|
Artemis-1
Artemis 1, officially Artemis I and formerly Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), was an uncrewed Moon-orbiting mission. As the first major spaceflight of NASA's Artemis program, Artemis 1 marked the return of the agency to lunar exploration originally begun as the Apollo program decades earlier. It was the first integrated flight test of the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Its main objective was to test the Orion spacecraft, especially its heat shield, in preparation for subsequent Artemis missions. These missions seek to reestablish a human presence on the Moon and demonstrate technologies and business approaches needed for future scientific studies, including exploration of Mars. The Orion spacecraft for Artemis 1 was stacked on October 20, 2021, marking the first time a super-heavy-lift vehicle has been stacked inside NASA's Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) since the final Saturn V in 1973. On August 17, 2022, the fully stacked vehicle was rolled out fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vehicle Assembly Building
The Vehicle Assembly Building (originally the Vertical Assembly Building), or VAB, is a large building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center (KSC), designed to assemble large pre-manufactured space vehicle components, such as the massive Saturn V and the Space Shuttle, and stack them vertically onto one of three mobile launcher platforms used by NASA. As of March 2022, the first Space Launch System (SLS) rocket was assembled inside in preparation for the Artemis 1 mission, which launched on November 16, 2022. At , it is the eighth-largest building in the world by volume as of 2022. The building is at Launch Complex 39 at KSC, south of Jacksonville, north of Miami, and due east of Orlando, on Merritt Island on the Atlantic coast of Florida. The VAB is the largest single-story building in the world, was the tallest building () in Florida until 1974, and is the tallest building in the United States outside an urban area. History The VAB, which was completed in 1966, was originally bui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Launch System
The Space Launch System (SLS) is an American super heavy-lift expendable launch vehicle developed by NASA. As of 2022, SLS has the highest payload capacity of any rocket in operational service, as well as the greatest liftoff thrust of any rocket in operation. As the primary launch vehicle of the Artemis moon landing program, SLS is designed to launch the crewed Orion spacecraft on a trans-lunar trajectory. The first uncrewed launch, Artemis 1, took place on 16 November 2022. Development of SLS began in 2011, as a replacement for the retired Space Shuttle as well as the cancelled Ares I and Ares V launch vehicles. As a Shuttle-derived vehicle, the Space Launch System reuses hardware from the Space Shuttle program, including the solid rocket boosters and RS-25 first stage engines. An original flight date of late 2016 was delayed by nearly 6 years. The SLS program has attracted criticism for such delays, high cost, and non-competitive use of Space Shuttle components an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artemis 2
Artemis 2 (officially Artemis II) is the second scheduled mission of NASA's Artemis program, and the first scheduled crewed mission of NASA's Orion spacecraft, currently planned to be launched by the Space Launch System (SLS) in May 2024. The crewed Orion spacecraft will perform a lunar flyby test and return to Earth. This is planned to be the first crewed spacecraft to travel beyond low Earth orbit since Apollo 17 in 1972. Formerly known as Exploration Mission-2 (EM-2), the mission was renamed after the introduction of the Artemis program. Originally, the crewed mission was intended to collect samples from a captured asteroid in lunar orbit by the now canceled robotic Asteroid Redirect Mission. Overview The Artemis 2 mission plan objective is to send four astronauts in the first crewed Orion MPCV Spacecraft into a lunar flyby for a maximum of 21 days using the Block 1 variant of the Space Launch System. The mission profile is a multi-trans lunar injection (MTLI), o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distant Retrograde Orbit
A distant retrograde orbit (DRO), as most commonly conceived, is a spacecraft orbit around a moon>M2>>M3. So DRO is a general three-body problem solution. It's just that most practical near-term uses for the concept at three-body problems in our Solar System where M1 = a planet, and M2 = a moon of that planet, and M3 = a human-made spacecraft. --> that is highly stable because of its interactions with two Lagrange points ( and ) of the planet–moon system. In more general terms, an object of negligible mass can be in a DRO around the smaller body of any two-body system, such as planet–Sun or exoplanet–star. Using the example of a spacecraft in a DRO around a moon, the craft would orbit in the direction opposite to the direction in which the moon orbits the planet. The orbit is "distant" in the sense that it passes above the Lagrange points, rather than being near the moon. If we consider more and more distant orbits, the synodic period (the period between two moments when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flyby (spaceflight)
A flyby () is a spaceflight operation in which a spacecraft passes in proximity to another body, usually a target of its space exploration mission and/or a source of a gravity assist to impel it towards another target. Spacecraft which are specifically designed for this purpose are known as flyby spacecraft, although the term has also been used in regard to asteroid flybys of Earth for example. Important parameters are the time and distance of closest approach. Spacecraft flyby Flyby maneuvers can be conducted with a planet, a natural satellite or a non-planetary object such as a small Solar System body. Planetary flybys have occurred with Mars or Earth for example: * List of Earth flybys * Mars flyby An example of a comet flyby is when International Cometary Explorer (formerly ISEE-3) passed about from the nucleus of Comet Giacobini-Zinner in September 1985. Another application of the flyby is of Earth's Moon, usually called a lunar flyby. The Apollo 13 spacecraft had an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
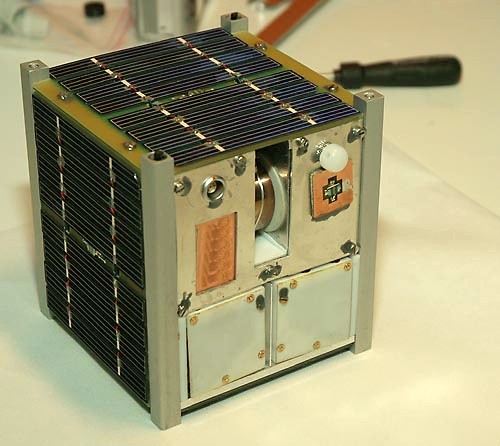
CubeSat
A CubeSat is a class of miniaturized satellite based around a form factor consisting of cubes. CubeSats have a mass of no more than per unit, and often use commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components for their electronics and structure. CubeSats are put into orbit by deployers on the International Space Station, or launched as secondary payloads on a launch vehicle. , more than 1,600 CubeSats have been launched. In 1999, California Polytechnic State University (Cal Poly) professor Jordi Puig-Suari and Bob Twiggs, a professor at Stanford University Space Systems Development Laboratory, developed the CubeSat specifications to promote and develop the skills necessary for the design, manufacture, and testing of small satellites intended for low Earth orbit (LEO) that perform a number of scientific research functions and explore new space technologies. Academia accounted for the majority of CubeSat launches until 2013, when more than half of launches were for non-academic purpose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trans-lunar Injection
A trans-lunar injection (TLI) is a propulsive maneuver used to set a spacecraft on a trajectory that will cause it to arrive at the Moon. History The first space probe to attempt TLI was the Soviet Union's Luna 1 on January 2, 1959 which was designed to impact the Moon. The burn however didn't go exactly as planned and the spacecraft missed the Moon by more than three times its radius and was sent into a heliocentric orbit. Luna 2 performed the same maneuver more accurately on September 12, 1959 and crashed into the Moon two days later. The Soviets repeated this success with 22 more Luna missions and 5 Zond missions travelling to the Moon between 1959 and 1976. The United States launched its first lunar impactor attempt, Ranger 3, on January 26, 1962, which failed to reach the Moon. This was followed by the first US success, Ranger 4, on April 23, 1962. Another 27 US missions to the Moon were launched from 1962 to 1973, including five successful Surveyor soft landers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Orbit
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.60 million km (92.96 million mi) in a counterclockwise direction as viewed from above the Northern Hemisphere. One complete orbit takes days (1 sidereal year), during which time Earth has traveled 940 million km (584 million mi). Jean Meeus, ''Astronomical Algorithms'' 2nd ed, (Richmond, VA: Willmann-Bell, 1998) 238. See Ellipse#Circumference. The formula by Ramanujan is accurate enough. Ignoring the influence of other Solar System bodies, Earth's orbit is an ellipse with the Earth-Sun barycenter as one focus and a current eccentricity of 0.0167. Since this value is close to zero, the center of the orbit is relatively close to the center of the Sun (relative to the size of the orbit). As seen from Earth, the planet's orbital prograde motion makes the Sun appear to move with respect to other stars at a rate of about 1° eastward per solar day (or a Sun or Moon diameter every 12 hours).Our planet takes abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn V
Saturn V is a retired American super heavy-lift launch vehicle developed by NASA under the Apollo program for human exploration of the Moon. The rocket was human-rated, with three stages, and powered with liquid fuel. It was flown from 1967 to 1973. It was used for nine crewed flights to the Moon, and to launch Skylab, the first American space station. the Saturn V remains the only launch vehicle to carry humans beyond low Earth orbit (LEO). Saturn V holds records for the heaviest payload launched and largest payload capacity to low Earth orbit: , which included the third stage and unburned propellant needed to send the Apollo command and service module and Lunar Module to the Moon. The largest production model of the Saturn family of rockets, the Saturn V was designed under the direction of Wernher von Braun at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama; the lead contractors were Boeing, North American Aviation, Douglas Aircraft Company, and IBM. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Super Heavy-lift Launch Vehicle
A super heavy-lift launch vehicle can lift to low Earth orbit more than by United States (NASA) classification or by Russian classification. It is the most capable launch vehicle classification by mass to orbit, exceeding that of the heavy-lift launch vehicle classification. Crewed lunar and interplanetary missions are often developed around these launch vehicles' payload capacity. Many early super heavy-lift launch vehicle concepts were made in the 1960s, such as the Sea Dragon. During the Space Race, the Saturn V and N1 were built by the United States and Soviet Union. After the Saturn V's successful Apollo program and the N1's failures, the Soviets' Energia launched twice in the 1980s, once with the Buran spaceplane. The next two decades saw multiple concepts drawn out once again, most notably Shuttle-derived vehicles and Rus-M, but none would be built. In the 2010s, super heavy-lift launch vehicles received interest once again, leading to the launch of the Falcon Heav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stacking (rocketry)
A multistage rocket or step rocket is a launch vehicle that uses two or more rocket ''stages'', each of which contains its own engines and propellant. A ''tandem'' or ''serial'' stage is mounted on top of another stage; a ''parallel'' stage is attached alongside another stage. The result is effectively two or more rockets stacked on top of or attached next to each other. Two-stage rockets are quite common, but rockets with as many as five separate stages have been successfully launched. By jettisoning stages when they run out of propellant, the mass of the remaining rocket is decreased. Each successive stage can also be optimized for its specific operating conditions, such as decreased atmospheric pressure at higher altitudes. This ''staging'' allows the thrust of the remaining stages to more easily accelerate the rocket to its final speed and height. In serial or tandem staging schemes, the first stage is at the bottom and is usually the largest, the second stage and subsequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exploration Of Mars
The planet Mars has been explored remotely by spacecraft. Probes sent from Earth, beginning in the late 20th century, have yielded a large increase in knowledge about the Martian system, focused primarily on understanding its geology and habitability potential. Engineering interplanetary journeys is complicated and the exploration of Mars has experienced a high failure rate, especially the early attempts. Roughly sixty percent of all spacecraft destined for Mars failed before completing their missions and some failed before their observations could begin. Some missions have met with unexpected success, such as the twin Mars Exploration Rovers, '' Spirit'' and '' Opportunity'' which operated for years beyond their specification. Current status , there are three operational rovers on the surface of Mars, the ''Curiosity'' and ''Perseverance'' rovers, both operated by the United States of America space agency NASA, as well as the ''Zhurong'' rover, part of the '' Tianwen-1' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)





