|
Andromeda (Chinese Astronomy)
The modern constellation Andromeda (constellation), Andromeda lies across two of the quadrants, symbolized by the Black Tortoise, Black Tortoise of the North (北方玄武, ''Běi Fāng Xuán Wǔ'') and the White Tiger (Chinese astronomy), White Tiger of the West (西方白虎, ''Xī Fāng Bái Hǔ''), that divide the sky in traditional Traditional Chinese star names#Categories of Chinese traditional uranography, Chinese uranography. The name of the western constellation in modern Chinese is 仙女座 (''xiān nǚ zuò''), meaning "the immortal woman / fairy constellation". Stars The map of Chinese constellation in constellation Andromeda area consists of: See also *Chinese astronomy *Traditional Chinese star names *Chinese constellations References {{reflist External linksAndromeda – Chinese associations https://web.archive.org/web/2012081 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
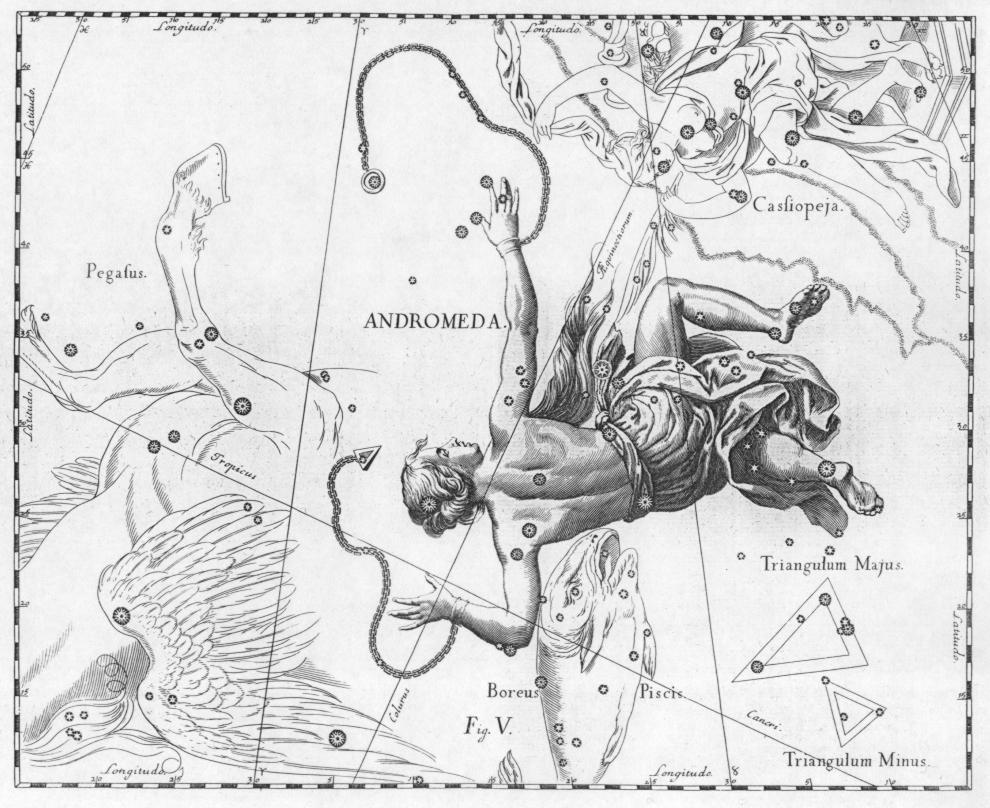
Andromeda (constellation)
Andromeda is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century Greco-Roman astronomer Ptolemy, and one of the 88 modern constellations. Located in the northern celestial hemisphere, it is named for Andromeda, daughter of Cassiopeia, in the Greek myth, who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus. Andromeda is most prominent during autumn evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with several other constellations named for characters in the Perseus myth. Because of its northern declination, Andromeda is visible only north of 40° south latitude; for observers farther south, it lies below the horizon. It is one of the largest constellations, with an area of 722 square degrees. This is over 1,400 times the size of the full moon, 55% of the size of the largest constellation, Hydra, and over 10 times the size of the smallest constellation, Crux. Its brightest star, Alpha Andromedae, is a binary star that has also been counted as a part of Pegasus, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9 Andromedae
9 Andromedae, abbreviated 9 And by convention, is a variable binary star system in the northern constellation Andromeda. ''9 Andromedae'' is the Flamsteed designation, while it bears the variable star designation AN Andromedae, or AN And. The maximum apparent visual magnitude of the system is 5.98, which places it near the lower limit of visibility to the human eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of , it is located 460 light years from the Earth. This system was determined to be a single-lined spectroscopic binary in 1916 by American astronomer W. S. Adams, and the initial orbital elements were computed by Canadian astronomer R. K. Young in 1920. The pair orbit each other with a period of 3.2196 days and an eccentricity of 0.03. It is an eclipsing binary, which means the orbital plane is inclined close to the line of sight and, from the perspective of the Earth, the stars pass in front of each other, causing two partial eclipses every orbit. Duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rooftop (Chinese Constellation)
The Roof mansion () is one of the twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellations. It is one of the northern mansions of the Black Tortoise The Black Tortoise () is one of the Four Symbols of the Chinese constellations. Despite its English name, it is usually depicted as a tortoise entwined together with a snake. The name used in East Asian languages does not mention either anima .... Asterisms References {{Chinese constellation Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
23 Andromedae
23 Andromedae, abbreviated 23 And, is a presumed single star in the constellation Andromeda, although it has been a suspected spectroscopic binary. ''23 Andromedae'' is the Flamsteed designation. Its apparent visual magnitude is 5.71, which indicates it is dimly visible to the naked eye under good viewing conditions. The distance to 23 And, as determined from its annual parallax shift of , is 121.6 light years. The star is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −27 km/s. It has a relatively high proper motion, traversing the celestial sphere at the rate of per year. The stellar classification of 23 And is F0 IV, matching an F-type subgiant star that is in the process of evolving into a red giant. It displays a slight microvariability with a frequency of 0.85784 d−1 and an amplitude of 0.0062 magnitude. The star is around 759 million years old with a projected rotational velocity of 36 km/s. It has 1.43 tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma Andromedae
Sigma Andromedae, Latinized from σ Andromedae, is the Bayer designation for a single star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +4.5, which is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye from most locations. Parallax measurements made during the Gaia mission place it at a distance of about . The magnitude of the star is diminished by 0.08 from extinction caused by intervening gas and dust. It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of –8 km/s. This star has a stellar classification of A2 V, which matches the spectrum of an A-type main sequence star. It is about 450 million years old and is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 123 km/s. The star has 2.12 times the mass of the Sun and 2.13 times the Sun's girth. It is radiating 21 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 8,929 K, giving it the white-hued glow of an A-type star. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rho Andromedae
Rho Andromedae, Latinized from ρ Andromedae, is the Bayer designation for a star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +5.19, which, according to the Bortle Dark-Sky Scale, is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye from dark suburban skies. Based upon parallax measurements, this star is at a distance of approximately from the Sun. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +10 km/s. The stellar classification of this star is F5IV-V, showing mixed spectral features of a main sequence and subgiant stage. It is about 1.3 billion years old with 3.4 times the girth of the Sun and is spinning with a projected rotational velocity of 44 km/s. The outer envelope is radiating around 18 times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 6,471 K, giving it the yellow-white hue of an F-type star. X-ray emissions were detected from this star during the EXOSAT mission. Nami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theta Andromedae
Theta Andromedae is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Andromeda. ''Theta Andromedae'', Latinized from θ Andromedae, is its Bayer designation. It is located at a distance of approximately from the Sun, and has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.6. On the Bortle Dark-Sky Scale, this makes it visible to the naked eye from outside urban regions. Based on its motion through space, this system appears to be a member of the Sirius supercluster. The brighter component is a white hued A-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of A2 V. It is one of the least photometrically variable stars known. The star shows a high rate of rotation with a projected rotational velocity of 102 km/s. It has an estimated 2.8 times the mass of the Sun and is radiating 113 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 8,960 K. The relatively high chemical abundances of iron and heavier elements suggests it may be a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Andromedae
Alpha Andromedae (α Andromedae, abbreviated Alpha And or α And), officially named Alpheratz , is 97 light-years from the Sun and is the brightest star in the constellation of Andromeda when Beta Andromedae undergoes its periodical dimming. Immediately northeast of the constellation of Pegasus, it is the upper left star of the Great Square of Pegasus. Although it appears to the naked eye as a single star, with overall apparent visual magnitude +2.06, it is actually a binary system composed of two stars in close orbit. The chemical composition of the brighter of the two stars is unusual as it is a mercury-manganese star whose atmosphere contains abnormally high levels of mercury, manganese, and other elements, including gallium and xenon.Alpheratz, Kaler Star2/14/2013 It is the brightest mercury-manganese star known. Nomenclature ''α Andromedae'' ( Latinisation of names, Latinised to ''Alpha Andromedae'') is the star's Bayer designation. Ptolemy considered t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wall (Chinese Constellation)
The Wall mansion () is one of the Twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellations. It is one of the northern mansions of the Black Tortoise The Black Tortoise () is one of the Four Symbols of the Chinese constellations. Despite its English name, it is usually depicted as a tortoise entwined together with a snake. The name used in East Asian languages does not mention either anima .... Asterisms {{Chinese constellation Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HD 219962
This is the list of notable stars in the constellation Andromeda, sorted by decreasing brightness. ; Notes: See also *List of stars by constellation All stars but one can be associated with an IAU constellation. IAU constellations are areas of the sky. Although there are only 88 IAU constellations, the sky is actually divided into 89 irregularly shaped boxes as the constellation Serpens is spli ... References * * * * * * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:List of stars in Andromeda *List Andromeda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18 Andromedae
18 Andromedae, abbreviated 18 And, is a single star in the northern constellation of Andromeda. ''18 Andromedae'' is the Flamsteed designation. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.350. The annual parallax shift of can be used to estimate a distance of 413 light years. It is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +10 km/s. This is a B-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of B9 Ve, where the 'e' notation indicates this is a Be star. The stellar spectrum of 18 And displays an emission line in the hydrogen Brackett series due to a dense gaseous circumstellar envelope. The star is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 183 km/s and has about three times the mass of the Sun. It is radiating 147 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
22 Andromedae
22 Andromedae, abbreviated 22 And, is a single star in the constellation Andromeda. ''22 Andromedae'' is the Flamsteed designation. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.04. The distance to 22 And can be estimated from its annual parallax shift of just , which shows it to be around 1,500 light years away. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −8.2 km/s. This is a bright giant with a stellar classification of F5 II. Gray et al. (2001) classify it as F5 Ib–II metal-weak, with the metallic lines matching a class of F0 whereas hydrogen lines match an F5. It is around 62 million years old with a projected rotational velocity of 46. The star has six times the mass of the Sun and has expanded to about 17 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 1,436 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature The effective temperature of a body such as a star or plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |