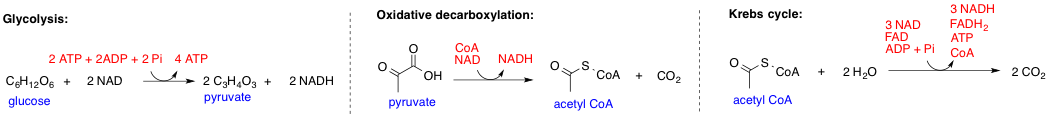|
Archaea Described In 2014
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of ''Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes involved in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoarchean
The Paleoarchean (), also spelled Palaeoarchaean (formerly known as early Archean), is a Geologic time scale#Terminology, geologic era within the Archean, Archaean Eon. The name derives from Greek "Palaios" ''ancient''. It spans the period of time . The era is defined Absolute dating, chronometrically and is not referenced to a specific level of a rock section on Earth. The Abiogenesis, earliest confirmed evidence of life comes from this era, and Vaalbara, one of Earth's earliest Supercontinent, supercontinents, may have formed during this era. Early life The geological record from the Paleoarchean era is very limited. Due to deformation and metamorphism, most rocks from the Paleoarchean era cannot provide any useful information. There are only two locations in the world containing rock formations that are intact enough to preserve evidence of early life: the Kaapvaal Craton in Southern Africa and the Pilbara Craton in Western Australia. The Pilbara Craton, Dresser Formation, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). Euka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeol
Archaeol is composed of two phytanyl chains linked to the sn-2 and sn-3 positions of glycerol. As its phosphate ester, it is a common component of the membranes of archaea. Structure and contrast with other lipids Archaeol is a diether. The 2,3-sn-glycerol structure and ether bond linkage are two key differences between lipids found in archaea vs those of bacteria and eukarya. The latter use 1,2-sn-glycerol, and mostly, ester bonds. Natural archaeol has 3R, 7R, 11R configurations for the three chiral centers in the isoprenoid chains. There are four structural variations, contributing to the complexity of the membrane lipids in function and properties. The two phytanyl chains can form a 36-member ring to yield macrocyclic archaeol. Hydroxylated archaeol has phytanyl chains hydroxylated at the first tertiary carbon atom, while sesterterpanyl archaeol have the phytanyl side chains with C25 sesterterpanyl chains, substituting at C2 of glycerol or at both carbons. Unsaturated arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ether Lipid
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl or aryl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent C–O–C linkages. In dimethyl ether, the Molecular geometry#Bonding, bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 Picometre, pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of oxy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translation (biology)
In molecular biology and genetics, translation is the process in which ribosomes in the cytoplasm or endoplasmic reticulum synthesize proteins after the process of transcription (biology), transcription of DNA to RNA in the cell's nucleus (cell), nucleus. The entire process is called gene expression. In translation, mRNA, messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded in a ribosome, outside the nucleus, to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide. The polypeptide later protein folding, folds into an Activation energy, active protein and performs its functions in the Cell (biology), cell. The ribosome facilitates decoding by inducing the binding of Base pair, complementary tRNA anticodon sequences to mRNA codons. The tRNAs carry specific amino acids that are chained together into a polypeptide as the mRNA passes through and is "read" by the ribosome. Translation proceeds in three phases: # Initiation: The ribosome assembles around the target mRNA. The first tRNA is attached a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). mRNA comprises only 1–3% of total RNA samples. Less than 2% of the human genome can be transcribed into mRNA ( Human genome#Coding vs. noncoding DNA), while at least 80% of mammalian genomic DNA can be actively transcribed (in one or more types of cells), with the majority of this 80% considered to be ncRNA. Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. Transcription proceeds in the following general steps: # RNA polymerase, together with one or more general transcription factors, binds to promoter DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Pathway
In biochemistry, a metabolic pathway is a linked series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. The reactants, products, and intermediates of an enzymatic reaction are known as metabolites, which are modified by a sequence of chemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes. In most cases of a metabolic pathway, the product of one enzyme acts as the substrate for the next. However, side products are considered waste and removed from the cell. These enzymes often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors to function. Different metabolic pathways function based on the position within a eukaryotic cell and the significance of the pathway in the given compartment of the cell. For instance, the, electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation all take place in the mitochondrial membrane. In contrast, glycolysis, pentose phosphate pathway, and fatty acid biosynthesis all occur in the cytosol of a cell. There are two types of metabolic pathways that are character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (biology)
Morphology is a branch of biology dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features. This includes aspects of the outward appearance (shape, structure, colour, pattern, size), i.e. external morphology (or eidonomy), as well as the form and structure of the internal parts like bones and organs, i.e. internal morphology (or anatomy). This is in contrast to physiology, which deals primarily with function. Morphology is a branch of life science dealing with the study of gross structure of an organism or taxon and its component parts. History The etymology of the word "morphology" is from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "form", and (), meaning "word, study, research". While the concept of form in biology, opposed to function, dates back to Aristotle (see Aristotle's biology), the field of morphology was developed by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1790) and independently by the German anatomist and physiologist Karl Friedrich Burdach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haloquadratum Walsbyi
''Haloquadratum walsbyi'' is of the genus ''Haloquadratum,'' within the archaea domain known for its square halophilic nature. First discovered in a brine pool in the Sinai peninsula of Egypt, ''H. walsbyi'' is noted for its flat, square-shaped cells, and its unusual ability to survive in aqueous environments with high concentrations of sodium chloride and magnesium chloride. The species' genus name ''Haloquadratum'' translates from Greek and Latin as "salt square". This archaean is also commonly referred to as "Walsby's Square Bacterium" because of its identifying square shape which makes it very unique. In accordance with its name, ''Haloquadratum walsbyi'' are most abundantly observed in salty environments. ''Haloquadratum walsbyi'' is a phototrophic halophilic archaeon. It was the only recognized species of the genus ''Haloquadratum'' until 1999 when Haloarcula quadrata was reported as recovered from a brine pool. ''Haloquadratum walsbyi'' is very unusual because of its u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)