|
Anales De Los Cakchiqueles
The ''Annals of the Cakchiquels'' (in es, Anales de los Cakchiqueles, also known by the alternative Spanish titles, ''Anales de los Xahil'', ''Memorial de Tecpán-Atitlán'' or ''Memorial de Sololá'') is a manuscript written in Kaqchikel by Francisco Hernández Arana Xajilá in 1571, and completed by his grandson, Francisco Rojas, in 1604. The manuscript — which describes the legends of the Kaqchikel nation and has historical and mythological components — is considered an important historical document on post-classic Maya civilization in the highlands of Guatemala. The manuscript, initially kept by the Xahil lineage in the town of Sololá in Guatemala, was later discovered in the archives of the ''San Francisco de Guatemala'' convent in 1844. It was subsequently translated by the abbot Charles Étienne Brasseur de Bourbourg in 1855 (the same translator of the Rabinal Achí), and then passed through several more hands before being published in an English translation by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuscript
A manuscript (abbreviated MS for singular and MSS for plural) was, traditionally, any document written by hand – or, once practical typewriters became available, typewritten – as opposed to mechanically printing, printed or reproduced in some indirect or automated way. More recently, the term has come to be understood to further include ''any'' written, typed, or word-processed copy of an author's work, as distinguished from the rendition as a printed version of the same. Before the arrival of printing, all documents and books were manuscripts. Manuscripts are not defined by their contents, which may combine writing with mathematical calculations, maps, music notation, explanatory figures, or illustrations. Terminology The study of the writing in surviving manuscripts, the "hand", is termed palaeography (or paleography). The traditional abbreviations are MS for manuscript and MSS for manuscripts, while the forms MS., ms or ms. for singular, and MSS., mss or ms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel G
Daniel is a masculine given name and a surname of Hebrew origin. It means "God is my judge"Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 68. (cf. Gabriel—"God is my strength"), and derives from two early biblical figures, primary among them Daniel from the Book of Daniel. It is a common given name for males, and is also used as a surname. It is also the basis for various derived given names and surnames. Background The name evolved into over 100 different spellings in countries around the world. Nicknames (Dan, Danny) are common in both English and Hebrew; "Dan" may also be a complete given name rather than a nickname. The name "Daniil" (Даниил) is common in Russia. Feminine versions (Danielle, Danièle, Daniela, Daniella, Dani, Danitza) are prevalent as well. It has been particularly well-used in Ireland. The Dutch names "Daan" and "Daniël" are also variations of Daniel. A related surname develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayan Literature
The traditions of indigenous Mesoamerican literature extend back to the oldest-attested forms of early writing in the Mesoamerican region, which date from around the mid-1st millennium BCE. Many of the pre-Columbian cultures of Mesoamerica are known to have been literate societies, who produced a number of Mesoamerican writing systems of varying degrees of complexity and completeness. Mesoamerican writing systems arose independently from other writing systems in the world, and their development represents one of the very few such origins in the history of writing. The literature and texts created by indigenous Mesoamericans are the earliest-known from the Americas for primarily two reasons: Firstly the fact that the native populations of Mesoamerica were the first to enter into intensive contact with Europeans, assuring that many samples of Mesoamerican literature have been documented in surviving and intelligible forms. Secondly, the long tradition of Mesoamerican writing which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conquistador
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (, ; meaning 'conquerors') were the explorer-soldiers of the Spanish and Portuguese Empires of the 15th and 16th centuries. During the Age of Discovery, conquistadors sailed beyond Europe to the Americas, Oceania, Africa, and Asia, colonizing and opening trade routes. They brought much of the Americas under the dominion of Spain and Portugal. After arrival in the West Indies in 1492, the Spanish, usually led by hidalgos from the west and south of Spain, began building an American empire in the Caribbean using islands such as Hispaniola, Cuba, and Puerto Rico as bases. From 1519 to 1521, Hernán Cortés waged a campaign against the Aztec Empire, ruled by Moctezuma II. From the territories of the Aztec Empire, conquistadors expanded Spanish rule to northern Central America and parts of what is now the southern and western United States, and from Mexico sailing the Pacific Ocean to the Philippines. Other conquistadors took over the Inca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chichicastenango
Chichicastenango, also known as Santo Tomás Chichicastenango, is a town, with a population of 71,394 (2018 census), and the municipal seat for the surrounding municipality of the same name in the El Quiché department of Guatemala. It is located in a mountainous region about northwest of Guatemala City, at an altitude of 1,965 m (6,447 ft). The Spanish conquistadors gave the town its name from the Nahuatl name used by their soldiers from Tlaxcala: Tzitzicaztenanco, or ''City of Nettles''. Its original name was ''Chaviar''. Chichicastenango is a K'iche' Maya cultural centre. According to the 2012 census, 98.5% of the municipality's population is indigenous Mayan K'iche. Of the population, 21% speak only K'iche, 71% speak both K'iche and Spanish, and the remaining 8% speak only Spanish. Market Chichicastenango hosts market days on Thursdays and Sundays where vendors sell handicrafts, food, flowers, pottery, wooden boxes, condiments, medicinal plants, candles, pom and copa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
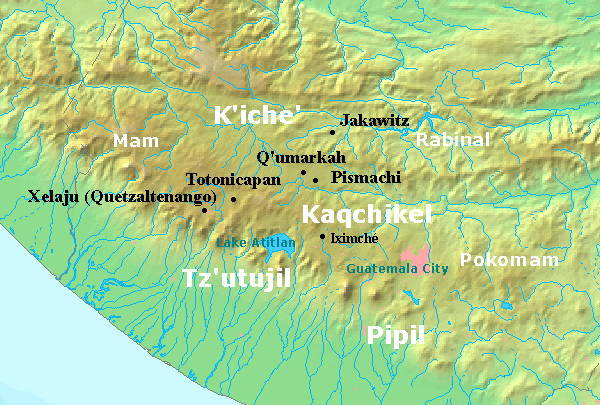
Kʼicheʼ Kingdom Of Qʼumarkaj
The Kʼicheʼ kingdom of Qʼumarkaj was a state in the highlands of modern-day Guatemala which was founded by the Kʼicheʼ (Quiché) Maya in the thirteenth century, and which expanded through the fifteenth century until it was conquered by Spanish and Nahua forces led by Pedro de Alvarado in 1524. The Kʼicheʼ kingdom reached its height under the king Kʼiqʼab who ruled from the fortified town of Qʼumarkaj (also called by its Nahuatl name Utatlán) near the modern town of Santa Cruz del Quiché. During his rule the Kʼicheʼ ruled large areas of highland Guatemala extending into Mexico, and they subdued other Maya peoples such as the Tzʼutujil, Kaqchikel and Mam, as well as the Nahuan Pipil people. Historical sources The history of the Quiché Kingdom is described in a number of documents written in postcolonial times both in Spanish and in indigenous languages such as Classical Kʼicheʼ and Kaqchikel. Important sources include the Popol Vuh which, apart from the well- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Título De Totonicapán
The ''Título de Totonicapán'' (Spanish for "Title of Totonicapán"), sometimes referred to as the ''Título de los Señores de Totonicapán'' ("Title of the Lords of Totonicapán") is the name given to a Kʼicheʼ language document written around 1554 in Guatemala. The ''Título de Totonicapán'' is one of the two most important surviving colonial period Kʼicheʼ language documents, together with the ''Popol Vuh''. The document contains history and legend of the Kʼicheʼ people from their mythical origins down to the reign of their most powerful king, Kʼiqʼab. History of the document In 1834 the Kʼicheʼ inhabitants of Totonicapán asked the departmental governor to persuade Dionisio José Chonay, the curate of Sacapulas, to translate the document into Spanish. The Spanish translation was archived in Totonicapán where it was found by French historian Charles Étienne Brasseur de Bourbourg in 1860. Brasseur de Bourbourg made a copy of the document and took it with him back t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historia De Los Xpantzay De Tecpán Guatemala
Historia may refer to: * Historia, the local version of the History channel in Spain and Portugal * Historia (TV channel), a Canadian French language specialty channel * Historia (newspaper), a French monthly newspaper devoted to History topics * Historia (video), a compilation video released by Def Leppard * Historia (Antiquity journal), a peer-reviewed history journal specialised in Greek and Roman Antiquity * Historia (history of the Americas journal), a peer-reviewed history journal dealing with the history of the Americas * the Latin word for historiography * Historia (drama), an unfinished drama of Polish writer Witold Gombrowicz, compiled from the author's notes by Konstanty Jeleński * Historia Reiss, a fictional character in Japanese manga and anime series ''Attack on Titan'' * Historia (Romanian magazine), history magazine owned by Adevărul See also * ''Historias'', by Ricardo Arona * Herstory, feminism * History (other) * Histories (other) * Histoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popol Vuh
''Popol Vuh'' (also ''Popol Wuj'' or ''Popul Vuh'' or ''Pop Vuj'') is a text recounting the mythology and history of the Kʼicheʼ people, one of the Maya peoples, who inhabit Guatemala and the Mexican states of Chiapas, Campeche, Yucatan and Quintana Roo, as well as areas of Belize, Honduras and El Salvador. The ''Popol Vuh'' is a foundational sacred narrative of the Kʼicheʼ people from long before the Spanish conquest of the Maya. It includes the Mayan creation myth, the exploits of the Maya Hero Twins, Hero Twins Hunahpú and Xbalanqué, and a chronicle of the Kʼicheʼ people. The name "Popol Vuh" translates as "Book of the Community" or "Book of Counsel" (literally "Book that pertains to the mat", since a woven mat was used as a royal throne in ancient Kʼicheʼ society and symbolised the unity of the community). It was originally preserved through oral tradition until approximately 1550, when it was recorded in writing. The documentation of the ''Popol Vuh'' is credited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iximché
Iximcheʼ () (or Iximché using Spanish orthography) is a Pre-Columbian Mesoamerican archaeological site in the western highlands of Guatemala. Iximche was the capital of the Late Postclassic Kaqchikel Maya kingdom from 1470 until its abandonment in 1524. The architecture of the site included a number of pyramid-temples, palaces and two Mesoamerican ballcourts. Excavators uncovered the poorly preserved remains of painted murals on some of the buildings and ample evidence of human sacrifice. The ruins of Iximche were declared a Guatemalan National Monument in the 1960s.Centro de Acción Legal - Ambiental y Social de Guatemala (CALAS). The site has a small museum displaying a number of pieces found there, including sculptures and ceramics. It is open daily. For many years the Kaqchikel served as loyal allies of the Kʼicheʼ Maya.Schele & Mathews 1999, p.295. The growing power of the Kaqchikel within the alliance eventually caused such friction that the Kaqchikel were forced t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabinal Achí
The ''Rabinal Achí'' is a Maya theatrical play written in the Kʼicheʼ language and performed annually in Rabinal, Baja Verapaz, Guatemala. Its original name is ''Xajoj Tun'', meaning "Dance of the Tun" instrument also known as wooden drum. This is one of the few surviving performance pieces from before colonization. It takes place every year on January 25 and involves the entire community of Rabinal. A combination of movement, song, and instrumentation meld the piece together. This performance has been a part of Rabinal history for centuries, and continues to be a part of the culture today. The story of the ''Rabinal Achí'' centers on a historical feud between Rabinal and Kʼicheʼ, two neighboring cities. Colorful costumes and wooden masks are used to differentiate the characters as they play out their roles in the song-dance-drama. Origins The ''Rabinal Achí'' is a Maya song-dance-drama from the fifteenth century that uses vibrant costumes and wooden masks to tell the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaqchikel Language
The Kaqchikel language (in modern orthography; formerly also spelled Cakchiquel or Cachiquel) is an indigenous Mesoamerican language and a member of the Quichean–Mamean branch of the Mayan languages family. It is spoken by the indigenous Kaqchikel people in central Guatemala. It is closely related to the Kʼicheʼ (Quiché) and Tzʼutujil languages. Kaqchikel is taught in public schools through Guatemala's intercultural bilingual education programs. History Before conquest Kaqchikel is spoken by the indigenous Maya in Central Guatemala. The Mayan civilization dates back to the Pre-classic period (2000 BC to 300 AD). Geographically, the Maya expanded from Mexico, Belize and Guatemala. This changed between 900 AD and when the Spanish arrived. Their settlement moved west and into the highlands of Guatemala. Archaeological evidence shows suggestions of Kaqchikel living in Iximcheʼ, which today is located near Tecpan, Guatemala. After conquest In 1523, the Spania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
