|
Anne Mandall Johnson
Dame Anne Mandall Johnson DBE FMedSci (born 30 January 1954) is a British epidemiologist, known for her work in public health, especially the areas of HIV, sexually transmitted infections and infectious diseases. "One day, a journalist rang us up... the survey had been banned by then Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher" Education Johnson's family were involved in medicine. She chose to study at the University of Cambridge and received a Bachelor of Arts (BA) in Medical Sciences, Tripos Part I in 1974, intercalating a year studying social and political sciences during this degree. After graduating, uncertain whether to continue with medicine, she took a gap year in South America that gave her direction for her career. She spent most of her time in Caracas, Venezuela but also with Yanomami people who lived along the Orinoco river. This made her understand the importance to people's health of their environment and socioeconomic status. In 1978, she completed her clinical training at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcastle-upon-Tyne
Newcastle upon Tyne ( RP: , ), or simply Newcastle, is a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England. The city is located on the River Tyne's northern bank and forms the largest part of the Tyneside built-up area. Newcastle is also the most populous city of North East England. Newcastle developed around a Roman settlement called Pons Aelius and the settlement later took the name of a castle built in 1080 by William the Conqueror's eldest son, Robert Curthose. Historically, the city’s economy was dependent on its port and in particular, its status as one of the world's largest ship building and repair centres. Today, the city's economy is diverse with major economic output in science, finance, retail, education, tourism, and nightlife. Newcastle is one of the UK Core Cities, as well as part of the Eurocities network. Famous landmarks in Newcastle include the Tyne Bridge; the Swing Bridge; Newcastle Castle; St Thomas’ Church; Grainger Town including Grey's M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yanomami
The Yanomami, also spelled Yąnomamö or Yanomama, are a group of approximately 35,000 indigenous people who live in some 200–250 villages in the Amazon rainforest on the border between Venezuela and Brazil. Etymology The ethnonym ''Yanomami'' was produced by anthropologists on the basis of the word , which, in the expression , signifies "human beings." This expression is opposed to the categories (game animals) and (invisible or nameless beings), but also (enemy, stranger, non-Indian). According to ethnologist : History The first report of the Yanomami to the Northern world is from 1654, when an El Salvadorian expedition under Apolinar Diez de la Fuente visited some Ye'kuana people living on the Padamo River. Diez wrote: From approximately 1630 to 1720, the other river-based indigenous societies who lived in the same region were wiped out or reduced as a result of slave-hunting expeditions by the conquistadors and bandeirantes. How this affected the Yanomami is unk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
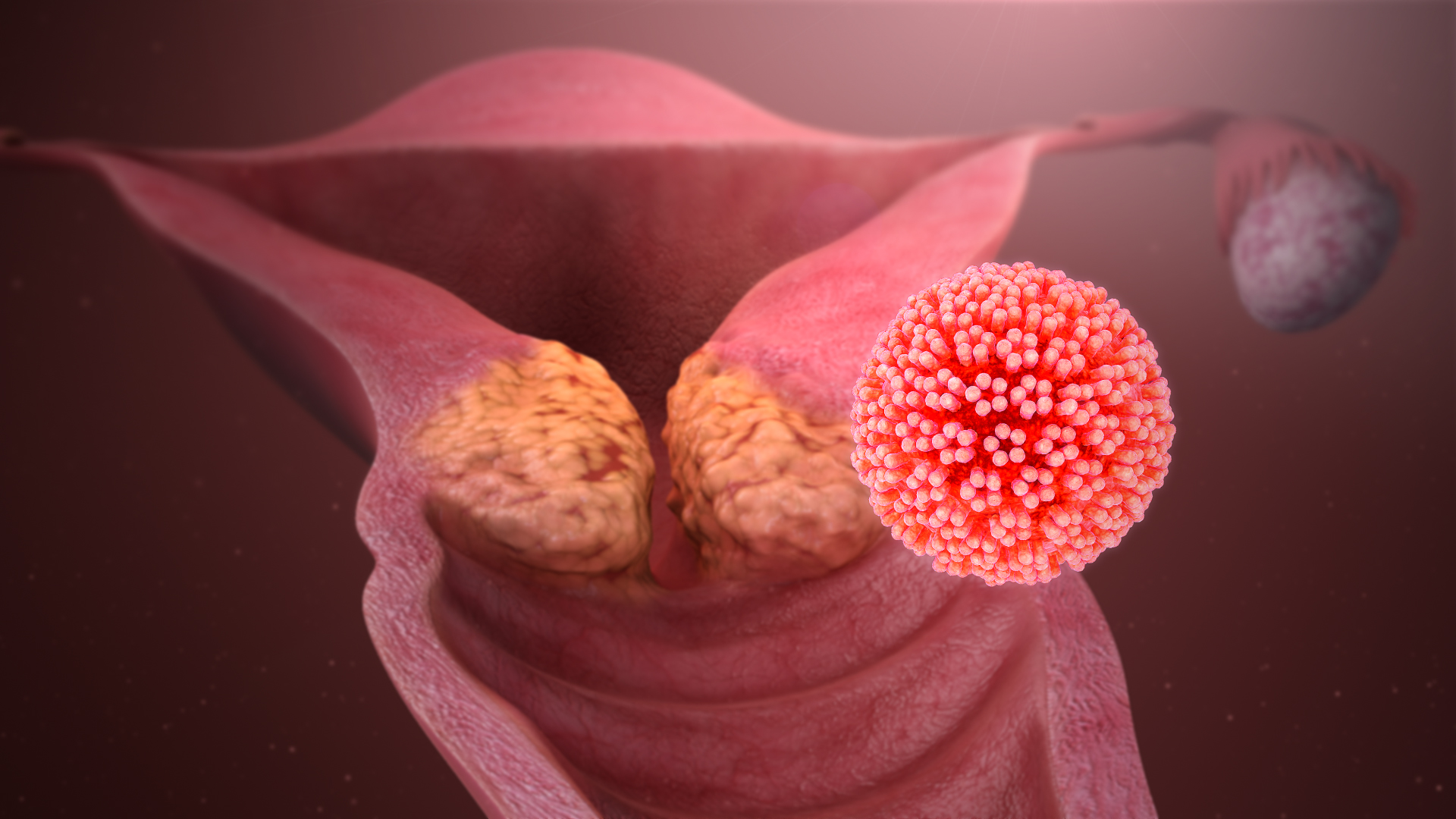
Human Papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV and two strains – HPV16 and HPV18 – account for 70% of cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis. An HPV infection is caused by ''human papillomavirus'', a DNA virus from the papillomavirus family. Over 170 types have been described. An individual can become infected with more than one type of HPV, and the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea, colloquially known as the clap, is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium '' Neisseria gonorrhoeae''. Infection may involve the genitals, mouth, or rectum. Infected men may experience pain or burning with urination, discharge from the penis, or testicular pain. Infected women may experience burning with urination, vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding between periods, or pelvic pain. Complications in women include pelvic inflammatory disease and in men include inflammation of the epididymis. Many of those infected, however, have no symptoms. If untreated, gonorrhea can spread to joints or heart valves. Gonorrhea is spread through sexual contact with an infected person. This includes oral, anal, and vaginal sex. It can also spread from a mother to a child during birth. Diagnosis is by testing the urine, urethra in males, or cervix in females. Testing all women who are sexually active and less than 25 years of age each year as well as thos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlamydia Infection
Chlamydia, or more specifically a chlamydia infection, is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Chlamydia trachomatis''. Most people who are infected have no symptoms. When symptoms do appear they may occur only several weeks after infection; the incubation period between exposure and being able to infect others is thought to be on the order of two to six weeks. Symptoms in women may include vaginal discharge or burning with urination. Symptoms in men may include discharge from the penis, burning with urination, or pain and swelling of one or both testicles. The infection can spread to the upper genital tract in women, causing pelvic inflammatory disease, which may result in future infertility or ectopic pregnancy. Chlamydia infections can occur in other areas besides the genitals, including the anus, eyes, throat, and lymph nodes. Repeated chlamydia infections of the eyes that go without treatment can result in trachoma, a common cause of blindness i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellcome Trust
The Wellcome Trust is a charitable foundation focused on health research based in London, in the United Kingdom. It was established in 1936 with legacies from the pharmaceutical magnate Henry Wellcome (founder of one of the predecessors of GlaxoSmithKline) to fund research to improve human and animal health. The aim of the Trust is to "support science to solve the urgent health challenges facing everyone." It had a financial endowment of Pound sterling, £29.1 billion in 2020, making it the fourth List of wealthiest charitable foundations, wealthiest charitable foundation in the world. In 2012, the Wellcome Trust was described by the ''Financial Times'' as the United Kingdom's largest provider of non-governmental funding for scientific research, and one of the largest providers in the world. According to their annual report, the Wellcome Trust spent GBP Pound sterling, £1.1Bn on charitable activities across their 2019/2020 financial year. According to the OECD, the Wellcome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaye Wellings
Kaye Wellings is an active Sexual and Reproductive Health educator and has worked within this field of study for over 20 years. She has a strong interest in evaluation research, particularly in relation to preventive intervention and has assessed major national and international sexual health programmes, including AIDS preventive strategies in European countries and the English government's Teenage Pregnancy Strategy. Much of her working life has been spent researching sensitive topics, including not only sexual behaviour but also risk practices relating to drug use and in prison populations and the taboo of birth contraceptives in her early years. Early and current career After graduation, Wellings moved to London as a public health and social scientist. For some time, Wellings worked in journalism with journal New Society until continuing on to work with the Family Planning Association in health policy research. The next few years brought on the continuing HIV/AIDS epidemic in w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Survey Of Sexual Attitudes And Lifestyles
The National Survey of Sexual Attitudes and Lifestyles (Natsal) are a series of surveys of people in the Great Britain regarding their sexual behaviour and patterns, and are among the largest scientific studies of sexual behaviours in the world. The rounds of surveys completed to date are Natsal-1 (1990–1991) and Natsal-2 (2000–2001) and Natsal-3 (2010–2012), as well as Natsal-COVID (2020-2021). Data collection for Natsal-4 is taking place from September 2022 to December 2023. Natsal-4's Principal Co-investigators are Pam Sonnenberg and Cath Mercer, both professors at University College, London. Natsal's findings are widely used in research and policy making, and have influenced public health policy in areas such as: The National Sexual Health & HIV Strategy in England; the Scottish Sexual Health Strategy (2005-) and the Welsh Sexual Health Strategy, The Teenage Pregnancy Strategy (2000-2010), the National Chlamydia Screening Programme (NCSP), the national human papillomavirus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Randomized Controlled Trial
A randomized controlled trial (or randomized control trial; RCT) is a form of scientific experiment used to control factors not under direct experimental control. Examples of RCTs are clinical trials that compare the effects of drugs, surgical techniques, medical devices, diagnostic procedures or other medical treatments. Participants who enroll in RCTs differ from one another in known and unknown ways that can influence study outcomes, and yet cannot be directly controlled. By Random assignment, randomly allocating participants among compared treatments, an RCT enables ''statistical control'' over these influences. Provided it is designed well, conducted properly, and enrolls enough participants, an RCT may achieve sufficient control over these confounding factors to deliver a useful comparison of the treatments studied. Definition and examples An RCT in clinical research typically compares a proposed new treatment against an existing Standard of care#Medical standard of care, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diana, Princess Of Wales
Diana, Princess of Wales (born Diana Frances Spencer; 1 July 1961 – 31 August 1997) was a member of the British royal family. She was the first wife of King Charles III (then Prince of Wales) and mother of Princes William and Harry. Her activism and glamour made her an international icon, and earned her enduring popularity, as well as almost unprecedented public scrutiny. Diana was born into the British nobility, and grew up close to the royal family on their Sandringham estate. In 1981, while working as a nursery teacher's assistant, she became engaged to the Prince of Wales, the eldest son of Queen Elizabeth II. Their wedding took place at St Paul's Cathedral in 1981 and made her Princess of Wales, a role in which she was enthusiastically received by the public. The couple had two sons, William and Harry, who were then second and third in the line of succession to the British throne. Diana's marriage to Charles suffered due to their incompatibility and extramarital af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middlesex Hospital
Middlesex Hospital was a teaching hospital located in the Fitzrovia area of London, England. First opened as the Middlesex Infirmary in 1745 on Windmill Street, it was moved in 1757 to Mortimer Street where it remained until it was finally closed in 2005. Its staff and services were transferred to various sites within the University College London Hospitals NHS Trust. The Middlesex Hospital Medical School, with a history dating back to 1746, merged with the medical school of University College London in 1987. History Development of the hospital The first Middlesex Hospital, which was named after the county of Middlesex, opened as the Middlesex Infirmary in Windmill Street in 1745. The infirmary started with 15 beds to provide medical treatment for the poor. Funding came from subscriptions and, in 1747, the hospital became the first in England to add lying-in (maternity) beds. Prior to 1773, the wards in the hospital were named as 'Mens long ward', 'Mens square ward up one pai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute For Health And Care Research
The National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) is the British government’s major funder of clinical, public health, social care and translational research. With a budget of over £1.2 billion in 2020–21, its mission is to "improve the health and wealth of the nation through research". The NIHR was established in 2006 under the government's Best Research for Best Health strategy, and is funded by the Department of Health and Social Care. As a research funder and research partner of the NHS, public health and social care, the NIHR complements the work of the Medical Research Council. NIHR focuses on translational research (translating discoveries from the laboratory to the clinic), clinical research and applied health and social care research. History The NIHR (originally named National Institute for Health Research) was created in April 2006 under the government's health research strategy, Best Research for Best Health. This strategy outlined the direction that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |