|
Archie Battersbee Case
Archie Battersbee, a British boy, was the subject of several court hearings between April and August 2022, regarding whether or not to withdraw his life support, after he was found unconscious and subsequently considered to have suffered brainstem death. The courts ruled in favour of Barts Health NHS Trust, and against his parents, and allowed his life support to be withdrawn. Incident On 7 April 2022, a 12-year-old boy, Archie Battersbee, from Southend, Essex, England, was found unconscious by his mother, Hollie Dance, with a dressing gown cord around his neck. Dance performed CPR, and called for an ambulance. The paramedics who attended found that Archie Battersbee had suffered a cardiac arrest and his Glasgow Coma Scale score was three, the lowest possible, indicating "no eye-opening, verbal or motor response". CPR was continued and he was taken to Southend University Hospital. On arrival at the hospital, he had no pulse, before regaining spontaneous circulation around 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
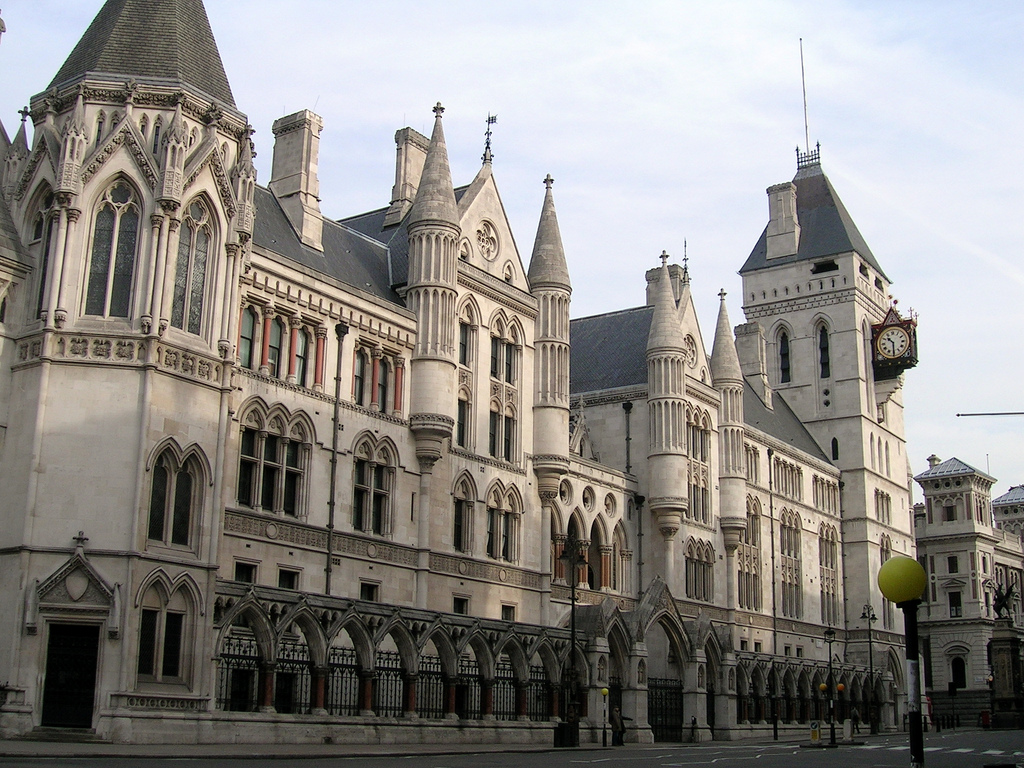
High Court Of Justice
The High Court of Justice in London, known properly as His Majesty's High Court of Justice in England, together with the Court of Appeal of England and Wales, Court of Appeal and the Crown Court, are the Courts of England and Wales, Senior Courts of England and Wales. Its name is abbreviated as EWHC (England and Wales High Court) for legal citation purposes. The High Court deals at Court of first instance, first instance with all high value and high importance Civil law (common law), civil law (non-criminal law, criminal) cases; it also has a supervisory jurisdiction over all subordinate courts and tribunals, with a few statutory exceptions, though there are debates as to whether these exceptions are effective. The High Court consists of three divisions: the King's Bench Division, the #Chancery Division, Chancery Division and the #Family Division, Family Division. Their jurisdictions overlap in some cases, and cases started in one division may be transferred by court order to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal London Hospital
The Royal London Hospital is a large teaching hospital in Whitechapel in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. It is part of Barts Health NHS Trust. It provides district general hospital services for the City of London and Tower Hamlets and specialist tertiary care services for patients from across London and elsewhere. The current hospital building has 845 beds, 110 wards and 26 operating theatres, and opened in February 2012. The hospital was founded in September 1740 and was originally named the London Infirmary. The name changed to the London Hospital in 1748, and in 1990 to the Royal London Hospital. The first patients were treated at a house in Featherstone Street, Moorfields. In May 1741, the hospital moved to Prescot Street, and remained there until 1757 when it moved to its current location on the south side of Whitechapel Road, Whitechapel, in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. The hospital's roof-top helipad is the London's Air Ambulance operating base. The helicop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of helping the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation is used for many reasons, including to protect the airway due to mechanical or neurologic cause, to ensure adequate oxygenation, or to remove excess carbon dioxide from the lungs. Various healthcare providers are involved with the use of mechanical ventilation and people who require ventilators are typically monitored in an intensive care unit. Mechanical ventilation is termed invasive if it involves an instrument to create an airway that is placed inside the trachea. This is done through an endotracheal tube or nasotracheal tube. For non-invasive ventilation in people who are conscious, face or nasal mask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Court Of Human Rights
The European Court of Human Rights (ECHR or ECtHR), also known as the Strasbourg Court, is an international court of the Council of Europe which interprets the European Convention on Human Rights. The court hears applications alleging that a contracting state has breached one or more of the human rights enumerated in the Convention or its optional protocols to which a member state is a party. The European Convention on Human Rights is also referred to by the initials "ECHR". The court is based in Strasbourg, France. An application can be lodged by an individual, a group of individuals, or one or more of the other contracting states. Aside from judgments, the court can also issue advisory opinions. The convention was adopted within the context of the Council of Europe, and all of its 46 member states are contracting parties to the convention. Russia, having been expelled from the Council of Europe as of 16 March 2022, ceased to be a party to the convention with effect from 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committee On The Rights Of Persons With Disabilities
The Committee on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities is a United Nations body of 18 experts that meets two times a year in Geneva to consider the reports submitted by 164 UN member statesAs of March 2015. on their compliance with the '' Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities'' (CRPD), and to examine individual petitions concerning 94 States PartiesAs of March 2015. to the Optional Protocol. The committee is one of ten UN human rights treaty bodies, each responsible for overseeing the implementation of a particular treaty. The Human Rights Committee, the Committee on the Elimination of Discrimination Against Women, and the Committee on the Rights of the Child are among the other United Nations treaty bodies. UN member states that have ratified or acceded to the Optional Protocol have agreed to allow persons within their jurisdiction to submit complaints to the Committee requesting a determination whether provisions of the Convention have been violated. All ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations. It is the world's largest and most familiar international organization. The UN is headquarters of the United Nations, headquartered on extraterritoriality, international territory in New York City, and has other main offices in United Nations Office at Geneva, Geneva, United Nations Office at Nairobi, Nairobi, United Nations Office at Vienna, Vienna, and Peace Palace, The Hague (home to the International Court of Justice). The UN was established after World War II with Dumbarton Oaks Conference, the aim of preventing future world wars, succeeding the League of Nations, which was characterized as ineffective. On 25 April 1945, 50 governments met in San Francisco for United Nations Conference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Court Of The United Kingdom
The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom (initialism: UKSC or the acronym: SCOTUK) is the final court of appeal in the United Kingdom for all civil cases, and for criminal cases originating in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. As the United Kingdom’s highest appellate court for these matters, it hears cases of the greatest public or constitutional importance affecting the whole population. The Court usually sits in the Middlesex Guildhall in Westminster, though it can sit elsewhere and has, for example, sat in the Edinburgh City Chambers, the Royal Courts of Justice in Belfast, and the Tŷ Hywel Building in Cardiff. The United Kingdom has a doctrine of parliamentary sovereignty, so the Supreme Court is much more limited in its powers of judicial review than the constitutional or supreme courts of some other countries. It cannot overturn any primary legislation made by Parliament. However, as with any court in the UK, it can overturn secondary legislation if, for an examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of Appeal (England And Wales)
The Court of Appeal (formally "His Majesty's Court of Appeal in England", commonly cited as "CA", "EWCA" or "CoA") is the highest court within the Senior Courts of England and Wales, and second in the legal system of England and Wales only to the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom. The Court of Appeal was created in 1875, and today comprises 39 Lord Justices of Appeal and Lady Justices of Appeal. The court has two divisions, Criminal and Civil, led by the Lord Chief Justice and the Master of the Rolls and Records of the Chancery of England respectively. Criminal appeals are heard in the Criminal Division, and civil appeals in the Civil Division. The Criminal Division hears appeals from the Crown Court, while the Civil Division hears appeals from the County Court, High Court of Justice and Family Court. Permission to appeal is normally required from either the lower court or the Court of Appeal itself; and with permission, further appeal may lie to the Supreme Court. The C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Children And Family Court Advisory And Support Service
The Children and Family Court Advisory and Support Service (Cafcass) is a non-departmental public body in England set up to promote the welfare of children and families involved in family court. It was formed in April 2001 under the provisions of the Criminal Justice and Court Services Act 2000 and is accountable to Parliament through the Ministry of Justice. Cafcass is independent of the courts, social services, education, health authorities and all similar agencies. Activities Court proceedings for which Cafcass may provide support include: *Parental applications under Section 8 of the Children Act 1989 for a Child Arrangements Order, this includes where a child lives, spends time, or otherwise has contact with each parent *Other parental applications under Section 8 of the Children Act 1989, such as a Prohibited Steps Order or a Specific Issue Order *Adoption cases *Children who are subject to a social services application for a care and/ or supervision order. Cafcass' functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Legal Centre
The Christian Legal Centre (CLC) is a private company which was set up in December 2007 which acts in a number of high-profile cases on behalf of Christians in the United Kingdom who have found themselves in court on account of their faith, handling about 1,000 cases every year.‘We are not the mouthpiece of any organisation. The Gospel is not right or left wing’ The Times. Retrieved 15 October 2022 They are linked to the Christian Concern campaigning organisation. Cases Since its inception, the CLC has involved itself in a number of high-profile cases in the UK including:Other activities In 2010 the Christian Legal Centre, Chri ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brainstem Death
Brainstem death is a clinical syndrome defined by the absence of reflexes with pathways through the brainstem – the "stalk" of the brain, which connects the spinal cord to the mid-brain, cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres – in a deeply comatose, ventilator-dependent patient. Identification of this state carries a very grave prognosis for survival; cessation of heartbeat often occurs within a few days, although it may continue for weeks if intensive support is maintained.A Code of Practice for the Diagnosis and Confirmation of Death. Academy of Medical Royal Colleges, London, 2008 In the United Kingdom, death can be certified on the basis of a formal diagnosis of brainstem death, so long as this is done in accordance with a procedure established in "A Code of Practice for the Diagnosis and Confirmation of Death", published in 2008 by the Academy of Medical Royal Colleges. The premise of this is that a person is dead when consciousness and the ability to breathe are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Children Act 1989
The Children Act 1989 is a United Kingdom Act of Parliament which allocates duties to local authorities, courts, parents, and other agencies in the United Kingdom, to ensure children are safeguarded and their welfare is promoted. It centres on the idea that children are best cared for within their own families; however, it also makes provisions for instances when parents and families do not co-operate with statutory bodies. Passage The Children Bill was announced as part of the Queen's Speech on 22 November 1988 and formally introduced to the House of Lords the following day by the Lord Chancellor, Lord Mackay of Clashfern. The Bill was given its second reading in the Lords on 6 December, and was passed to the committee stage on 13 December. Committee debates were held on 19 and 20 December and 23 January 1989. It reached the report stage on 2 February, with debates on 6, 7 and 16 February. On 16 March the Bill was given its third reading in the Lords before being passed to the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |