dante), Paradiso''. The ''Inferno'' describes Dante's journey through Christian views on Hell, Hell, guided by the Ancient Rome, ancient Roman poet Virgil. In the poem, Hell is depicted as nine concentric circles of torment located within the Earth; it is the "realm ... of those who have rejected spiritual values by yielding to bestial appetites or violence, or by perverting their human intellect to fraud or malice against their fellowmen". As an allegory, the ''Divine Comedy'' represents the journey of the soul toward God, with the ''Inferno'' describing the recognition and rejection of sin. Prelude to Hell Canto I The poem begins on the night of Maundy Thursday on March 24 (or April 7), 1300, shortly before the dawn of Good Friday. The narrator, Dante himself, is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agam Kuan
Agam Kuan ( hi, अगम कुआं ,"unfathomable well") is an ancient well and archaeological site in Patna, India. It is said to date back to the period of Mauryan emperor, Ashoka (304–232 BCE). Circular in shape, the well is lined with brick in the upper and contains wooden rings in the remaining . The Agam Kuan is set within an archaeological site identified by the Archaeological Survey of India which also contains the adjacent Shitala Devi temple where the folk deity Shitala Devi is venerated. Inside this temple, the pindas of the Saptamatrikas (the seven mother goddesses) are worshipped. The temple is widely revered for its belief in curing smallpox and chicken pox. Location Agam Kuan is situated close to the Gulzarbagh railway station, on the way to Panch Pahadi, on the outskirts of Patna, Bihar state. It is east of Patna and south-west of Gulzarbagh Station. India According to the legend During the 1890s, the British explorer, Laurence Waddell, while exploring t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurence Waddell
Lieutenant Colonel Laurence Austine Waddell, CB, CIE, F.L.S., L.L.D, M.Ch., I.M.S. RAI, F.R.A.S (29 May 1854 – 19 September 1938) was a Scottish explorer, Professor of Tibetan, Professor of Chemistry and Pathology, Indian Army surgeon, collector in Tibet, and amateur archaeologist. Waddell also studied Sumerian and Sanskrit; he made various translations of seals and other inscriptions. His reputation as an Assyriologist gained little to no academic recognition and his books on the history of civilization have caused controversy. Some of his book publications however were popular with the public, and he is regarded by some today to have been a real-life precursor of the fictional character Indiana Jones. Life Laurence Waddell was born on 29 May 1854, and was the son of Rev. Thomas Clement Waddell, a Doctor of Divinity at Glasgow University and Jean Chapman, daughter of John Chapman of Banton, Stirlingshire.Thomas, 1939. Laurence Waddell obtained a bachelor's degre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faxian
Faxian (法顯 ; 337 CE – c. 422 CE), also referred to as Fa-Hien, Fa-hsien and Sehi, was a Chinese Buddhist monk and translator who traveled by foot from China to India to acquire Buddhist texts. Starting his arduous journey about age 60, he visited sacred Buddhist sites in Central, South and Southeast Asia between 399 and 412 CE, of which 10 years were spent in India. He described his journey in his travelogue, ''A Record of Buddhist Kingdoms'' (''Foguo Ji'' 佛國記). His memoirs are notable independent record of early Buddhism in India. He took with him a large number of Sanskrit texts, whose translations influenced East Asian Buddhism and which provide a ''terminus ante quem'' for many historical names, events, texts, and ideas therein.Faxian ''Encyclopaedia Britannica'', 2019. Biography ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xuanzang
Xuanzang (, ; 602–664), born Chen Hui / Chen Yi (), also known as Hiuen Tsang, was a 7th-century Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making contributions to Chinese Buddhism, the travelogue of his journey to India in 629–645 CE, his efforts to bring over 657 Indian texts to China, and his translations of some of these texts.Li Rongxi (1996), ''The Great Tang Dynasty Record of the Western Regions'', Bukkyo Dendo Kyokai and Numata Center for Buddhist Translation and Research, Berkeley, , pp. xiii-xiv Xuanzang was born on 6 April 602 in Chenliu, what is now Kaifeng municipality in Henan province. As a boy, he took to reading religious books, and studying the ideas therein with his father. Like his elder brother, he became a student of Buddhist studies at Jingtu monastery. Xuanzang was ordained as a ''śrāmaṇera'' (novice monk) at the age of thirteen. Due to the political and social unrest caused by the fall of the Sui dynasty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stupas
A stupa ( sa, स्तूप, lit=heap, ) is a mound-like or hemispherical structure containing relics (such as ''śarīra'' – typically the remains of Bhikkhu, Buddhist monks or Bhikkhuni, nuns) that is used as a place of meditation. In Buddhism, circumambulation or ''pradakhshina'' has been an important ritual and devotional practice since the earliest times, and stupas always have a ''pradakhshina'' path around them. The original South Asian form is a large solid dome above a tholobate or drum with vertical sides, which usually sits on a square base. There is no access to the inside of the structure. In large stupas there may be walkways for circumambulation on top of the base as well as on the ground below it. Large stupas have or had ''vedikā'' railings outside the path around the base, often highly decorated with sculpture, especially at the torana gateways, of which there are usually four. At the top of the dome is a thin vertical element, with one of more horizo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dharma
Dharma (; sa, धर्म, dharma, ; pi, dhamma, italic=yes) is a key concept with multiple meanings in Indian religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism and others. Although there is no direct single-word translation for ''dharma'' in European languages, it is commonly translated as "righteousness", "merit" or "religious and moral duties" governing individual conduct.Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopaedia. (9 April 2019)Dharma. ''Encyclopedia Britannica''. Accessed 14 September 2021. In Hinduism, dharma is one of the four components of the ''Puruṣārtha'', the aims of life, and signifies behaviours that are considered to be in accord with '' Ṛta'', the order that makes life and universe possible. It includes duties, rights, laws, conduct, virtues and "right way of living".see: *"Dharma", ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'', 6th Ed. (2013), Columbia University Press, Gale, ; *Steven Rosen (2006), Essential Hinduism, Praeger, , Chapter 3. It had a transtempor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
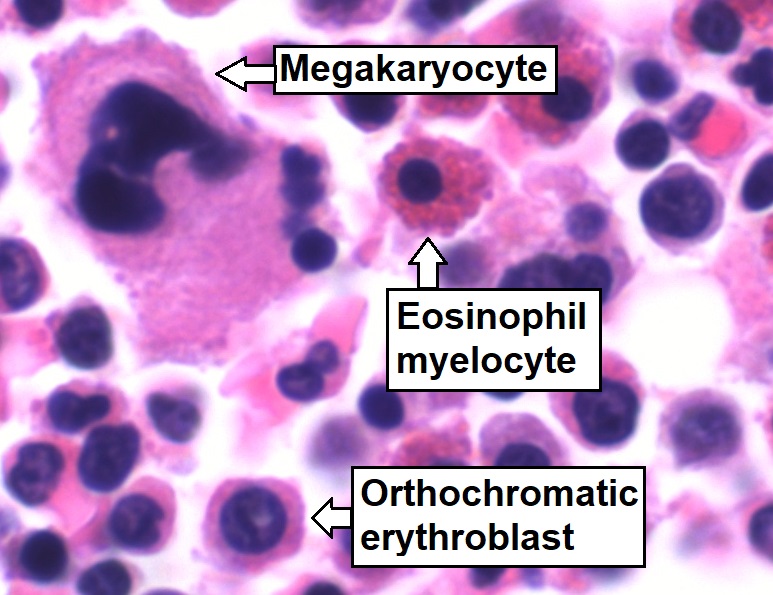
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a man weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of hematopoietic cells, including both myeloid and lymphoid lineages, are created in bone marrow; however, lymphoid cells must migrate to other lymphoid organs (e.g. thymus) in order to complete maturation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

-_water_drops_W_IMG_8657.jpg)