|
Artayctes
Artaÿctes is a historical figure described in Herodotus' '' The Histories''. Artayctes, the son of Cherasmis, was a Persian general who commanded the Macrones and Mossynoeci forces in the army of Xerxes during the second Persian invasion of Greece in 480-479 BC. During that period, Artayctes was also a tyrant in Sestos where he was captured and crucified by Athenian forces in 479. Background After the defeat of the Persian army in the Battle of Plataea and the Battle of Mycale, the remaining Persians and their allies made for Sestos, the strongest town in the Thracian Chersonesos. The Greek fleet sailed to the Hellespont to destroy the pontoon bridges placed there by the Persians when they had crossed from Asia Minor to Greece but found that this had already been done. The Peloponnesians then sailed home, but the Athenians, commanded by Xanthippus, decided to try to retake the Thracian Chersonesos from the Persians. The Athenian army landed on the Thracian Chersonesos near S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xanthippus
Xanthippus (; el, Ξάνθιππος, ; c. 525-475 BC) was a wealthy Athenian politician and general during the early part of the 5th century BC. His name means "Yellow Horse." He was the son of Ariphron and father of Pericles. A marriage to Agariste, niece of Cleisthenes, linked Xanthippus with the Alcmaeonid clan, whose interests he often represented in government. He distinguished himself in the Athenian political arena, championing the aristocratic party. His rivalry with Themistocles led to his ostracism, but he was recalled from exile when the Persians invaded Greece. Xanthippus' actions in the ensuing Greco-Persian Wars contributed significantly to the victory of the Greeks and the subsequent ascendancy of the Athenian Empire. Early political career and ostracism As a citizen-soldier of Athens and a member of the aristocracy, Xanthippus most likely fought during the Battle of Marathon in 490 BC. He first appears in the historical record the following year (489 BC), head ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protesilaus
In Greek mythology, Protesilaus (; Ancient Greek: Πρωτεσίλᾱος ''Prōtesilāos'') was a hero in the ''Iliad'' who was venerated at cult sites in Thessaly and Thrace. Protesilaus was the son of Iphiclus, a "lord of many sheep"; as grandson of the eponymous Phylacos, he was the leader of the Phylaceans. Hyginus surmised that he was originally known as Iolaus—not to be confused with Iolaus, the nephew of Heracles—but was referred to as "Protesilaus" after being the first (, ''protos'') to leap ashore at Troy, and thus the first to die in the war.Hyginus. ''Fabulae'', 103. Description In the account of Dares the Phrygian, Protesilaus was illustrated as ". . .fair-skinned, and dignified. He was swift, self-confident, even rash." Mythology Protesilaus was one of the suitors of Helen. He brought forty black ships with him to Troy, drawing his men from "flowering" Pyrasus, coastal Antron and Pteleus, "deep in grass", in addition to his native Phylace. Protesilaus wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
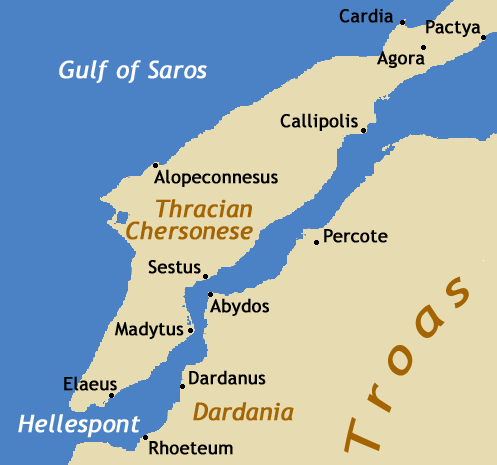
Sestos
Sestos ( el, Σηστός, la, Sestus) was an ancient city in Thrace. It was located at the Thracian Chersonese peninsula on the European coast of the Hellespont, opposite the ancient city of Abydos, and near the town of Eceabat in Turkey. In Greek mythology, Sestos is presented in the myth of Hero and Leander as the home of Hero. History Classical period Sestos is first mentioned in Homer's ''Iliad'' as a Thracian settlement, and was allied with Troy during the Trojan War. The city was settled by colonists from Lesbos in c. 600 BC. In c. 512, Sestos was occupied by the Achaemenid Empire, and Darius I ferried across from the city to Asia Minor after his Scythian campaign. Alongside Byzantium, Sestos was considered to be one of the foremost Achaemenid ports on the European coast of the Bosphorus and the Hellespont. In 480, at the onset of the Second Persian invasion of Greece, Xerxes I bridged the Hellespont near Sestos. In 479 BC, after the Greek victory at the Battle of M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elaeus
Elaeus ( grc, Ἐλαιοῦς ''Elaious'', later ''Elaeus''), the “Olive City”, was an ancient Greek city located in Thrace, on the Thracian Chersonese. Elaeus was located at the southern end of the Hellespont (now the Dardanelles) near the southernmost point of the Thracian Chersonese (now the Gallipoli peninsula) in modern-day Turkey. According to the geographer Scymnus, Elaeus was founded by settlers from Ionian Teos, while the Pseudo-Scymnus writes that it was a colony of Athens and was founded by Phorbas History The most important cities of the Chersonese were Lysimachia, Pactya, Gallipoli, Alokopennesos, Sestos, Madytos and Elaeus. The peninsula was renowned for its wheat. It also profited from its strategic location on the main trade route between Europe and Asia, as well as the possibility of controlling shipping to Crimea. For these reasons, Elaeus later received colonists from Athens, who built fortifications there. According to Plutarch, the city was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histories (Herodotus)
The ''Histories'' ( el, Ἱστορίαι, ; also known as ''The History'') of Herodotus is considered the founding work of history in Western literature. Written around 430 BC in the Ionic dialect of classical Greek, ''The Histories'' serves as a record of the ancient traditions, politics, geography, and clashes of various cultures that were known in Greece, Western Asia and Northern Africa at that time. Although not a fully impartial record, it remains one of the West's most important sources regarding these affairs. Moreover, it established the genre and study of history in the Western world (despite the existence of historical records and chronicles beforehand). ''The'' ''Histories'' also stands as one of the earliest accounts of the rise of the Persian Empire, as well as the events and causes of the Greco-Persian Wars between the Persian Empire and the Greek city-states in the 5th century BC. Herodotus portrays the conflict as one between the forces of slavery (the Pers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known for having written the '' Histories'' – a detailed account of the Greco-Persian Wars. Herodotus was the first writer to perform systematic investigation of historical events. He is referred to as " The Father of History", a title conferred on him by the ancient Roman orator Cicero. The ''Histories'' primarily cover the lives of prominent kings and famous battles such as Marathon, Thermopylae, Artemisium, Salamis, Plataea, and Mycale. His work deviates from the main topics to provide a cultural, ethnographical, geographical, and historiographical background that forms an essential part of the narrative and provides readers with a wellspring of additional information. Herodotus has been criticized for his inclusion of "legends and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Unknown
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Leaders Of The Achaemenid Empire
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian People Of The Greco-Persian Wars
Persian may refer to: * People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language ** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples ** Persian language, an Iranian language of the Indo-European family, native language of ethnic Persians *** Persian alphabet, a writing system based on the Perso-Arabic script * People and things from the historical Persian Empire Other uses * Persian (patience), a card game * Persian (roll), a pastry native to Thunder Bay, Ontario * Persian (wine) * Persian, Indonesia, on the island of Java * Persian cat, a long-haired breed of cat characterized by its round face and shortened muzzle * The Persian, a character from Gaston Leroux's ''The Phantom of the Opera'' * Persian, a generation I Pokémon species * Alpha Indi, star also known as "The Persian" See also * Persian Empire (other) * Persian expedition (other) or Persian campaign * Persian Gulf (disambiguat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People Executed By Crucifixion
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
479 BC Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 479 ( CDLXXIX) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Zeno without colleague (or, less frequently, year 1232 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 479 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Britannia * Ambrosius Aurelianus, war leader of the Romano-British, is proclaimed king of the Britons (according to ''Historia Regum Britanniae''). He rules probably in the south of Britain, and continues the war against the Anglo-Saxons. Europe * King Theodoric the Great starts a 4-year campaign against the Byzantine Empire. The Ostrogoths ravage the Roman provinces (Moesia and Thrace), and threaten the capital of Constantinople itself. * Julius Nepos, former emperor of the Western Roman Empire, plots military plans in Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persis
Persis ( grc-gre, , ''Persís''), better known in English as Persia ( Old Persian: 𐎱𐎠𐎼𐎿, ''Parsa''; fa, پارس, ''Pârs''), or Persia proper, is the Fars region, located to the southwest of modern-day Iran, now a province. The Persians are thought to have initially migrated either from Central Asia or, more probably, from the north through the Caucasus. They would then have migrated to the current region of Persis in the early 1st millennium BC. The country name Persia was derived directly from the Old Persian ''Parsa''. Achaemenid Empire The ancient Persians were present in the region of Persis from about the 10th century BC. They became the rulers of the largest empire the world had yet seen under the Achaemenid dynasty which was established in the late 6th century BC, at its peak stretching from Thrace- Macedonia, Bulgaria- Paeonia and Eastern Europe proper in the west, to the Indus Valley in its far east. The ruins of Persepolis and Pasargadae, two o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_1938.jpg)
