|
Argentine Monte
The Argentine Monte (NT0802), or Low Monte, is an ecoregion of dry thorn scrub and grasslands in Argentina. It is one of the driest regions in the country. Human settlements are mainly near water supplies such as rivers or oases. Deforestation and over-grazing around these settlements have caused desertification. Location The Argentine Monte is in north-central Argentina, and has an area of . It is to the east of the Andes and extends from Salta Province in the north to Chubut Province in the south. It extends from the eastern foothills of the Andes to the Atlantic Ocean. The ecoregion merges into the Patagonian steppe in the south and southwest. The Dry Chaco lies to the northeast, and the Argentine Espinal, Espinal is to the east. In the northwest it borders the High Monte. Some consider the High Monte a separate ecoregion, while others consider it a part of the Argentine Monte. Physical Elevations range from sea level on the Atlantic coast to . The region contains parts of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuquén Province
Neuquén () is a province of Argentina, located in the west of the country, at the northern end of Patagonia. It borders Mendoza Province to the north, Rio Negro Province to the southeast, and Chile to the west. It also meets La Pampa Province at its northeast corner. History The Neuquén Province receives its name from the Neuquén River. The term ''"Neuquén"'' derives from the Mapudungun word ''"Nehuenken"'' meaning ''drafty'', which the aborigines used for the river. The word (without the accentuation) is a palindrome. Lácar Department in Neuquén Province has the southernmost known remains of maize before it was further diffused by the Inca Empire. Maize remains were found as far south as 40°19' S in Melinquina, with it being found inside pottery dated to 730 ±80 BP and 920 ±60 BP. This maize was probably brought across the Andes from Chile. Inhabited by Tehuelches and Pehuenche, the territory was initially explored by conquistadores coming from Chile. In 1670 a Jesu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mendoza Province
Mendoza, officially Province of Mendoza, is a province of Argentina, in the western central part of the country in the Cuyo region. It borders San Juan to the north, La Pampa and Neuquén to the south, San Luis to the east, and the republic of Chile to the west; the international limit is marked by the Andes mountain range. Its capital city is the homonymous city of Mendoza. Covering an area of 148,827 km2, it is the seventh biggest province of Argentina with 5.35% of the country's total area. The population for 2010 is 1,741,610 inhabitants, which makes it the fourth most populated province of the country, or 4.35% of the total national population. History Pre-Columbian times Archeological studies have determined that the first inhabitants in the area date from the Holocene, but there are few remains of those people to know their habits. The earliest sites of human occupation in Mendoza Province, Agua de la Cueva and Gruta del Indio, are 12,000–13,000 years old. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montea Aphyla
''Moutya'' or Moutia, is a traditional African dance similar to the Sega, but with often more pronounced suggestive movements. Female and male dancers move in rhythm to the beat of the often single drum made of dried goatskin and lightly heated up by a bonfire A bonfire is a large and controlled outdoor fire, used either for informal disposal of burnable waste material or as part of a celebration. Etymology The earliest recorded uses of the word date back to the late 15th century, with the Catho ... prior to the start of the Dance (and regular during the evening). Dancing starts off slowly in time to the beat of the drums, but speeds up and becomes more erotic as the beating becomes faster and faster and faster. The beat and dance are always accompanied by singing which usually recounts the hardships and joys of everyday life. Until the late 1970s, the Moutya was considered more of a risqué dance and generally shunned. Seychellois culture {{Dance-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulnesia
''Bulnesia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the caltrop family, Zygophyllaceae. The wood of some – particularly '' B. arborea'' and '' B. sarmientoi'' – is traded as verawood (colloquially "vera") or ''"lignum vitae"''. They are close relatives of the "true" ''lignum vitae'' trees of genus ''Guaiacum''. Species * ''Bulnesia arborea'' – Maracaibo ''lignum vitae''; 'True' Verawood * ''Bulnesia bonariensis'' Griseb. * '' Bulnesia carrapo'' Killip & Dugand * ''Bulnesia chilensis'' Gay * ''Bulnesia foliosa'' Griseb. * ''Bulnesia loraniensis'' Griseb. * ''Bulnesia macrocarpa'' Phil. * ''Bulnesia rivas-martinezii'' G.Navarro * ''Bulnesia retama'' (Gillies ex Hook. & Arn.) Griseb * ''Bulnesia sarmientoi'' – Argentine ''lignum vitae'', Paraguay ''lignum vitae'', ''"palo santo"'', ''ibiocaí'' * ''Bulnesia schickendantzii ''Bulnesia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the caltrop family, Zygophyllaceae. The wood of some – particularly '' B. arborea'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larrea
''Larrea'' is a genus of flowering plants in the caltrop family, Zygophyllaceae. It contains five species of evergreen shrubs that are native to the Americas. The generic name honours Bishop Juan Antonio Hernández Pérez de Larrea, a patron of science."Larrea" is itself a Basque surname, where ''larrea'' stands for a village in Álava (Spain), ultimatelmeaning 'meadow'(plus article -a). South American members of this genus are known as ''jarillas'' and can produce fertile interspecific hybrids. One of the more notable species is the creosote bush ('' L. tridentata'') of the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. The King Clone ring in the Mojave Desert is a creosote bush clonal colony estimated to be about 11,700 years old. Species *''Larrea ameghinoi'' *''Larrea cuneifolia'' *''Larrea divaricata'' Cav. *''Larrea nitida'' *''Larrea tridentata'' (DC.) Coville – creosote bush References * T. J. Mabry, J. H. Hunziker, and D. R. Di Feo, D. R. (Eds.). ''Creo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygophyllaceae
Zygophyllaceae is a family of flowering plants that contains the bean-caper and caltrop. The family includes around 285 species in 22 genera. Plants in the family Zygophyllaceae may be trees, shrubs, or herbs. They are often found in dry habitats. The leaves are usually opposite, often with stipules and spines. Some are cultivated as ornamental plants, such as species of the ''Guaiacum'', ''Zygophyllum'', ''Tribulus'', and ''Larrea'' genera. i L. Watson and M.J. Dallwitz (1992 onwards). The families of flowering plants: descriptions, illustrations, identification, information retrieval. |
Xerophilous
A xerophile () is an extremophilic organism that can grow and reproduce in conditions with a low availability of water, also known as water activity. Water activity (aw) is measured as the humidity above a substance relative to the humidity above pure water (Aw = 1.0). Xerophiles are "xerotolerant", meaning tolerant of dry conditions. They can often survive in environments with water activity below 0.8; above which is typical for most life on Earth. Typically xerotolerance is used with respect to matric drying, where a substance has a low water concentration. These environments include arid desert soils. The term osmotolerance is typically applied to organisms that can grow in solutions with high solute concentrations (salts, sugars), such as halophiles. The common food preservation method of reducing water (food drying) activities may not prevent the growth of xerophilic organisms, often resulting in food spoilage. Some mold and yeast species are xerophilic. Mold growth on bre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cactus
A cactus (, or less commonly, cactus) is a member of the plant family Cactaceae, a family comprising about 127 genera with some 1750 known species of the order Caryophyllales. The word ''cactus'' derives, through Latin, from the Ancient Greek word (''káktos''), a name originally used by Theophrastus for a spiny plant whose identity is now not certain. Cacti occur in a wide range of shapes and sizes. Although some species live in quite humid environments, most cacti live in habitats subject to at least some drought. Many live in extremely dry environments, even being found in the Atacama Desert, one of the driest places on Earth. Because of this, cacti show many adaptations to conserve water. For example, almost all cacti are succulents, meaning they have thickened, fleshy parts adapted to store water. Unlike many other succulents, the stem is the only part of most cacti where this vital process takes place. Most species of cacti have lost true leaves, retaining only spines, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperate Grasslands, Savannas, And Shrublands
Temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands is a terrestrial biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. The predominant vegetation in this biome consists of grass and/or shrubs. The climate is temperate and ranges from Semi-arid climate, semi-arid to semi-humid. The habitat type differs from tropical grasslands in the annual temperature regime as well as the types of species found here. The habitat type is known as prairie in North America, pampas in South America, veld in Southern Africa and steppe in Asia. Generally speaking, these regions are devoid of trees, except for riparian or gallery forests associated with streams and rivers. Steppes/shortgrass prairies are short grasslands that occur in semi-arid climates. Tallgrass prairies are tall grasslands in areas of higher rainfall. Heath (habitat), Heaths and pastures are, respectively, low shrublands and grasslands where forest growth is hindered by human activity but not the climate. Tall grasslands, including the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
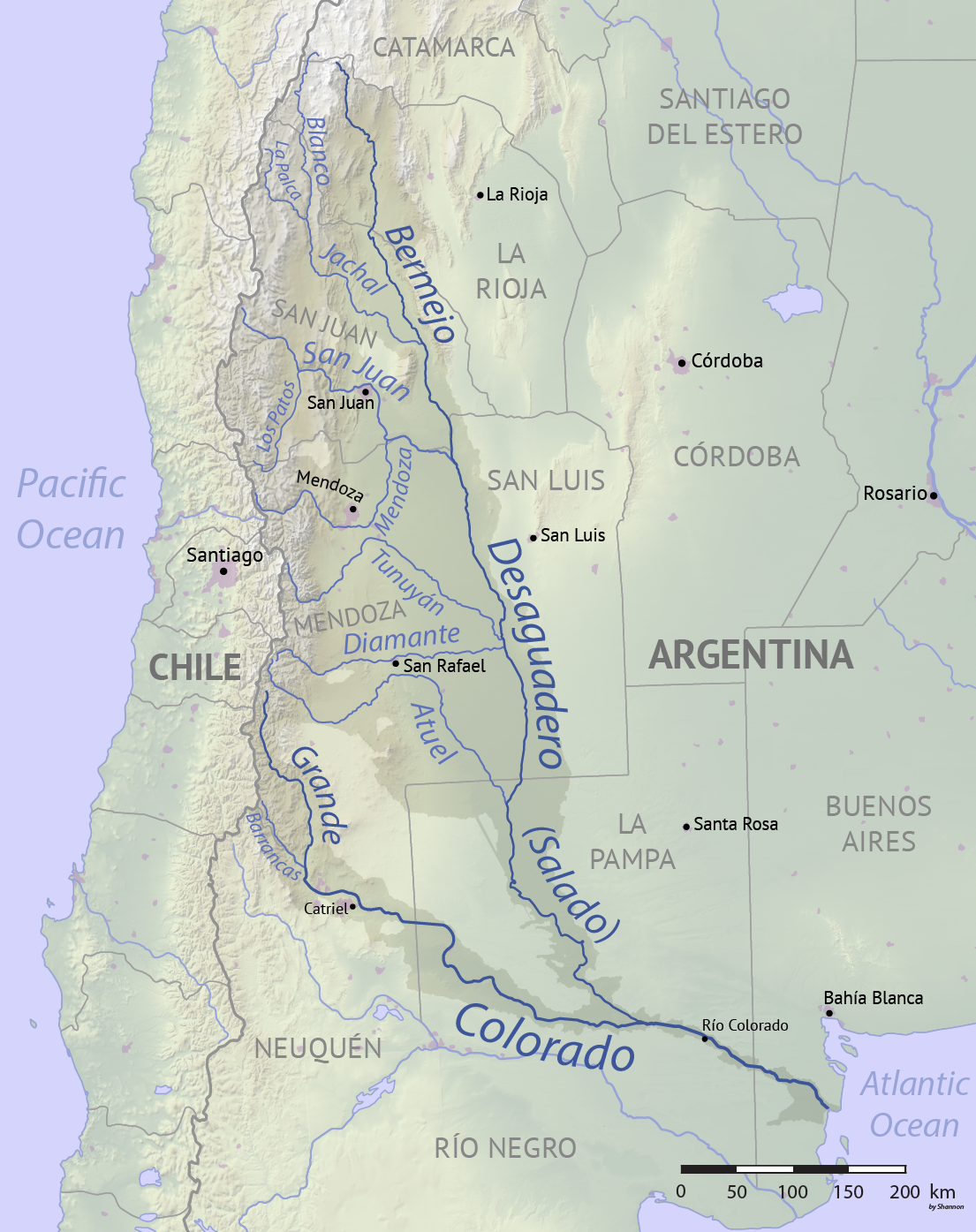
Desaguadero River (Argentina)
The Desaguadero River ( es, Río Desaguadero, ) is a river in Argentina. Originating near the Tipas volcano in La Rioja at about elevation, the river is known in its upper reaches as the Bermejo or Vinchina. In its lower reaches it is also known as the Salado. It joins the Colorado River in La Pampa Province near Pichi Mahuida. The Desaguadero River has a total length of and its drainage basin is about . It is one of the major rivers that supplies the irrigated areas of Cuyo, and it flows in the eastern border of that region. Due to use of its waters for irrigation, the river is a small, shallow stream for most of the year despite its great length, and only occasionally does surface flow reach the Colorado. Tributaries include the Jáchal, San Juan, Tunuyán, Diamante and Atuel Rivers. History The river marked the traditional boundary between the vice-royalties of Buenos Aires and Peru , image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg , image_coat = Escudo na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |