|
Arab (automobile)
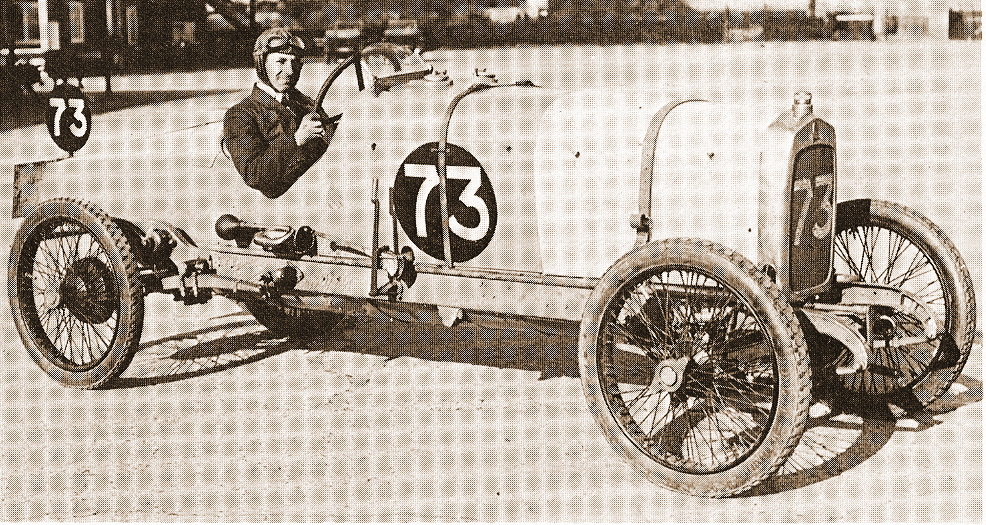
The Arab was a high-performance English automobile designed by Reid Railton and manufactured in Letchworth, Hertfordshire, between 1926 and 1928. The factory had previously been used by the Phoenix (British automobile company), Phoenix car company. History The car came about following discussions between J. G. Parry-Thomas, design engineer at Leyland Motors, Reid Railton, his assistant and Henry Spurrier, chairman of Leyland Motors. Leyland had made 50 four-cylinder engine blocks intended to be used in fast delivery vans, but the project was not proceeded with. The three discussed what to do with the blocks, and the building of a 2-litre sporting car was agreed. A prototype was built to test the new engine using an Enfield-Allday chassis and the car taken to Brooklands for the 1924 Easter Meeting. The engine had an overhead camshaft with the same unusual valve springing using leaf springs as those found on Parry Thomas's Leyland Eight. Drive was to the rear wheels via a Moss 4-sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reid Railton
Reid A. Railton (1895–1977) was a British automotive engineer, and designer of land and water speed record vehicles. Biography Reid Antony Railton was the son of a Manchester stockbroker: Charles Withingon Railton and his wife Charlotte Elizabeth (née Sharman), Reid was born in Chorley, Alderley Edge, Cheshire and was christened on 13 August 1895 at the local parish church. He was educated at Rugby School and Manchester University. He joined Leyland Motors in 1917 where he worked with J.G. Parry-Thomas on the Leyland Eight luxury car. He left in 1922 to set up the Arab Motor Company where he was chief designer. Only about twelve cars were built, of which two low-chassis cars survive. One is in the Isle of Man and the other one (chassis number 6, engine number 10, registration UW 2) is now in Austria having been rebuilt and rebodied by David Barker in the early 1990s. In 1927, on the death of his friend Parry-Thomas, Railton closed the Arab factory and moved to Brooklands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Letchworth
Letchworth Garden City, commonly known as Letchworth, is a town in the North Hertfordshire district of Hertfordshire, England. It is noted for being the first garden city. The population at the time of the 2011 census was 33,249. Letchworth was an ancient parish, appearing in the Domesday Book of 1086. It remained a small rural village until the start of the twentieth century. The development of the modern town began in 1903, when much of the land in Letchworth and the neighbouring parishes of Willian and Norton was purchased by a company called First Garden City Limited, founded by Ebenezer Howard and his supporters with the aim of building the first "garden city", following the principles Howard had set out in his 1898 book, ''To-morrow: A Peaceful Path to Real Reform''. Their aim was to create a new type of settlement which provided jobs, services, and good housing for residents, whilst retaining the environmental quality of the countryside, in contrast to most industria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenix (British Automobile Company)
Phoenix was an England, English manufacturer of automobiles, motorcycles and Three-wheeled car, tricars (Tricycle#Motorized tricycles, motor tricycles) active from 1903–1926. It was founded by a Belgian, Joseph van Hooydonk, at his factory in A1 road (London), Holloway Road, North London, and named after the Phoenix Cycle Club. The company moved from its London base to Letchworth, Hertfordshire, in 1911, but failed to survive the 1920s going into liquidation in 1924 but assembling a few more cars in the following two years. at motorbase.com The Letchworth factory went on to be used for car manufacture by Ascot (1928 automobile), Ascot and Arab (automobile), Arab. Production [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leyland Motors
Leyland Motors Limited (later known as the Leyland Motor Corporation) was a British vehicle manufacturer of lorries, buses and trolleybuses. The company diversified into car manufacturing with its acquisitions of Triumph and Rover in 1960 and 1967, respectively. It gave its name to the British Leyland Motor Corporation, formed when it merged with British Motor Holdings in 1968, to become British Leyland after being nationalised. British Leyland later changed its name to simply BL, then in 1986 to Rover Group. After the various vehicle manufacturing businesses of BL and its successors went defunct or were divested, the following marques survived: Jaguar and Land Rover, now built by Jaguar Land Rover owned by TATA Motors; MG, now built by MG Motor, and Mini, now built by BMW. The truck building operation survived largely intact as Leyland Trucks, a subsidiary of Paccar. History Beginning Leyland Motors has a long history dating from 1896, when the Sumner and Spurrier fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Spurrier
Sir Henry Spurrier (16 June 1898 – 17 June 1964) was a British engineer and industrialist, and the third generation of the Spurrier family to head Leyland Motors.Trevor Boyns, 'Spurrier, Sir Henry (1898–1964)', Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, 200accessed 1 May 2010/ref> Biography Spurrier's grandfather, also Henry, was one of the two Spurrier brothers who founded a company in 1896 to produce steam powered, and later petrol powered, commercial vehicles. The company was renamed ''Leyland Motors'' in 1907. In 1919 Spurrier's father, another Henry, took charge of the company. Spurrier (Henry III) was educated at Repton School, and started working life as an apprentice in his grandfather's firm. During World War I he was a pilot lieutenant with the Royal Flying Corps, and served in Mesopotamia and India. Immediately after the war Spurrier involved himself in car development, working with the chief engineer at ''Leyland Motors'', J.G. Parry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enfield-Allday
The Enfield-Allday was an English car manufactured in Sparkbrook, Birmingham, from 1919 to 1924. The marque was created from the merged ranges of Alldays & Onions and Enfield and the Enfield Autocar Co Ltd. History Prior to World War I Alldays & Onions had produced a range of cars and in 1908 took over the short lived Enfield Autocar Company based in Redditch which had been formed to take over the car making interests of the Enfield Cycle Company. The Enfield designed cars were phased out before World War I leaving them as badge engineered Alldays. Following the armistice in 1918 the companies were rationalised and in 1919 became Enfield-Allday Motors Ltd based in Sparkbrook. All the old designs were dropped and a new 10 hp car called the Bullet was designed by A,W. Reeves who had been at Crossley Motors. This radical design had an air cooled, five cylinder, sleeve valve, radial engine The radial engine is a reciprocating type internal combustion engine configuratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brooklands
Brooklands was a motor racing circuit and aerodrome built near Weybridge in Surrey, England, United Kingdom. It opened in 1907 and was the world's first purpose-built 'banked' motor racing circuit as well as one of Britain's first airfields, which also became Britain's largest aircraft manufacturing centre by 1918, producing military aircraft such as the Wellington and civil airliners like the Viscount and VC-10. The circuit hosted its last race in August 1939 and today part of it forms the Brooklands Museum, a major aviation and motoring museum, as well as a venue for vintage car, motorcycle and other transport-related events. History Brooklands motor circuit The Brooklands motor circuit was the brainchild of Hugh Fortescue Locke-King, and was the first purpose-built banked motor race circuit in the world. Following the Motor Car Act 1903, Britain was subject to a blanket speed limit on public roads: at a time when nearly 50% of the world's new cars were produced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leyland Eight
The Leyland Eight was a luxury car produced by Leyland Motors from 1920 to 1923. The car was designed by the chief engineer of Leyland Motors, J.G. Parry-Thomas and his assistant Reid Railton, and was intended to be the finest car available. It was the first British car with a straight-eight engine. The Eight was introduced to the public at the 1920 International Motor Exhibition at Olympia, London, where it was referred to as the "Lion of Olympia". Engine and transmission The engine, with cylinder block and upper crankcase cast in one piece, had a single centrally mounted overhead camshaft, hemispherical combustion chambers, and an bore. The engine was offered in one of two capacities: with a stroke, producing at 2,500 rpm or with a stroke and twin carburettors, producing at 3,500 rpm. The crankshaft ran in five bearings. Ignition was by coil and distributor rather than magneto which was the more usual British practice at the time. Transmission was through a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Speed Record
The land speed record (or absolute land speed record) is the highest speed achieved by a person using a vehicle on land. There is no single body for validation and regulation; in practice the Category C ("Special Vehicles") flying start regulations are used, officiated by regional or national organizations under the auspices of the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). The land speed record (LSR) is standardized as the speed over a course of fixed length, averaged over two runs (commonly called "passes"). Two runs are required in opposite directions within one hour, and a new record mark must exceed the previous one by at least one percent to be validated. History The first regulator was the ''Automobile Club de France'', which proclaimed itself arbiter of the record in about 1902. Until 1903, trains held the land speed record for fastest vehicles in which people could travel. Different clubs had different standards and did not always recognize the same wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babs (land Speed Record Car)
''Babs'' was the land speed record car built and driven by John Parry-Thomas. It was powered by a 27-litre Liberty aero-engine. ''Babs'' began as ' Chitty 4', one of Count Louis Zborowski's series of aero-engined cars named 'Chitty Bang Bang'. As it was built at Zborowski's estate of Higham Park near Canterbury, it was also known as the Higham Special. Using a V12 Liberty aero engine of 27 litres capacity, with a gearbox and chain-drive from a pre-war Blitzen Benz, it was the largest capacity racing car ever to run at Brooklands. Still not fully developed by the time of Zborowski's death in 1924, it was purchased from his estate by J.G. Parry-Thomas for the sum of £125. Parry-Thomas rechristened the car ''Babs'' and rebuilt it with four Zenith carburettors and his own design of pistons. In April 1926, Parry-Thomas used the car to break the land speed record at 171.02 mph (273.6 km/h). ''Babs'' used exposed chains (covered by a fairing) to take power to the dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomson & Taylor
Thomson & Taylor were a motor-racing engineering and car-building firm, based within the Brooklands race track. They were active between the wars and built several of the famous land speed record breaking cars of the day. Thomas Inventions Development Co. Ltd. The firm was founded as ''Thomas Inventions Development Co. Ltd.'' by J. G. Parry-Thomas & Major Ken Thomson. Their workshops were based in the 'flying village' inside the circuit at Brooklands, a convenient location for their customers, who raced there. Parry-Thomas lived in an adjacent former Royal Flying Corps building named ''The Hermitage''. Thomson & Taylor After Parry-Thomas' death whilst driving ''Babs'' at Pendine Sands in 1927, Major Ken Thomson carried on, joined by Ken Taylor, under the new name of ''Thomson & Taylor''. Reid Railton, who had previously worked for Parry-Thomas at Leyland joined them as Technical Director and chief designer. In 1926 Malcolm Campbell had opened the 'Campbell Shed' at Brookla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monobloc Engine
A ''monobloc'' or ''en bloc'' engine is an internal-combustion piston engine some of whose major components (such as cylinder head, cylinder block, or crankcase) are formed, usually by casting, as a single integral unit, rather than being assembled later. This has the advantages of improving mechanical stiffness, and improving the reliability of the sealing between them. ''Monobloc'' techniques date back to the beginnings of the internal combustion engine. Use of the term has changed over time, usually to address the most pressing mechanical problem affecting the engines of its day. There have been three distinct uses of the technique: * Cylinder head and cylinder * Cylinder block * Cylinder block and crankcase In most cases, any use of the term describes single-unit construction that is opposed to the more common contemporary practice. Where the monobloc technique has later become the norm, the specific term fell from favour. It is now usual practice to use monobloc cylinders and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)