|
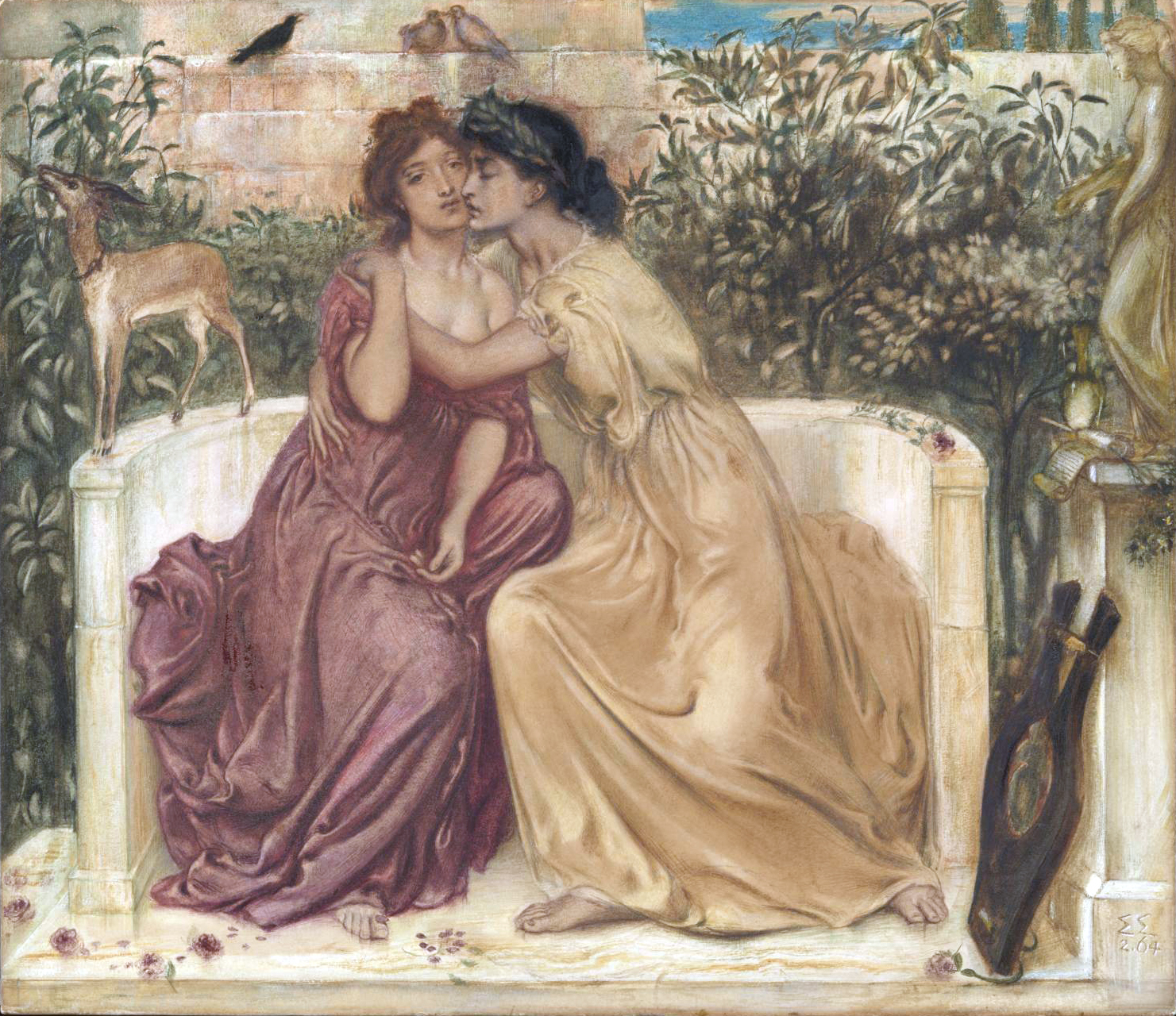
Anactoria
Anactoria (or Anaktoria) is the name of a woman mentioned by poet Sappho as a lover of hers in Sappho's Fragment 16 (Lobel-Page edition often referred to by the title "To an Army Wife, in Sardis". Sappho 31 is traditionally called the "Ode to Anactoria", though no name appears in it (A. C. Swinburne, quoted in Lipking 1988 Algernon Charles Swinburne wrote a long poem in ''Poems and Ballads'' titled ''Anactoria'', in which Sappho addresses Anactoria in a long monologue written in pentameter with rhyming couplets. The poem created a sensation amongst contemporary readers by openly approaching hitherto taboo topics such as Lesbianism and dystheism. Swinburne's Sappho is heavily inspired by Milton's Satan and John Donne's poem, also on Sappho. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sappho's Fragment 16
Sappho 16 is a fragment of a poem by the archaic Greece, archaic Greek lyric poet Sappho. It is from Book I of the Alexandrian edition of Sappho's poetry, and is known from a second-century papyrus discovered at Oxyrhynchus in Egypt at the beginning of the twentieth century. Sappho 16 is a love poem – the genre for which Sappho was best known – which praises the beauty of the narrator's beloved, Anactoria, and expresses the speaker's desire for her now that she is absent. It makes the case that the most beautiful thing in the world is whatever one desires, using Helen of Troy's elopement with Paris (mythology), Paris as a mythological exemplum to support this argument. The poem is at least 20 lines long, though it is uncertain whether the poem ends at line 20 or continues for another stanza. Preservation Fragment 16 was preserved on Papyrus Oxyrhynchus 1231, a second-century manuscript of Book I of an edition of Sappho, published by Bernard Pyne Grenfell and Arthur Surridg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dystheism
Dystheism (from Greek δυσ- ''dys-'', "bad" and θεός theos, "god") is the belief that a god is not wholly good and can even be considered evil. Definitions of the term somewhat vary, with one author defining it as "where God decides to become malevolent". The broad theme of dystheism has existed for millennia, as shown by trickster gods found in polytheistic belief systems and by the view of other representations of supreme beings (such as those of the Abrahamic religions, particularly the Old Testament) through a nonreligious lens as angry, vengeful, smiting and hypocritical. The modern concept dates back many decades, with the Victorian era figure Algernon Charles Swinburne writing in his work ''Anactoria'' about the ancient Greek poet Sappho and her lover Anactoria in explicitly dystheistic imagery that includes cannibalism and sadomasochism. Background and details The concept has been used frequently in popular culture and is a part of several religious traditions in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algernon Charles Swinburne
Algernon Charles Swinburne (5 April 1837 – 10 April 1909) was an English poet, playwright, novelist, and critic. He wrote several novels and collections of poetry such as ''Poems and Ballads'', and contributed to the famous Eleventh Edition of the ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Swinburne wrote about many taboo topics, such as lesbianism, sado-masochism, and anti-theism. His poems have many common motifs, such as the ocean, time, and death. Several historical people are featured in his poems, such as Sappho ("Sapphics"), Anactoria ("Anactoria"), and Catullus ("To Catullus"). Biography Swinburne was born at 7 Chester Street, Grosvenor Place, London, on 5 April 1837. He was the eldest of six children born to Captain (later Admiral) Charles Henry Swinburne (1797–1877) and Lady Jane Henrietta, daughter of the 3rd Earl of Ashburnham, a wealthy Northumbrian family. He grew up at East Dene in Bonchurch on the Isle of Wight. The Swinburnes also had a London home at Whitehall G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poems And Ballads
''Poems and Ballads, First Series'' is the first collection of poems by Algernon Charles Swinburne, published in 1866. The book was instantly popular, and equally controversial. Swinburne wrote about many taboo topics, such as lesbianism, sado-masochism, and anti-theism. The poems have many common elements, such as the Ocean, Time, and Death. Several historical persons are mentioned in the poems, such as Sappho, Anactoria, Jesus ('' Galilaee'', La. "Galilean") and Catullus. Poems *A Ballad of Life *A Ballad of Death * Laus Veneris *Phædra *The Triumph of Time *Les Noyades *A Leave-Taking *Itylus *Anactoria *Hymn to Proserpine *Ilicet *Hermaphroditus *Fragoletta *Rondel *Satia te Sanguine *A Litany *A Lamentation *Anima Anceps *In the Orchard *A Match *Faustine *A Cameo *Song before Death *Rococo *Stage Love *The Leper *A Ballad of Burdens *Rondel *Before the Mirror *Erotion *In Memory of Walter Savage Landor *A Song in Time of Order. 1852 *A Song in Time of Revolution. 1860 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sappho
Sappho (; el, Σαπφώ ''Sapphō'' ; Aeolic Greek ''Psápphō''; c. 630 – c. 570 BC) was an Archaic Greek poet from Eresos or Mytilene on the island of Lesbos. Sappho is known for her Greek lyric, lyric poetry, written to be sung while accompanied by music. In ancient times, Sappho was widely regarded as one of the greatest lyric poets and was given names such as the "Tenth Muse" and "The Poetess". Most of Poetry of Sappho, Sappho's poetry is now lost, and what is extant has mostly survived in fragmentary form; only the "Ode to Aphrodite" is certainly complete. As well as lyric poetry, ancient commentators claimed that Sappho wrote elegiac and iambic poetry. Three epigrams attributed to Sappho are extant, but these are actually Hellenistic imitations of Sappho's style. Little is known of Sappho's life. She was from a wealthy family from Lesbos, though her parents' names are uncertain. Ancient sources say that she had three brothers; Charaxos (Χάραξος), Larichos ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sardis
Sardis () or Sardes (; Lydian: 𐤳𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣 ''Sfard''; el, Σάρδεις ''Sardeis''; peo, Sparda; hbo, ספרד ''Sfarad'') was an ancient city at the location of modern ''Sart'' (Sartmahmut before 19 October 2005), near Salihli, in Turkey's Manisa Province. Sardis was the capital of the ancient kingdom of Lydia, an important city of the Persian Empire, the seat of a Seleucid satrap, the seat of a proconsul under the Roman Empire, and the metropolis of the province Lydia in later Roman and Byzantine times. It is mentioned in the New Testament. Its importance was due first to its military strength, secondly to it being situated on an important highway leading from the interior to the Aegean coast, and thirdly to its commanding the wide and fertile plain of the Hermus. Geography Sardis was situated in the middle of Hermus valley, at the foot of Mount Tmolus, a steep and lofty spur which formed the citadel. It was about south of that Hermus. Today, the site is loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sappho 31
Sappho 31 is an archaic Greek lyric poem by the ancient Greek poet Sappho of the island of Lesbos. The poem is also known as phainetai moi (φαίνεταί μοι) after the opening words of its first line. It is one of Sappho's most famous poems, describing her love for a young woman. Fragment 31 is one of Sappho's most famous works, and has been the subject of numerous translations and adaptations from ancient times to the present day. Celebrated for its portrayal of intense emotion, the poem has influenced modern conceptions of lyric poetry, and its depiction of desire continues to influence writers today. Preservation Fragment 31 was one of the few substantial fragments of Sappho to survive from ancient times, preserved in the first-century AD treatise on aesthetics ''On the Sublime''. Four stanzas are well-preserved, followed by part of one more line; this, as well as Catullus' adaptation of the poem, suggests that there was originally one more stanza of the poem, often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesbianism
A lesbian is a homosexual woman.Zimmerman, p. 453. The word is also used for women in relation to their sexual identity or sexual behavior, regardless of sexual orientation, or as an adjective to characterize or associate nouns with female homosexuality or same-sex attraction. The concept of "lesbian" to differentiate women with a shared sexual orientation evolved in the 20th century. Throughout history, women have not had the same freedom or independence as men to pursue homosexual relationships, but neither have they met the same harsh punishment as homosexual men in some societies. Instead, lesbian relationships have often been regarded as harmless, unless a participant attempts to assert privileges traditionally enjoyed by men. As a result, little in history was documented to give an accurate description of how female homosexuality was expressed. When early sexologists in the late 19th century began to categorize and describe homosexual behavior, hampered by a lack of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th-century BC Greek Women
The 7th century is the period from 601 ( DCI) through 700 ( DCC) in accordance with the Julian calendar in the Common Era. The spread of Islam and the Muslim conquests began with the unification of Arabia by Muhammad starting in 622. After Muhammad's death in 632, Islam expanded beyond the Arabian Peninsula under the Rashidun Caliphate (632–661) and the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750). The Muslim conquest of Persia in the 7th century led to the downfall of the Sasanian Empire. Also conquered during the 7th century were Syria, Palestine, Armenia, Egypt, and North Africa. The Byzantine Empire suffered setbacks during the rapid expansion of the Caliphate, a mass incursion of Slavs in the Balkans which reduced its territorial limits. The decisive victory at the Siege of Constantinople in the 670s led the empire to retain Asia Minor which assured the existence of the empire. In the Iberian Peninsula, the 7th century was known as the ''Siglo de Concilios'' (century of councils) refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6th-century BC Greek Women
The 6th century is the period from 501 through 600 in line with the Julian calendar. In the West, the century marks the end of Classical Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages. The collapse of the Western Roman Empire late in the previous century left Europe fractured into many small Germanic kingdoms competing fiercely for land and wealth. From the upheaval the Franks rose to prominence and carved out a sizeable domain covering much of modern France and Germany. Meanwhile, the surviving Eastern Roman Empire began to expand under Emperor Justinian, who recaptured North Africa from the Vandals and attempted fully to recover Italy as well, in the hope of reinstating Roman control over the lands once ruled by the Western Roman Empire. In its second Golden Age, the Sassanid Empire reached the peak of its power under Khosrau I in the 6th century.Roberts, J: "History of the World.". Penguin, 1994. The classical Gupta Empire of Northern India, largely overrun by the Huna, ended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexuality In Ancient Greece
The social construction of human sexuality and sexual behavior—along with its taboos, regulation, and social and political impact—has had a profound effect on the various cultures of the world since prehistoric times. The study of the history of human sexuality The work of Swiss jurist Johann Bachofen made a major impact on the study of the history of sexuality. Many authors, notably Lewis Henry Morgan and Friedrich Engels, were influenced by Bachofen, and criticized Bachofen's ideas on the subject, which were almost entirely drawn from a close reading of ancient mythology. In his 1861 book ''Mother Right: An Investigation of the Religious and Juridical Character of Matriarchy in the Ancient World'' Bachofen writes that in the beginning human sexuality was chaotic and promiscuous. This "aphroditic" stage was replaced by a matriarchal "demeteric" stage, which resulted from the mother being the only reliable way of establishing descendants. Only upon the switch to male-enfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Poems
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies. ** Britishness, the British identity and common culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in the United Kingdom or, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *''Brit(ish)'', a 2018 memoir by Afua Hirsch *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) See also * Terminology of the British Isles * Alternative names for the British * English (other) * Britannic (other) * British Isles * Brit (other) * Briton (d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |