|
Apple Scanner
In August 1988 Apple Computer introduced the Apple Scanner. It was their first A4 (8.5 in × 14.0 in) flatbed scanner. It was capable of a 4-bit image with 16 levels of grey in a maximum resolution of 300 dpi. The scanner could complete a full scan in 20.4 seconds. It shipped with a SCSI Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interface ... connection with an unused serial port. To control the scanner, it came with both AppleScan and HyperScan, the latter allowed users to scan directly from within HyperCard. Later, only AppleScan was offered. The scanner was upgraded to the short-lived Apple OneScanner in 1991 with 256 levels of grey. References {{Apple hardware before 1998, state=collapsed Apple Inc. peripherals Imaging Products introduced in 1988 it:Lis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple Scanner
In August 1988 Apple Computer introduced the Apple Scanner. It was their first A4 (8.5 in × 14.0 in) flatbed scanner. It was capable of a 4-bit image with 16 levels of grey in a maximum resolution of 300 dpi. The scanner could complete a full scan in 20.4 seconds. It shipped with a SCSI Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interface ... connection with an unused serial port. To control the scanner, it came with both AppleScan and HyperScan, the latter allowed users to scan directly from within HyperCard. Later, only AppleScan was offered. The scanner was upgraded to the short-lived Apple OneScanner in 1991 with 256 levels of grey. References {{Apple hardware before 1998, state=collapsed Apple Inc. peripherals Imaging Products introduced in 1988 it:Lis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple Inc
Apple Inc. is an American multinational technology company headquartered in Cupertino, California, United States. Apple is the largest technology company by revenue (totaling in 2021) and, as of June 2022, is the world's biggest company by market capitalization, the fourth-largest personal computer vendor by unit sales and second-largest mobile phone manufacturer. It is one of the Big Five American information technology companies, alongside Alphabet, Amazon, Meta, and Microsoft. Apple was founded as Apple Computer Company on April 1, 1976, by Steve Wozniak, Steve Jobs and Ronald Wayne to develop and sell Wozniak's Apple I personal computer. It was incorporated by Jobs and Wozniak as Apple Computer, Inc. in 1977 and the company's next computer, the Apple II, became a best seller and one of the first mass-produced microcomputers. Apple went public in 1980 to instant financial success. The company developed computers featuring innovative graphical user inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
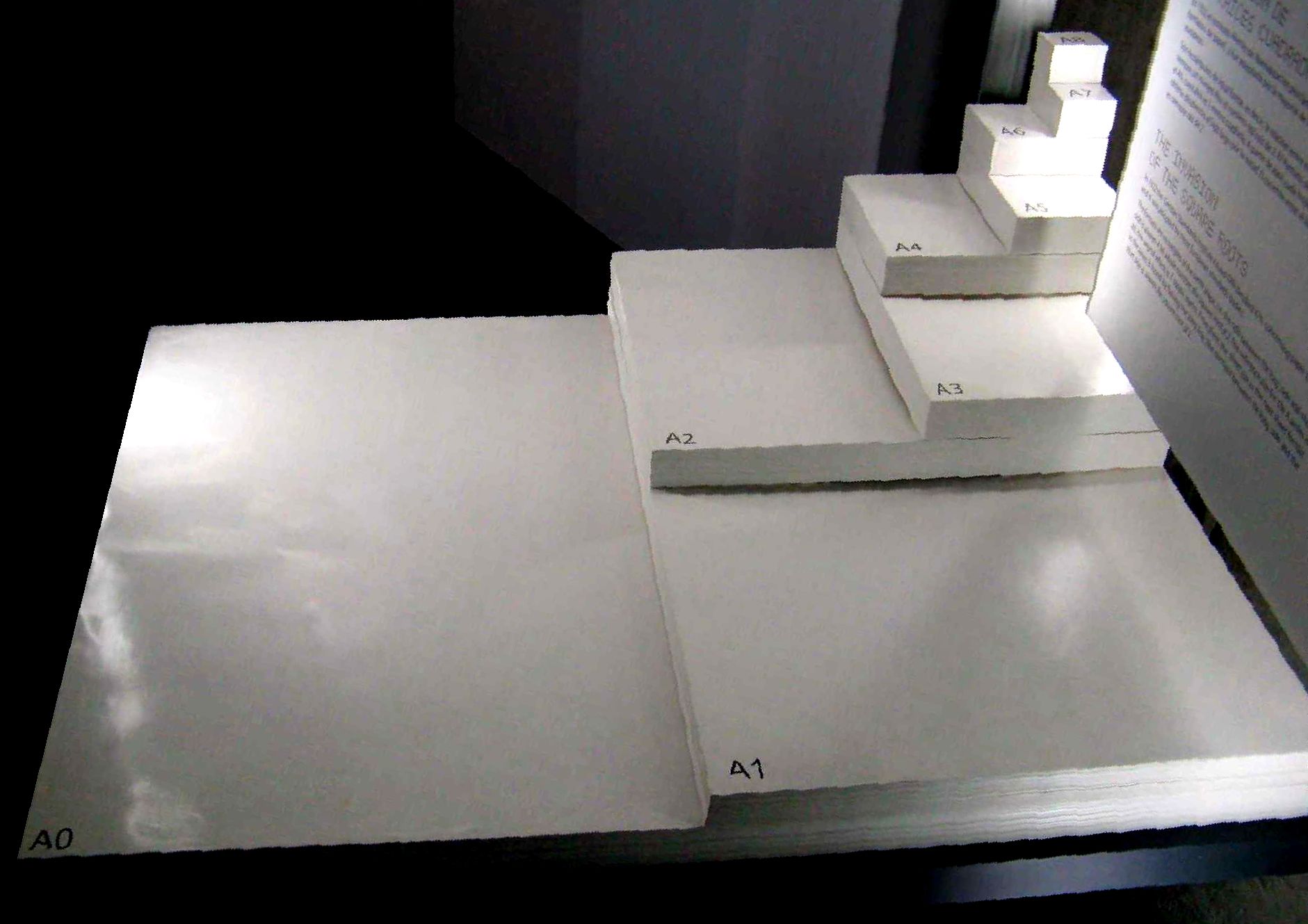
ISO 216
ISO 216 is an international standard for paper sizes, used around the world except in North America and parts of Latin America. The standard defines the "A", "B" and "C" series of paper sizes, including A4, the most commonly available paper size worldwide. Two supplementary standards, ISO 217 and ISO 269, define related paper sizes; the ISO 269 "C" series is commonly listed alongside the A and B sizes. All ISO 216, ISO 217 and ISO 269 paper sizes (except some envelopes) have the same aspect ratio, , within rounding to millimetres. This ratio has the unique property that when cut or folded in half widthways, the halves also have the same aspect ratio. Each ISO paper size is one half of the area of the next larger size in the same series. Dimensions of A, B and C series History The oldest known mention of the advantages of basing a paper size on an aspect ratio of is found in a letter written on 25 October 1786 by the German scientist Georg Christoph Lichtenberg to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flatbed Scanner
An image scanner—often abbreviated to just scanner—is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting or an object and converts it to a digital image. Commonly used in offices are variations of the desktop ''flatbed scanner'' where the document is placed on a glass window for scanning. ''Hand-held scanners'', where the device is moved by hand, have evolved from text scanning "wands" to 3D scanners used for industrial design, reverse engineering, test and measurement, orthotics, gaming and other applications. Mechanically driven scanners that move the document are typically used for large-format documents, where a flatbed design would be impractical. Modern scanners typically use a charge-coupled device (CCD) or a contact image sensor (CIS) as the image sensor, whereas ''drum scanners'', developed earlier and still used for the highest possible image quality, use a photomultiplier tube (PMT) as the image sensor. A ''rotary scanner,'' used for high-speed document ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-bit Computing
In computer architecture, 4-bit integers, or other data units are those that are 4 bits wide. Also, 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers, or data buses of that size. Memory addresses (and thus address buses) for 4-bit CPUs are generally much larger than 4-bit (since only 16 memory locations would be very restrictive), such as 12-bit or more, while they could in theory be 8-bit. A group of four bits is also called a nibble and has 24 = 16 possible values. Some of the first microprocessors had a 4-bit word length and were developed around 1970. Traditional (non-quantum) 4-bit computers are by now obsolete, while recent quantum computers are 4-bit, but also based on qubits, such as the IBM Q Experience. See also: Bit slicing#Bit-sliced quantum computers. The first commercial microprocessor was the binary-coded decimal (BCD-based) Intel 4004, developed for calculator applications in 1971; it had a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dots Per Inch
Dots per inch (DPI, or dpiThe acronym appears in sources as either "DPI" or lowercase "dpi". See "Print Resolution Understanding 4-bit depth – Xerox" (PDF). Xerox.com. September 2012.) is a measure of spatial printing, video or image scanner dot density, in particular the number of individual dots that can be placed in a line within the span of . Similarly, dots per centimetre (d/cm or dpcm) refers to the number of individual dots that can be placed within a line of . DPI measurement in printing DPI is used to describe the resolution number of dots per inch in a digital print and the printing resolution of a hard copy print dot gain, which is the increase in the size of the halftone dots during printing. This is caused by the spreading of ink on the surface of the media. Up to a point, printers with higher DPI produce clearer and more detailed output. A printer does not necessarily have a single DPI measurement; it is dependent on print mode, which is usually influenced b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InfoWorld
''InfoWorld'' (abbreviated IW) is an information technology media business. Founded in 1978, it began as a monthly magazine. In 2007, it transitioned to a web-only publication. Its parent company today is International Data Group, and its sister publications include '' Macworld'' and ''PC World''. InfoWorld is based in San Francisco, with contributors and supporting staff based across the United States. Since its founding, ''InfoWorld''s readership has largely consisted of IT and business professionals. ''InfoWorld'' focuses on how-to, analysis, and editorial content from a mixture of experienced technology journalists and working technology practitioners. The site averages 4.6 million monthly page views and 1.1 million monthly unique visitors. History The magazine was founded by Jim Warren in 1978 as ''The Intelligent Machines Journal'' (IMJ). It was sold to IDG in late 1979. On 18 February 1980, the magazine name was changed to ''InfoWorld''. In 1986, the Robert X. Cringel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements. The initial Parallel SCSI was most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and CD drives, although not all controllers can handle all devices. The ancestral SCSI standard, X3.131-1986, generally referred to as SCSI-1, was published by the X3T9 technical committee of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in 1986. SCSI-2 was published in August 1990 as X3.T9.2/86-109 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HyperCard
HyperCard is a software application and development kit for Apple Macintosh and Apple IIGS computers. It is among the first successful hypermedia systems predating the World Wide Web. HyperCard combines a flat-file database with a graphical, flexible, user-modifiable interface. HyperCard includes a built-in programming language called HyperTalk for manipulating data and the user interface. This combination of features – a database with simple form layout, flexible support for graphics, and ease of programming – suits HyperCard for many different projects such as rapid application development of applications and databases, interactive applications with no database requirements, command and control systems, and many examples in the demoscene. HyperCard was originally released in 1987 for $49.95 and was included free with all new Macs sold afterwards. It was withdrawn from sale in March 2004, having received its final update in 1998 upon the return of Steve Jobs to Apple. Hyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macworld
''Macworld'' is a website dedicated to products and software of Apple Inc., published by Foundry, a subsidiary of IDG Inc. It started life as a print magazine in 1984 and had the largest audited circulation (both total and newsstand) of Macintosh-focused magazines in North America, more than double its nearest competitor, ''MacLife'' (formerly ''MacAddict''). ''Macworld'' was founded by David Bunnell and Cheryl Woodard (publishers) and Andrew Fluegelman (editor). It was the oldest Macintosh magazine still in publication, until September 10, 2014, when IDG, its parent company, announced it was discontinuing the print edition and laid off most of the staff, while continuing an online version. History of Macworld In 1997, the publication was renamed ''Macworld, incorporating MacUser'' (a name reflected subtly on the magazine's Table of Contents page) to reflect the consolidation of the Ziff-Davis-owned ''MacUser'' magazine into the International Data Group-owned ''Macworld'' wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple OneScanner
Apple's OneScanner was a series of flatbed scanners introduced during the early 1990s. The original OneScanner model was introduced in 1991 to replace the earlier Apple Scanner, offering 8-bit (256 shades) greyscale scanning. It was joined by the Color OneScanner the next year, and a series of updated models followed. The series culminated with the Color OneScanner 1200/30, with a resolution of 600x1200 dpi and 30-bit color scanning. The 1200/30 included options for automatic page feeding and scanning transparent materials. press release. The entire OneScanner series u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imaging
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image). Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images. Imaging science is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the generation, collection, duplication, analysis, modification, and visualization of images,Joseph P. Hornak, ''Encyclopedia of Imaging Science and Technology'' (John Wiley & Sons, 2002) including imaging things that the human eye cannot detect. As an evolving field it includes research and researchers from physics, mathematics, electrical engineering, computer vision, computer science, and perceptual psychology. ''Imager'' are imaging sensors. Imaging chain The foundation of imaging science as a discipline is the "imaging chain" – a conceptual model describing all of the factors which must be considered when developing a system for creating visual renderings (images). In g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_clear_background.png)
