|
Arrowroot
Arrowroot is a starch obtained from the rhizomes (rootstock) of several tropical plants, traditionally ''Maranta arundinacea'', but also Florida arrowroot from ''Zamia integrifolia'', and tapioca from cassava (''Manihot esculenta''), which is often labelled as arrowroot. Polynesian arrowroot or pia (''Tacca leontopetaloides''), and Japanese arrowroot (''Pueraria lobata''), also called kudzu, are used in similar ways. History Archaeological studies in the Americas show evidence of arrowroot cultivation as early as 7,000 years ago. The name may come from ''aru-aru'' (meal of meals) in the language of the Caribbean Arawak peoples, Arawak people, for whom the plant was a staple. It has also been suggested that the name comes from arrowroot's use in treating poison-arrow wounds, as it draws out the poison when applied to the site of the injury. In the early days of carbonless copy paper, arrowroot, because of its fine grain-size, was a widely used ingredient. After an economical way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maranta Arundinacea
''Maranta (plant), Maranta arundinacea'', also known as arrowroot, maranta, West Indian arrowroot, obedience plant, Bermuda arrowroot, araru, araruta, ararao or hulankeeriya, is a large, perennial plant, perennial herb found in rainforest habitats. Arrowroot flour is now produced commercially mostly in St. Vincent and the Grenadines. Arrowroot was one of the earliest plants to be domesticated for food in northern South America, with evidence of exploitation or cultivation of the plant dating back to 8200 BCE. Description Arrowroot is a perennial plant growing to a height of between and . Its leaves are lanceolate. The edible part of the plant is the rhizome. Twin clusters of small white flowers bloom about 90 days after planting. The plant rarely produces seed and reproduction is typically by planting part of a rhizome with a bud. Rhizomes are ready for harvesting 10–12 months after planting as leaves of the plant begin to wilt and die. The rhizomes are fleshy, cylindri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tacca Leontopetaloides
''Tacca leontopetaloides'' is a species of flowering plant in the yam family Dioscoreaceae. It is native to Island Southeast Asia but have been introduced as canoe plants throughout the Indo-Pacific tropics by Austronesian peoples during prehistoric times. They have become naturalized to tropical Africa, South Asia, northern Australia, and Oceania. Common names include Polynesian arrowroot, Fiji arrowroot, East Indies arrowroot, and pia. History of cultivation Polynesian arrowroot is an ancient Austronesian root crop closely related to yams. It is originally native to Island Southeast Asia. It was introduced throughout the entire range of the Austronesian expansion during prehistoric times (c. 5,000 BP), including Micronesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar. Polynesian arrowroot have been identified as among the cultivated crops in Lapita sites in Palau, dating back to 3,000 to 2,000 BP. It was also introduced to Sri Lanka, southern India, and possibly also Australia through tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets, and is contained in large amounts in staple foods such as wheat, potatoes, maize (corn), rice, and cassava (manioc). Pure starch is a white, tasteless and odorless powder that is insoluble in cold water or alcohol. It consists of two types of molecules: the linear and helical amylose and the branched amylopectin. Depending on the plant, starch generally contains 20 to 25% amylose and 75 to 80% amylopectin by weight. Glycogen, the energy reserve of animals, is a more highly branched version of amylopectin. In industry, starch is often converted into sugars, for example by malting. These sugars may be fermented to produce ethanol in the manufacture of beer, whisky and biofuel. In addition, sugars produced from processed starch are used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kudzu
Kudzu (; also called Japanese arrowroot or Chinese arrowroot) is a group of climbing, coiling, and trailing deciduous perennial vines native to much of East Asia, Southeast Asia, and some Pacific islands, but invasive species, invasive in many parts of the world, primarily North America. The vine densely climbs over other plants and trees and grows so rapidly that it smothers and kills them by blocking most of the sunlight. The plants are in the genus ''Pueraria'', in the pea family Fabaceae, subfamily Faboideae. The name is derived from the Japanese language, Japanese name for the plant East Asian arrowroot, (''Pueraria montana'' var. ''lobata''), . Where these plants are Naturalisation (biology), naturalized, they can be invasive species, invasive and are considered noxious weeds. The plant is edible, but often sprayed with herbicides. Taxonomy and nomenclature The name kudzu describes one or more species in the genus ''Pueraria'' that are closely related, and some of them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zamia Integrifolia
''Zamia integrifolia'', also known as coontie palm is a small, tough, woody cycad native to the southeastern United States (in Florida and Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia), the Bahamas, Cuba, and the Cayman Islands. Description ''Zamia integrifolia'' produces reddish seed Conifer cone, cones with a distinct acuminate tip. The leaf, leaves are 20–100 cm long, with 5-30 pairs of leaflets (pinnae). Each leaflet is linear to lanceolate or oblong-obovate, 8–25 cm long and 0.5–2 cm broad, entire or with indistinct teeth at the tip. They are often revolute, with prickly petioles. It is similar in many respects to the closely related ''Zamia pumila'', but that species differs in the more obvious toothing on the leaflets. This is a low-growing plant, with a trunk that grows to 3–25 cm high, but is often subterranean. Over time, it forms a multi-branched cluster, with a large, tuberous root system, which is actually an extension of the above-ground stems. The le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida Arrowroot
Florida arrowroot was the commercial name of an edible starch extracted from '' Zamia integrifolia'' (coontie), a small cycad native to North America. Use Like other cycads, ''Zamia integrifolia'' is poisonous, producing a toxin that affects the gastrointestinal tract and nervous system. The toxin can however be removed by careful leaching, and the roots and half-buried stems of this cycad were used by Native American people (notably the Tequesta and Mayaimi Indians, the Seminole Indians and the Maroons) to produce this starch. The root is typically prepared by grinding (macerating) it using a wooden mortar and pestle. The pulp is then saturated in water and drained. The drained fluid is allowed to dry and the resulting yellowish powder is used in the preparation of various foods. In commercial production, multiple macerations achieved a whiter color. Commercial production of the starch (using roots gathered from wild plants) occurred in South Florida, from the 1830s until the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pueraria Lobata
''Pueraria montana'' var. ''lobata'', the East Asian arrowroot, or kudzu vine, is a perennial plant in the family Fabaceae. Names It is called ''gé'' () in Chinese, ''kuzu'' () in Japanese, and ''chik'' () or ''gal'' (갈; 葛) in Korean. Distribution The plant is native to East Asia (China, Taiwan, Japan, Korea), the Russian Far East, Southeast Asia (Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Thailand and Vietnam), and the Pacific (New Caledonia, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands, and Vanuatu). Use The starch powder made from the East Asian arrowroot is called kudzu powder. Kudzu powder is used to make arrowroot tea in traditional medicines of China, Japan and Korea (in Korea the root unprepared is also used). File:Chik 2.jpg, East Asian arrowroot. File:Chikcha.jpg, Arrowroot tea. File:140614 Yagyu Iris Garden Nara Japan07s.jpg, Kuzumochi is a Japanese term referring either to cakes made of () or cakes made from Lactobacillales-fermented wheat starch (), a spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
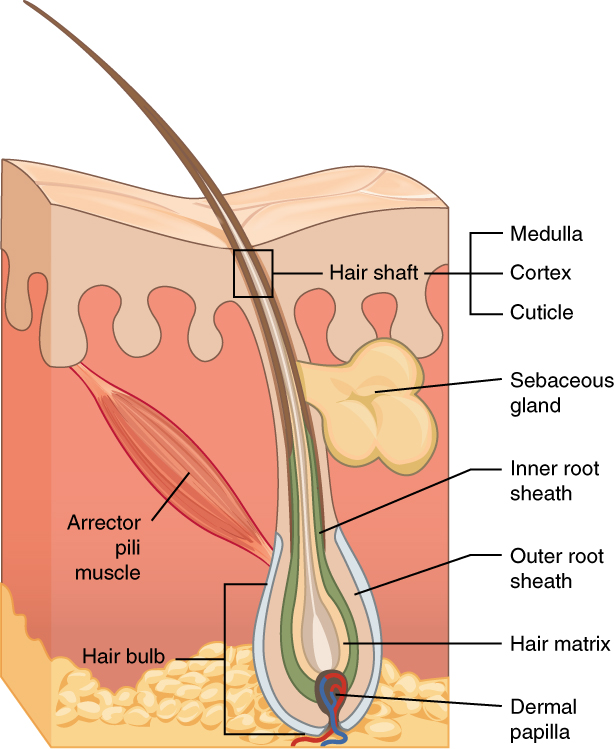
Hair Sieve
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals. The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and fine vellus hair. Most common interest in hair is focused on hair growth, hair types, and hair care, but hair is also an important biomaterial primarily composed of protein, notably alpha-keratin. Attitudes towards different forms of hair, such as hairstyles and hair removal, vary widely across different cultures and historical periods, but it is often used to indicate a person's personal beliefs or social position, such as their age, sex, or religion. Overview The word "hair" usually refers to two distinct structures: #the part beneath the skin, called the hair follicle, or, when pulled from the skin, the bulb or root. This organ is located in the dermis and maintains stem cells, which not only re-grow the hair after it falls out, but also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheel Rasp
A wheel is a circular component that is intended to rotate on an axle bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the six simple machines. Wheels, in conjunction with axles, allow heavy objects to be moved easily facilitating movement or transportation while supporting a load, or performing labor in machines. Wheels are also used for other purposes, such as a ship's wheel, steering wheel, potter's wheel, and flywheel. Common examples are found in transport applications. A wheel reduces friction by facilitating motion by rolling together with the use of axles. In order for wheels to rotate, a moment needs to be applied to the wheel about its axis, either by way of gravity or by the application of another external force or torque. Using the wheel, Sumerians invented a device that spins clay as a potter shapes it into the desired object. Terminology The English word '' wheel'' comes from the Old English word , from Proto-Germanic , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double sugars, are molecules made of two bonded monosaccharides; common examples are sucrose (glucose + fructose), lactose (glucose + galactose), and maltose (two molecules of glucose). White sugar is a refined form of sucrose. In the body, compound sugars are hydrolysed into simple sugars. Longer chains of monosaccharides (>2) are not regarded as sugars, and are called oligosaccharides or polysaccharides. Starch is a glucose polymer found in plants, the most abundant source of energy in human food. Some other chemical substances, such as glycerol and sugar alcohols, may have a sweet taste, but are not classified as sugar. Sugars are found in the tissues of most plants. Honey and fruits are abundant natural sources of simple sugars. Suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Process
Industrial processes are procedures involving chemical, physical, electrical or mechanical steps to aid in the manufacturing of an item or items, usually carried out on a very large scale. Industrial processes are the key components of heavy industry. Chemical processes by main basic material Certain chemical process yield important basic materials for society, e.g., (cement, steel, aluminum, and fertilizer). However, these chemical reactions contribute to climate change by emitting carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, through chemical reactions, as well as through the combustion of fossil fuels to generate the high temperatures needed to reach the activation energies of the chemical reactions. Cement (the paste within concrete) * Calcination – Limestone, which is largely composed of fossilized calcium carbonate (CaCO3), breaks down at high temperatures into useable calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide gas (), which gets released as a by-product. This chemical reaction, call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planting
Sowing is the process of planting seeds. An area or object that has had seeds planted in it will be described as a sowed or sown area. Plants which are usually sown Among the major field crops, oats, wheat, and rye are sown, grasses and legumes are seeded and maize and soybeans are planted. In planting, wider rows (generally 75 cm (30 in) or more) are used, and the intent is to have precise; even spacing between individual seeds in the row, various mechanisms have been devised to count out individual seeds at exact intervals. Depth of sowing In sowing, little if any soil is placed over the seeds, as seeds can be generally sown into the soil by maintaining a planting depth of about 2-3 times the size of the seed. Sowing types and patterns For hand sowing, several sowing types exist; these include: * Flat sowing * Ridge sowing * Wide bed sowing Several patterns for sowing may be used together with these types; these include: * Regular rows * Rows that are ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |