|
Amédée-François Lamy
Amédée-François Lamy was a French military officer. He was born at Mougins, in the French ''département'' of Alpes-Maritimes on 7 February 1858 and died in the battle of Kousséri on 22 April 1900. Early years Lamy's ambition to become an officer developed very early; at ten-years-old, he entered the Prytanée National Militaire, where he won the first prize in Geography in the general concourse of all the department's school, a possible sign of his future colonial career. In 1877 he entered at Saint-Cyr, the foremost French military academy. Military career Lamy began his career in 1879 as a Second Lieutenant in the First regiment of Algerian tirailleurs. He discovered Saharan Africa, and took part in the French occupation of Tunisia; he was sent in 1884 to Tonkin, where he remained until 1886. The following year he was back in Algeria, where he became ''aide-de-camp'' to the General in command of the division quartered in Algiers in 1887, and resumed his previous inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mougins
Mougins (; oc, Mogins ; la, Muginum ) is a commune in the Alpes-Maritimes département in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region in Southeastern France. In 2019, it had a population of 19,982. It is located on the heights of Cannes, in the arrondissement of Grasse. Mougins is a 15-minute drive from Cannes. The town is surrounded by forests, most notably the Valmasque forest. In the town there are pines, olives and cypress trees. History The hilltop of Mougins has been occupied since the pre-Roman period. Ancient Ligurian tribes who inhabited the coastal area between Provence and Tuscany, were eventually absorbed into the spread of the Roman Empire and then became part of an official Ligurian state that was created by Emperor Augustus (X Regio). On the Aurelia way linking from Rome to Arles, Muginum came into being during the 1st century BC. In 1056, Gillaume de Gauceron, the Count of Antibes, gave the Mougins hillside to the Monks of Saint Honorat (from the nearby Îles de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabih Az-Zubayr
Rabih az-Zubayr ibn Fadl Allah or Rabih Fadlallah ( ar, رابح فضل الله ,رابح الزبير ابن فضل الله), usually known as Rabah in French (c. 1842 – April 22, 1900), was a Sudanese warlord and slave trader who established a powerful empire east of Lake Chad, in today's Chad. Born around 1842 to an Arabic tribe in Halfaya Al-Muluk, a suburb of Khartoum, he first served with the irregular Egyptian cavalry in the Ethiopian campaign, during which he was wounded. When Rabih left the army in 1860s, he became the principal lieutenant of the Sudanese slaveholder Sebehr Rahma. Lieutenant of al-Zubayr (1870–1879) In the 19th century, Khartoum had become a very important Arab slave market, supplied through companies of ''Khartumi'' established in the region of Bahr el Ghazal, where they resided in zarības ( ar, زريْـبـة), thornbush-fortified bases kept by bāzinqirs (firearm-equipped slave soldiers). The warlord and slaveholder al-Zubayr Rahma Mans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
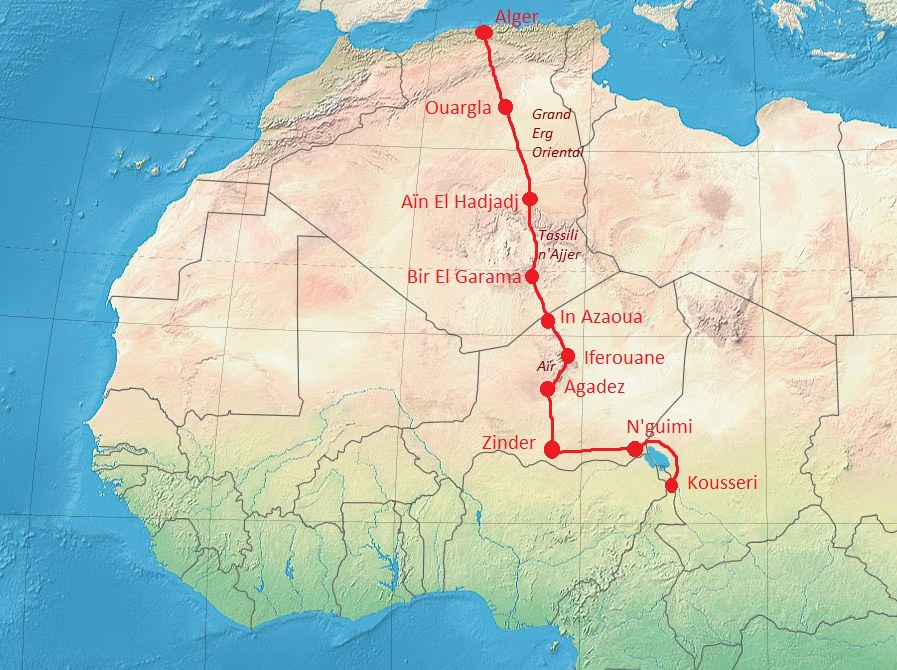
Kousséri
Kousséri (from ar, قصور ''quṣūr'' meaning "palaces"), founded and known as Mser in the indigenous Mser language is a city in Far North Province, Cameroon. It is the capital of the Logone-et-Chari department. It is a market town, and its population has recently been swollen by refugees from Chad. It had a population of 89,123 at the 2005 Census. The majority of the population are Shuwa Arabs with Chadian Arabic used as the lingua franca. It forms a transborder agglomeration with the city of N'Djamena, capital of Chad, from which it is separated by the Logone River and the Chari River. History Kousséri was part of the Bornu Empire. In March 1846 Omar (son of Sheik Mohammed), nominal general of the Bornu sultan Ibrahim suffered a defeat at Kousséri.Helmolt, Hans F. (ed.) (1903) ''The history of the world; a survey of a man's record, Volume III: West Asia and Africa'' Dodd, Meade and Co., New Yorkp. 536 In 1900 the village was occupied by soldiers of Rabij az-Zubayr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mort Du Commandant Lamy
''Mort'' is a fantasy novel by British writer Terry Pratchett. Published in 1987, it is the fourth ''Discworld'' novel and the first to focus on the character Death, who only appeared as a side character in the previous novels. The title is the name of its main character, and is also a play on words: in French and Catalan, ''mort'' means "death". The French language edition is titled ''Mortimer'', and the Catalan language edition is titled ''Morth''. In the BBC's 2003 Big Read contest, viewers voted on the "Nation's Best-loved Book"; ''Mort'' was among the Top 100 and chosen as the most popular of Pratchett's novels. In 2004, Pratchett stated that ''Mort'' was the first Discworld novel with which he was "pleased", stating that in previous books, the plot had existed to support the jokes, but that in ''Mort'', the plot was integral.Terry Pratchett [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone, and Togo, as well as Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha ( United Kingdom Overseas Territory).Paul R. Masson, Catherine Anne Pattillo, "Monetary union in West Africa (ECOWAS): is it desirable and how could it be achieved?" (Introduction). International Monetary Fund, 2001. The population of West Africa is estimated at about million people as of , and at 381,981,000 as of 2017, of which 189,672,000 are female and 192,309,000 male. The region is demographically and economically one of the fastest growing on the African continent. Early history in West Africa included a number of prominent regional powers that dominated different parts of both the coastal and internal trade networks, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chad
Chad (; ar, تشاد , ; french: Tchad, ), officially the Republic of Chad, '; ) is a landlocked country at the crossroads of North and Central Africa. It is bordered by Libya to the north, Sudan to the east, the Central African Republic to the south, Cameroon to the southwest, Nigeria to the southwest (at Lake Chad), and Niger to the west. Chad has a population of 16 million, of which 1.6 million live in the capital and largest city of N'Djamena. Chad has several regions: a desert zone in the north, an arid Sahelian belt in the centre and a more fertile Sudanian Savanna zone in the south. Lake Chad, after which the country is named, is the second-largest wetland in Africa. Chad's official languages are Arabic and French. It is home to over 200 different ethnic and linguistic groups. Islam (55.1%) and Christianity (41.1%) are the main religions practiced in Chad. Beginning in the 7th millennium BC, human populations moved into the Chadian basin in great numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gentil Mission
Gentil may refer to: People: *Jean-Paul Alaux, called Gentil, French landscape painter and lithographer *Émile Gentil, a French colonial administrator *Guillaume Le Gentil, a French astronomer *Jean-François Gentil, a French colonial officer *Joseph Philippe Gentil, Mauritian composer *Otto Gentil, German sculptor Places: *Gentil, Rio Grande do Sul, a municipality in Brazil *Port-Gentil Port-Gentil () or Mandji is the second-largest city of Gabon, and it is a leading seaport. It is the center of Gabon's petroleum and timber industries. The city is located on a delta island in the Ogooue delta with no bridges to the mainland. N ..., a city in Gabon Other: *Gentil, a white wine blend from Alsace {{disambig, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fernand Foureau
Fernand Foureau (17 October 1850 – 17 January 1914) was a French explorer and Governor of Martinique from 1908 to 1913. He was born at the Château de Frédière at Saint-Barbant in Haute-Vienne in the Limousin region of France. He studied under Henri Duveyrier, the Saharan explorer, who developed Foureau's own interest in the subject. Once in the Sahara, Foureau carried out the first artesian well drilling for the company Oued RIHR and then became famous for his numerous study trips in the desert from 1882, which earned him several awards from the French Société de géographie.''Nécrologie de Fernand Foureau'' by Henri Schirmer in the '' |
Alfred Le Châtelier
Frédéric Alfred Le Chatelier (23 November 1855 – 9 August 1929) was a French soldier, ceramicist and Islamologist. He spent most of his military career in the French African colonies. After leaving the army he was involved in a project to build a railway in the French Congo. He fought a duel and killed his opponent over mutual accusations of improper conduct concerning the Congo railways. He founded and ran a ceramics workshop for a few years before becoming a professor of Islamic Sociology at the Collège de France from 1902 to 1925. He exerted considerable influence over French policy towards the Muslim subjects of France's colonial empire, arguing for policy based on solidly documented facts, and for tolerance and sympathy to the rapidly changing Muslim societies. Early years (1855–76) Frédéric Alfred Le Chatelier was born on 12 November 1855 in Paris at 84 rue de Vaugirard in the center of a district of art and ceramic studios. He was one of seven children of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazzaville
Brazzaville (, kg, Kintamo, Nkuna, Kintambo, Ntamo, Mavula, Tandala, Mfwa, Mfua; Teke: ''M'fa'', ''Mfaa'', ''Mfa'', ''Mfoa''Roman Adrian Cybriwsky, ''Capital Cities around the World: An Encyclopedia of Geography, History, and Culture'', ABC-CLIO, USA, 2013, p. 60) is the capital and largest city of the Republic of the Congo (Congo Republic). Constituting the financial and administrative centre of the country, it is located on the north side of the Congo River, opposite Kinshasa, the capital city of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DR Congo). The population of the capital is estimated to exceed 1.8 million residents, comprising more than a third of the national populace. Some 40% are employed in non-agricultural professions. During World War II, Brazzaville was also the capital of Free France between 1940 and 1942. In 2013, Brazzaville was designated a City of Music by UNESCO; since then it has also been a member of the Creative Cities Network. Geography Brazzaville ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |