|
Army Of The Pyrenees
One of the French Revolutionary armies, the Army of the Pyrenees (''Armée des Pyrénées'') was created by a decree of the National Convention dated 1 October 1792 and formed out of the right wing of the Armée du Midi. At the outbreak of the War of the Pyrenees with the Kingdom of Spain, a decree of 30 April 1793 separated the Armée des Pyrénées into the Army of the eastern Pyrenees (''Armée des Pyrénées orientales'') and the Army of the western Pyrenees (''Armée des Pyrénées occidentales''). Commanders * General Joseph Servan de Gerbey, 3 October 1792 – 16 February 1793 * General Louis Dubouquet, 17 February - 4 April 1793 (interim) * General Servan de Gerbey, 5 April 1793 – 30 April 1793 ** General Mathieu Henri Marchant de La Houlière, from 17 April commander of the eastern division, committed suicide shortly after the loss of Céret on 20 AprilPrats, ''Ceret'' ** General Claude Souchon de Chameron, 25 April (provisional) Notes Sources''La Prise de Ceret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolutionary Armies
The French Revolutionary Army (french: Armée révolutionnaire française) was the French land force that fought the French Revolutionary Wars from 1792 to 1804. These armies were characterised by their revolutionary fervour, their poor equipment and their great numbers. Although they experienced early disastrous defeats, the revolutionary armies successfully expelled foreign forces from French soil and then overran many neighboring countries, establishing client republics. Leading generals included Napoleon Bonaparte, Jean-Baptiste Jourdan, André Masséna and Jean Victor Marie Moreau. As a general description of French military forces during this period, it should not be confused with the "revolutionary armies" (''armées révolutionnaires'') which were paramilitary forces set up during the Terror. Formation As the ''Ancien Regime'' gave way to a constitutional monarchy, and then to a republic, 1789–92, the entire structure of France was transformed to fall into line wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to Cap de Creus on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast. It reaches a maximum altitude of at the peak of Aneto. For the most part, the main crest forms a divide between Spain and France, with the microstate of Andorra sandwiched in between. Historically, the Crown of Aragon and the Kingdom of Navarre extended on both sides of the mountain range. Etymology In Greek mythology, Pyrene (mythology), Pyrene is a princess who eponym, gave her name to the Pyrenees. The Greek historiography, Greek historian Herodotus says Pyrene is the name of a town in Celts, Celtic Europe. According to Silius Italicus, she was the virgin daughter of Bebryx, a king in Narbonensis, Mediterranean Gaul by whom the hero Hercules was given hospitality during his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Convention
The National Convention (french: link=no, Convention nationale) was the parliament of the Kingdom of France for one day and the French First Republic for the rest of its existence during the French Revolution, following the two-year National Constituent Assembly and the one-year Legislative Assembly. Created after the great insurrection of 10 August 1792, it was the first French government organized as a republic, abandoning the monarchy altogether. The Convention sat as a single-chamber assembly from 20 September 1792 to 26 October 1795 (4 Brumaire IV under the Convention's adopted calendar). The Convention came about when the Legislative Assembly decreed the provisional suspension of King Louis XVI and the convocation of a National Convention to draw up a new constitution with no monarchy. The other major innovation was to decree that deputies to that Convention should be elected by all Frenchmen twenty-one years old or more, domiciled for a year and living by the produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armée Du Midi
The Army of the Midi (''Armée du Midi'') was a unit of the French army, stationed in the Midi region and created by royal decree of Louis XVI on 13 April 1792. The first leader of the army was Jacques Bernard d'Anselme. References 1792 establishments in France Midi MIDI (; Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a technical standard that describes a communications protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, computers, and re ... Military units and formations established in 1792 Military units and formations of the Peninsular War {{mil-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
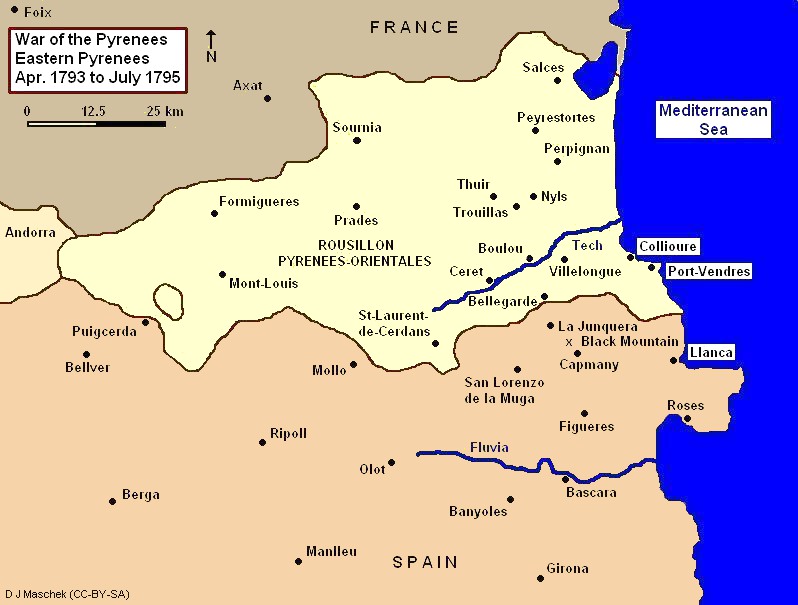
War Of The Pyrenees
The War of the Pyrenees, also known as War of Roussillon or War of the Convention, was the Pyrenean front of the First Coalition's war against the First French Republic. It pitted Revolutionary France against the kingdoms of Spain and Portugal from March 1793 to July 1795 during the French Revolutionary Wars. The war was fought in the eastern and western Pyrenees, at the French port of Toulon, and at sea. In 1793, a Spanish army invaded Roussillon in the eastern Pyrenees and maintained itself on French soil through April 1794. The French army drove the Spanish army back into Catalonia and inflicted a serious defeat in November 1794. After February 1795, the war in the eastern Pyrenees became a stalemate. In the western Pyrenees, the French began to win in 1794. By 1795, the French army controlled a portion of northeast Spain. The war was brutal in at least two ways. The Committee of Public Safety decreed that all French royalist prisoners be executed. Also, French generals w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg , image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg , national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond") , national_anthem = (English: "Royal March") , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Madrid , coordinates = , largest_city = Madrid , languages_type = Official language , languages = Spanish , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = , ethnic_groups_ref = , religion = , religion_ref = , religion_year = 2020 , demonym = , government_type = Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Felipe VI , leader_title2 = Prime Minister , leader_name2 = Pedro Sánchez , legislature = Cortes Gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of The Eastern Pyrenees
The Army of the Eastern Pyrenees (''Armée des Pyrénées Orientales'') was one of the French Revolutionary armies. It fought against the Kingdom of Spain in Roussillon, the Cerdanya and Catalonia during the War of the Pyrenees. This army and the '' Army of the Western Pyrenees'' were formed by splitting the original ''Army of the Pyrenees'' at the end of April 1793 soon after the war started. Shortly after the Peace of Basel on 22 July 1795, the fighting ended and the army was dissolved on 12 October that same year. Many of its units and generals were transferred to join the '' Army of Italy'' and fought under Napoleon Bonaparte in 1796. In the first dismal months of fighting, the ''Army of the Eastern Pyrenees'' was beaten at Mas Deu and Bellegarde and forced back under the walls of Perpignan. Then the French repelled two Spanish attacks at Perpignan and Peyrestortes. Though the army was defeated again at Truillas and in other actions, the Spanish invaders withdrew to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Servan De Gerbey
Joseph Marie Servan de Gerbey (14 February 1741 – 10 May 1808) was a French general. During the Revolution he served twice as Minister of War and briefly led the '' Army of the Western Pyrenees''. His surname is one of the names inscribed under the Arc de Triomphe, on Column 33. Biography Servan was born in the village of Romans in south-eastern France. His older brother was the lawyer and publicist Joseph Michel Antoine Servan. He volunteered for the regiment of Guyenne on 20 December 1760. He rose to Engineering Officer, then Deputy Governor of the pages of King Louis XVI, then colonel, then brigadier general on 8 May 1792. He was recommended as Minister of War by the Girondin leadership, and served a brief term from 9 May to 12 June 1792. Servan assumed the office in a time of war, the first year of the War of the First Coalition. Within days of his appointment he oversaw the dismissal of the royal Garde du Corps and the Swiss Guards; he also abolished corporal punishment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Dubouquet , names sometimes translated to English as "Louis"
{{disambiguation ...
Louis may refer to: * Louis (coin) * Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name * Louis (surname) * Louis (singer), Serbian singer * HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy See also Derived or associated terms * Lewis (other) * Louie (other) * Luis (other) * Louise (other) * Louisville (other) * Louis Cruise Lines * Louis dressing, for salad * Louis Quinze, design style Associated names * * Chlodwig, the origin of the name Ludwig, which is translated to English as "Louis" * Ladislav and László - names sometimes erroneously associated with "Louis" * Ludovic, Ludwig, Ludwick, Ludwik Ludwik () is a Polish given name. Notable people with the name include: * Ludwik Czyżewski, Polish WWII general * Ludwik Fleck (1896–1961), Polish medical doctor and biologist * Ludwik Gintel (1899–1973), Polish-Israeli Olympic soccer player ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathieu Henri Marchant De La Houlière
Mathieu is both a surname and a given name. Notable people with the name include: Surname * André Mathieu (1929–1968), Canadian pianist and composer * Anselme Mathieu (1828–1895), French Provençal poet * Claude-Louis Mathieu (1783–1875), French mathematician and astronomer * Émile Léonard Mathieu (1835–1890), French mathematician * Gail D. Mathieu, United States ambassador to Namibia * Georges Mathieu (1921–2012), French painter * Jérémy Mathieu (born 1983), French footballer * Luc Mathieu (born 1972), French journalist * Marie-Alexandrine Mathieu (1838–1908), French artist known for her etchings * Michel Mathieu (other), multiple people, including: ** Michel Mathieu (Canadian politician) (1838–1916), Canadian politician **Michel Mathieu (French politician) (1944–2010), French diplomat * Mireille Mathieu (born 1946), French singer * Paul-Henri Mathieu (born 1982), French tennis player * Simonne Mathieu (1908–1980), French tennis player * Tyrann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Céret
Céret (; ) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Orientales department in southern France. It is the capital of the historic Catalan comarca of Vallespir. Geography The town lies in the foothills of the Pyrénées mountains, in southern France. It has an altitude of 175–1400 meters. It is located from the Autoroute A9, from Montpellier, from Toulouse and from Barcelona. It lies on the river Tech. The GR 10 footpath runs close by. Céret is located in the canton of Vallespir-Albères and in the arrondissement of Céret. Toponymy The name of the town in Catalan is ''Ceret''. Former known names of Céret are, in order of appearance, ''vicus Sirisidum'' in 814, ''vico Cereto'' in 866, ''villa Cerseto'' in 915, ''vigo Ceresido'' in 930, also ''Cered'' and ''Ceriteto'' in the 10th century, ''Ceret'', ''Cericeto'' in the 11th and 12th centuries, ''Cirset'' around 1070, ''Cersed'' (one of the most common forms) in 1130 and ''Cerset'' in 1138, and from the 13th to 15th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |