|
Army Group G
Army Group G (''Heeresgruppe G'') fought on the Western Front of World War II and was a component of OB West. History When the Allied invasion of Southern France took place, Army Group G had eleven divisions with which to hold France south of the Loire.Pogue (referencesCHAPTER XII The Campaign in Southern Francep.227 Between August 17 and 18, the German Armed Forces High Command ordered Army Group G ( with the exception of the troops holding the fortress ports) to abandon southern France. The German LXIV Corps, which had been in charge of troops in the southwest since First Army had been withdrawn a few weeks earlier to hold the line on the River Seine southeast of Paris, formed three march groups and withdrew eastward toward Dijon. At the same time, the German Nineteenth Army, retreated northward through the Rhône valley toward the Plateau de Langres where it was joined by the German Fifth Panzer Army which was assigned to Army Group G so that a counter-attack could be de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Blaskowitz
Johannes Albrecht Blaskowitz (10 July 1883 – 5 February 1948) was a German ''Generaloberst'' during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves and Swords. After joining the Imperial German Army in 1901, Blaskowitz served throughout World War I, where he earned an Iron Cross for bravery. During WWII, Blaskowitz led the 8th Army during the Invasion of Poland and was the Commander in Chief of Occupied Poland from 1939 to 1940. He wrote several memoranda to the German high command speaking out against SS atrocities, and he handed out death sentences to SS members for crimes against Polish civilians. Based upon these actions against the SS, Adolf Hitler personally limited Blaskowitz's future advancement. He commanded Army Group G during the Allied invasion of Southern France and Operation Nordwind, the last major German offensive of World War II on the Western Front. Blaskowitz later commanded the remnants of Army Group H as it withd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Third Army
The United States Army Central, formerly the Third United States Army, commonly referred to as the Third Army and as ARCENT, is a military formation of the United States Army which saw service in World War I and World War II, in the 1991 Gulf War, and in the coalition occupation of Iraq. It is best known for its campaigns in World War II under the command of General George S. Patton. Third Army is headquartered at Shaw Air Force Base, South Carolina with a forward element at Camp Arifjan, Kuwait. It serves as the echelon above corps for the Army component of CENTCOM, US Central Command, whose area of responsibility (AOR) includes Southwest Asia, some 20 countries of the world, in Africa, Asia, and the Persian Gulf. Activation and World War I The Third United States Army was first activated as a formation during the First World War on 7 November 1918, at Chaumont, France, when the General Headquarters of the American Expeditionary Forces (AEF) issued General Order 198 organizi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
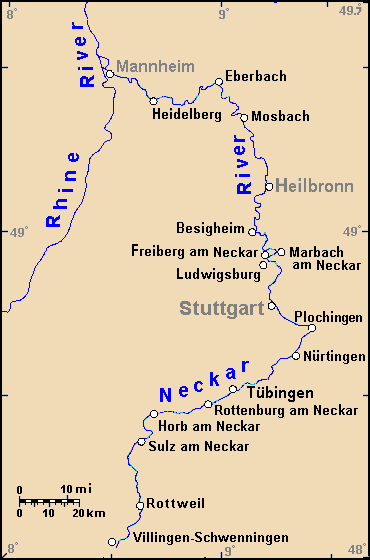
Heilbronn
Heilbronn () is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in northern Baden-Württemberg, Germany, surrounded by Heilbronn (district), Heilbronn District. With over 126,000 residents, it is the sixth-largest city in the state. From the late Middle Ages, it developed into an important trading centre. At the beginning of the 19th century, Heilbronn became one of the centres of early industrialisation in Württemberg. Heilbronn's old town was completely destroyed during the air raid of 4 December 1944 and rebuilt in the 1950s. Today Heilbronn is the economic centre of the Heilbronn-Franconia, Heilbronn-Franken region. Heilbronn is known for its wine industry and is nicknamed ''Käthchenstadt'', after Heinrich von Kleist's ''Das Käthchen von Heilbronn''. Geography Heilbronn is located in the northern corner of the Neckar Sedimentary basin, basin at the bottom of the Wartberg (Heilbronn), Wartberg (308 m). It occupies both banks of the Neckar, and the highest spot inside city limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhineland-Palatinate
Rhineland-Palatinate ( , ; german: link=no, Rheinland-Pfalz ; lb, Rheinland-Pfalz ; pfl, Rhoilond-Palz) is a western state of Germany. It covers and has about 4.05 million residents. It is the ninth largest and sixth most populous of the sixteen states. Mainz is the capital and largest city. Other cities are Ludwigshafen am Rhein, Koblenz, Trier, Kaiserslautern, Worms and Neuwied. It is bordered by North Rhine-Westphalia, Saarland, Baden-Württemberg and Hesse and by the countries France, Luxembourg and Belgium. Rhineland-Palatinate was established in 1946 after World War II, from parts of the former states of Prussia (part of its Rhineland and Nassau provinces), Hesse (Rhenish Hesse) and Bavaria (its former outlying Palatinate kreis or district), by the French military administration in Allied-occupied Germany. Rhineland-Palatinate became part of the Federal Republic of Germany in 1949 and shared the country's only border with the Saar Protectorate until the latter wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
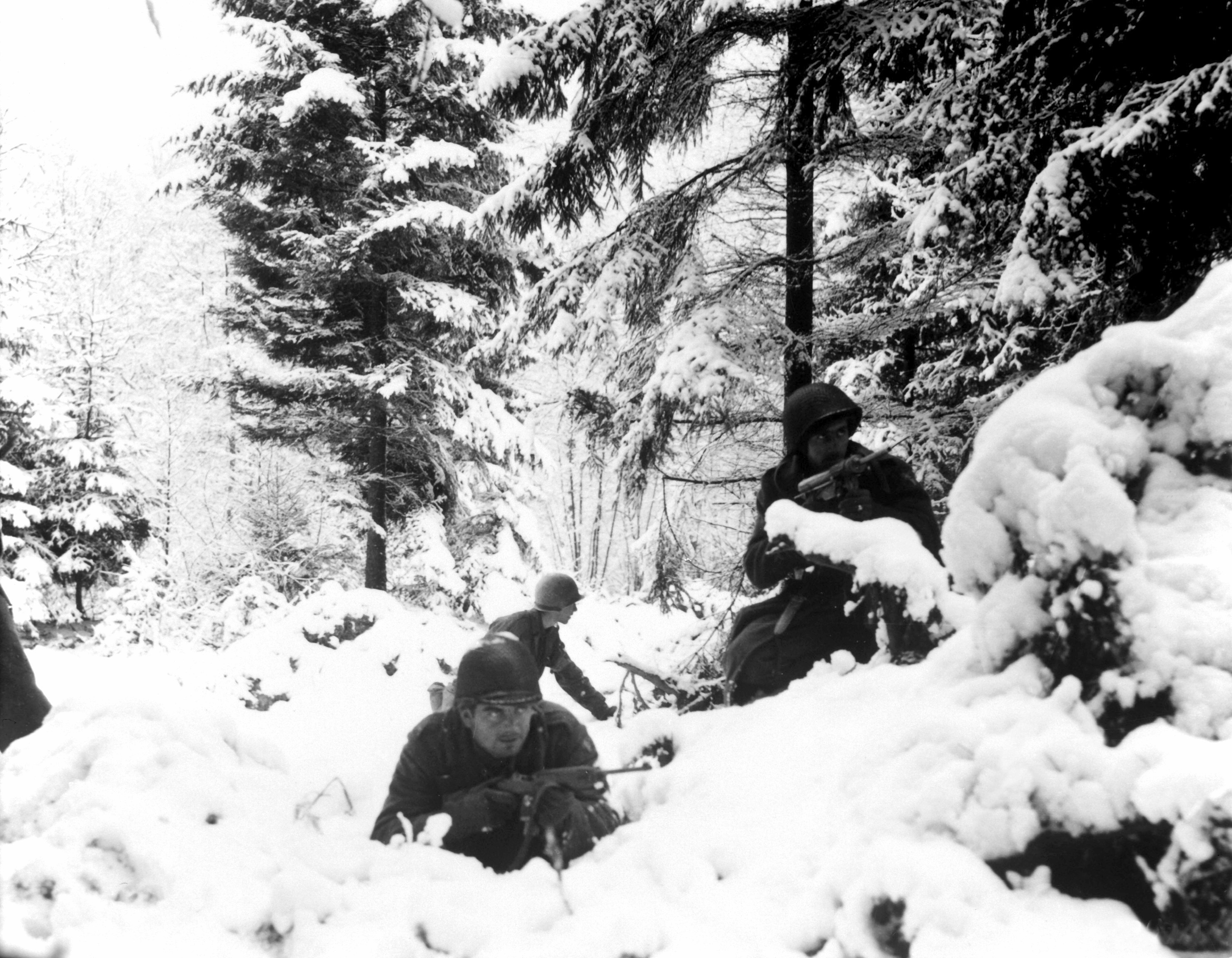
Operation Nordwind
Operation Northwind (german: Unternehmen Nordwind) was the last major German offensive of World War II on the Western Front. Northwind was launched to support the German Ardennes offensive campaign in the Battle of the Bulge, which by December of 1944 had decisively turned against the German forces. It began on 31 December 1944 in Rhineland-Palatinate, Alsace and Lorraine in southwestern Germany and northeastern France, and ended on 25 January 1945. The German offensive was an operational failure, with its main objectives not achieved. Objectives By 21 December 1944, the German momentum during the Battle of the Bulge had begun to dissipate, and it was evident that the operation was on the brink of failure. It was believed that an attack against the United States Seventh Army further south, which had extended its lines and taken on a defensive posture to cover the area vacated by the United States Third Army (which turned north to assist at the site of the German breakthrough ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Group Oberrhein (Germany)
The Upper Rhine High Command (german: Oberkommando Oberrhein), also incorrectly referred to as Army Group Upper Rhine (german: Heeresgruppe Oberrhein), was a short-lived headquarters unit of the German Armed Forces (''Wehrmacht'') created on the Western Front during World War II. The Upper Rhine High Command was formed on 26 November 1944 and deactivated on 25 January 1945. The sole commander of this headquarters unit was Heinrich Himmler. Although English language sources refer to this command as an "army group," the German term ''Oberkommando'' actually means "high command". As such, the ''Oberrhein'' command was not an army group subordinated to theater command, but a command of importance equal to that of a theater command and one which reported directly to Oberkommando der Wehrmacht (''OKW'') and Adolf Hitler. The German term ''Oberrhein'' refers to the upper reaches of the Rhine River, the geographical area for which this command had defense responsibility. Creation F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bienwald
The Bienwald is a large forested area in the southern Pfalz region of Germany near the towns of Kandel and Wörth am Rhein. The western edge defines the eastern extent of the Wissembourg Gap, a corridor of open terrain between the Bienwald and the hills of the Palatine Forest. In the northwest, the forest is bounded by the so-called "Cattle Line" (german: Viehstrich), running from Schweighofen to Kandel. In the north, the forest reaches as far as Hatzenbühl and Rheinzabern. The eastern boundary largely runs along the bank of the Rhine from Jockgrim to Hagenbach and Berg (Pfalz). The southern boundary follows the valley of the Lauter along the border of France and Germany. The bulk of the forest belongs to the municipality of Wörth am Rhein. At its greatest extent, the Bienwald is approximately wide along its east–west axis and from north to south. The forest has an area of some . Approximately one-third of the forest is deciduous woodland with the remainder conife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colmar Pocket
The Colmar Pocket (french: Poche de Colmar; de , Brückenkopf Elsass) was the area held in central Alsace, France, by the German Nineteenth Army from November 1944 to February 1945, against the U.S. 6th Army Group (6th AG) during World War II. It was formed when 6th AG liberated southern and northern Alsace and adjacent eastern Lorraine, but could not clear central Alsace. During Operation Nordwind in December 1944, the 19th Army attacked north out of the Pocket in support of other German forces attacking south from the Saar into northern Alsace. In late January and early February 1945, the French First Army (reinforced by the U.S. XXI Corps) cleared the Pocket of German forces. Background Formation of the Pocket A German bridgehead on the west bank of the Rhine long and deep was formed in November 1944 when the German defenses in the Vosges Mountains collapsed under the pressure of an offensive by the U.S. 6th Army Group. General Jean de Lattre de Tassigny's French First ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
References
Reference is a relationship between objects in which one object designates, or acts as a means by which to connect to or link to, another object. The first object in this relation is said to ''refer to'' the second object. It is called a ''name'' for the second object. The second object, the one to which the first object refers, is called the '' referent'' of the first object. A name is usually a phrase or expression, or some other symbolic representation. Its referent may be anything – a material object, a person, an event, an activity, or an abstract concept. References can take on many forms, including: a thought, a sensory perception that is audible (onomatopoeia), visual (text), olfactory, or tactile, emotional state, relationship with other, spacetime coordinate, symbolic or alpha-numeric, a physical object or an energy projection. In some cases, methods are used that intentionally hide the reference from some observers, as in cryptography. References feature in many sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had a population of 1,898,533. Alsatian culture is characterized by a blend of Germanic and French influences. Until 1871, Alsace included the area now known as the Territoire de Belfort, which formed its southernmost part. From 1982 to 2016, Alsace was the smallest administrative ''région'' in metropolitan France, consisting of the Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin departments. Territorial reform passed by the French Parliament in 2014 resulted in the merger of the Alsace administrative region with Champagne-Ardenne and Lorraine to form Grand Est. On 1 January 2021, the departments of Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin merged into the new European Collectivity of Alsace but remained part of the region Grand Est. Alsatian is an Alemannic dialect closely related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorraine
Lorraine , also , , ; Lorrain: ''Louréne''; Lorraine Franconian: ''Lottringe''; german: Lothringen ; lb, Loutrengen; nl, Lotharingen is a cultural and historical region in Northeastern France, now located in the administrative region of Grand Est. Its name stems from the medieval kingdom of Lotharingia, which in turn was named after either Emperor Lothair I or King Lothair II. Lorraine later was ruled as the Duchy of Lorraine before the Kingdom of France annexed it in 1766. From 1982 until January 2016, Lorraine was an administrative region of France. In 2016, under a reorganisation, it became part of the new region Grand Est. As a region in modern France, Lorraine consisted of the four departments Meurthe-et-Moselle, Meuse, Moselle and Vosges (from a historical point of view the Haute-Marne department is located in the region), containing 2,337 communes. Metz is the regional prefecture. The largest metropolitan area of Lorraine is Nancy, which had developed for centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vosges Mountains
The Vosges ( , ; german: Vogesen ; Franconian and gsw, Vogese) are a range of low mountains in Eastern France, near its border with Germany. Together with the Palatine Forest to the north on the German side of the border, they form a single geomorphological unit and low mountain range of around in area. It runs in a north-northeast direction from the Burgundian Gate (the Belfort–Ronchamp– Lure line) to the Börrstadt Basin (the Winnweiler– Börrstadt–Göllheim line), and forms the western boundary of the Upper Rhine Plain. The Grand Ballon is the highest peak at , followed by the Storkenkopf (), and the Hohneck ().IGN maps available oGéoportail/ref> Geography Geographically, the Vosges Mountains are wholly in France, far above the Col de Saverne separating them from the Palatinate Forest in Germany. The latter area logically continues the same Vosges geologic structure but traditionally receives this different name for historical and political reasons. From ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |