|
Andesitic
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predominantly of sodium-rich plagioclase plus pyroxene or hornblende. Andesite is the extrusive equivalent of plutonic diorite. Characteristic of subduction zones, andesite represents the dominant rock type in island arcs. The average composition of the continental crust is andesitic. Along with basalts, andesites are a component of the Martian crust. The name ''andesite'' is derived from the Andes mountain range, where this rock type is found in abundance. It was first applied by Christian Leopold von Buch in 1826. Description Andesite is an aphanitic (fine-grained) igneous rock that is intermediate in its content of silica and low in alkali metals. It has less than 20% quartz and 10% feldspathoid by volume, with at least 65% of the feldsp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Habit
In mineralogy, crystal habit is the characteristic external shape of an individual crystal or crystal group. The habit of a crystal is dependent on its crystallographic form and growth conditions, which generally creates irregularities due to limited space in the crystallizing medium (commonly in rocks).Klein, Cornelis, 2007, ''Minerals and Rocks: Exercises in Crystal and Mineral Chemistry, Crystallography, X-ray Powder Diffraction, Mineral and Rock Identification, and Ore Mineralogy,'' Wiley, third edition, Wenk, Hans-Rudolph and Andrei Bulakh, 2004, ''Minerals: Their Constitution and Origin,'' Cambridge, first edition, Recognizing the habit can aid in mineral identification and description, as the crystal habit is an external representation of the internal ordered atomic arrangement. Most natural crystals, however, do not display ideal habits and are commonly malformed. Hence, it is also important to describe the quality of the shape of a mineral specimen: * Euhedral: a cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyritic
Porphyritic is an adjective used in geology to describe igneous rocks with a distinct difference in the size of mineral crystals, with the larger crystals known as phenocrysts. Both extrusive and intrusive rocks can be porphyritic, meaning all types of igneous rocks can display some degree of porphyritic texture. Most Porphyritic rocks have bimodal size ranges, meaning the rock is composed of two distinct sizes of crystal. In extrusive rocks, the phenocrysts are surrounded by a fine-grained (aphanitic) matrix or groundmass of volcanic glass or non-visible crystals, commonly seen in porphyritic basalt. Porphyritic intrusive rocks have a matrix with individual crystals easily distinguished with the eye, but one group of crystals appearing clearly much bigger than the rest, as in a porphyritic granite. The term comes from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "purple". Purple was the color of royalty, and the "imperial porphyry" was a deep purple igneous rock with large crystals of pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feldspars and the ''alkali'' (potassium-sodium) feldspars. Feldspars make up about 60% of the Earth's crust, and 41% of the Earth's continental crust by weight. Feldspars crystalize from magma as both intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks and are also present in many types of metamorphic rock. Rock formed almost entirely of calcic plagioclase feldspar is known as anorthosite. Feldspars are also found in many types of sedimentary rocks. Compositions The feldspar group of minerals consists of tectosilicates, silicate minerals in which silicon ions are linked by shared oxygen ions to form a three-dimensional network. Compositions of major elements in common feldspars can be expressed in terms of three endmembers: * potassium feldspar (K-spar) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feldspathoid
The feldspathoids are a group of tectosilicate minerals which resemble feldspars but have a different structure and much lower silica content. They occur in rare and unusual types of igneous rocks, and are usually not found in rocks containing primary quartz. A notable exception where feldspathoids and quartz-bearing rocks are found together is the Red Hill Syenite. Foid, a contraction of the term ''feldspathoid'', is applied to any igneous rock containing up to 60% modal feldspathoid minerals. For example, a syenite with significant nepheline Nepheline, also called nephelite (), is a rock-forming mineral in the feldspathoid groupa silica-undersaturated aluminosilicate, Na3 K Al4 Si4 O16, that occurs in intrusive and volcanic rocks with low silica, and in their associated pegmatite ... present can be termed a ''nepheline-bearing syenite'' or ''nepheline syenite'', with the term ''nepheline'' replaceable by any foid mineral. Such terminology is used in the Streckeisen ( QAPF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkali Metals
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names for the elements in some languages, such as German and Russian. rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). Together with hydrogen they constitute group 1, which lies in the s-block of the periodic table. All alkali metals have their outermost electron in an s-orbital: this shared electron configuration results in their having very similar characteristic properties. Indeed, the alkali metals provide the best example of group trends in properties in the periodic table, with elements exhibiting well-characterised homologous behaviour. This family of elements is also known as the lithium family after its leading element. The alkali metals are all shiny, soft, highly reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure and readily lose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalt Qapf
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flows that can spread over great areas before cooling and solidifying. Flood basalts are thick sequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Leopold Von Buch
Christian Leopold von Buch (26 April 1774 – 4 March 1853), usually cited as Leopold von Buch, was a German geologist and paleontologist born in Stolpe an der Oder (now a part of Angermünde, Brandenburg) and is remembered as one of the most important contributors to geology in the first half of the nineteenth century. His scientific interest was devoted to a broad spectrum of geological topics: volcanism, petrology, fossils, stratigraphy and mountain formation. His most remembered accomplishment is the scientific definition of the Jurassic system. Biography Buch studied with Alexander von Humboldt under Abraham Gottlob Werner at the mining school in Freiberg, Saxony. He afterwards completed his education at the universities of Halle and Göttingen. German and Italian explorations He began writing on geological topics early in life. His ''Versuch einer mineralogischen Beschreibung von Landeck'' (Breslau, 1797) was translated into French (Paris, 1805), and into English as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S latitude), and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from north to south through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, El Alto and La Paz. The Altiplano plateau is the world's second-highest after the Tibetan plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three major divisions based on climate: the Tropical Andes, the Dry Andes, and the Wet Andes. The Andes Mountains are the highest m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
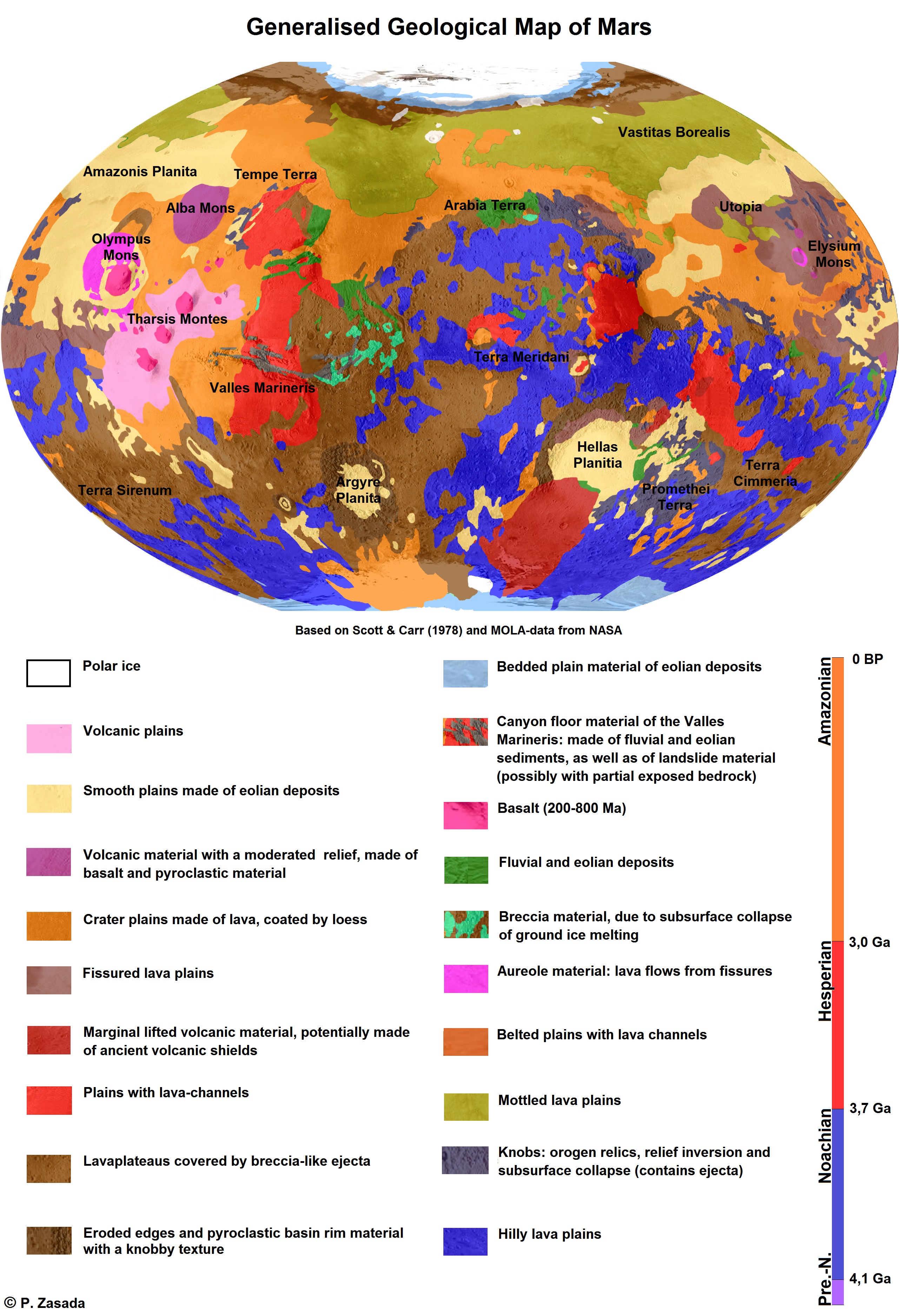
Geology Of Mars
The geology of Mars is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term ''geology'' is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term incorporates aspects of geophysics, geochemistry, mineralogy, geodesy, and cartography. A neologism, areology, from the Greek word ''Arēs'' (Mars), sometimes appears as a synonym for Mars's geology in the popular media and works of science fiction (e.g. Kim Stanley Robinson, Kim Stanley Robinson's Mars trilogy). The term areology is also used by the Areological Society. Geological map of Mars (2014) File:Geologic Map of Mars figure2.pdf, Figure 2 for the geologic map of Mars Global Martian topography and large-scale features Composition of Mars Mars is a terrestrial planet, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
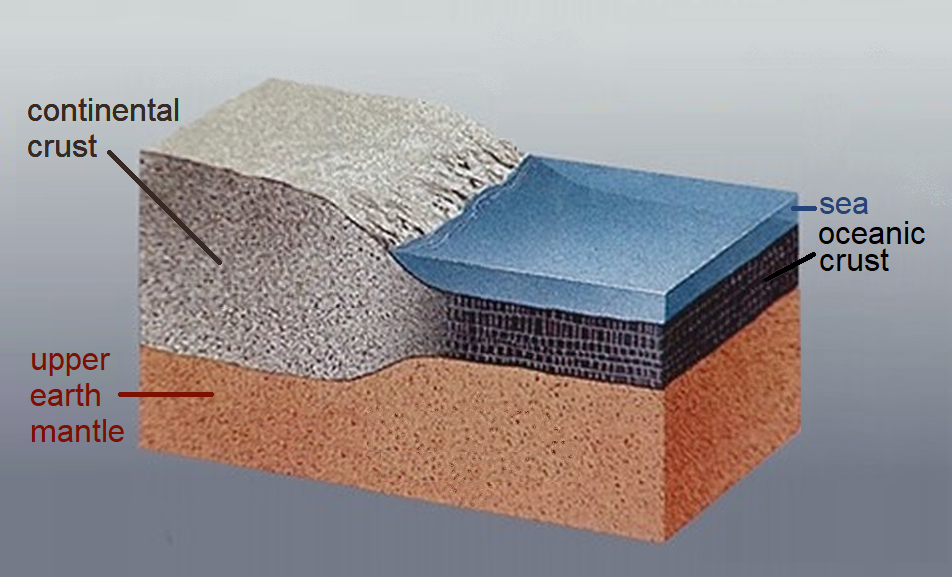
Continental Crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called ''sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called ''sima'' which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. The continental crust consists of various layers, with a bulk composition that is intermediate (SiO2 wt% = 60.6). The average density of continental crust is about , less dense than the ultramafic material that makes up the mantle, which has a density of around . Continental crust is also less dense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Arc
Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle along the subduction, subduction zone. They are the principal way by which continental growth is achieved. Island arcs can either be active or inactive based on their seismicity and presence of volcanoes. Active arcs are ridges of recent volcanoes with an associated deep seismic zone. They also possess a distinct curved form, a chain of active or recently extinct volcanoes, a Oceanic trench, deep-sea trench, and a large negative Bouguer anomaly on the convex side of the volcanic arc. The small positive gravity anomaly associated with volcanic arcs has been interpreted by many authors as due to the presence of dense volcanic rocks beneath the arc. Inactive arcs are a chain of islands which contains older volcanic and volcaniclastic rocks. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)