|
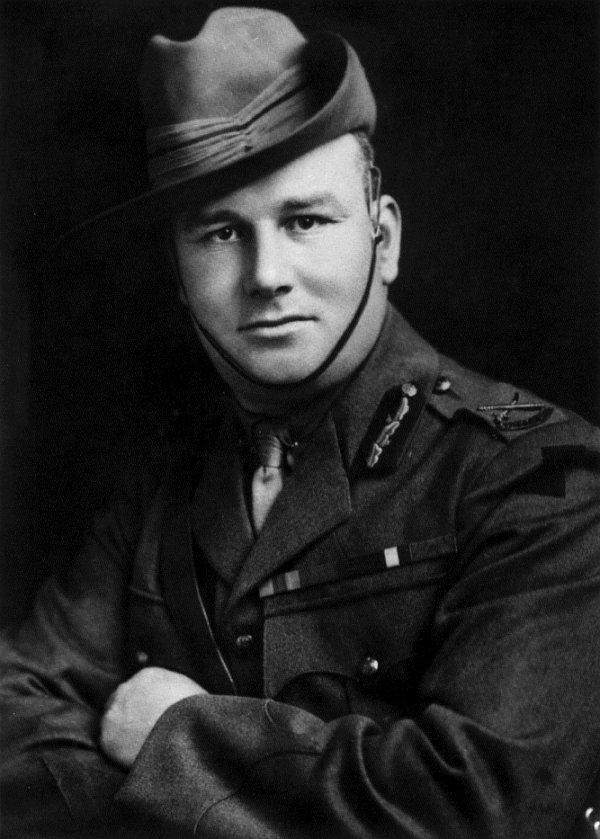
Amedeo Mecozzi
Amedeo Mecozzi (17 January 1892 – 2 November 1971) was an Italian fighter ace of World War I, a general of the Italian and a military theorist credited as the founding father of the "Attack air force" doctrine, which made him a strong opponent to general Giulio Douhet's theories. Early life and World War I Amedeo Mecozzi was born on 17 January 1892 in Rome.Franks et al 1997, pp. 145–146. Mecozzi was orphaned when young, and raised by his grandparents.Varriale 2009, pp. 62–63. He joined the Italian Army as an engineer and spent a year as a volunteer in Somalia before applying for pilot's training in 1915. In June 1915, he began training at Malpensa on 2 September. January 1916 saw him qualifying on Maurice Farman 12 and Maurice Farman 14 machines. On 1 February 1916 he received his pilot's certificate. In March 1916 he began flying reconnaissance missions for ''45a Squadriglia'', at some hazard; he often brought home an airplane damaged by enemy fire. On 1 January 1917, he w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fighter Ace
A flying ace, fighter ace or air ace is a military aviator credited with shooting down five or more enemy aircraft during aerial combat. The exact number of aerial victories required to officially qualify as an ace is varied, but is usually considered to be five or more. The concept of the "ace" emerged in 1915 during World War I, at the same time as aerial dogfighting. It was a propaganda term intended to provide the home front with a cult of the hero in what was otherwise a war of attrition. The individual actions of aces were widely reported and the image was disseminated of the ace as a chivalrous knight reminiscent of a bygone era. For a brief early period when air-to-air combat was just being invented, the exceptionally skilled pilot could shape the battle in the skies. For most of the war, however, the image of the ace had little to do with the reality of air warfare, in which fighters fought in formation and air superiority depended heavily on the relative availability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albatros D
An albatross is one of a family of large winged seabirds. Albatross or Albatros may also refer to: Animals * Albatross (butterfly) or ''Appias'', a genus of butterfly * Albatross (horse) (1968–1998), a Standardbred horse Literature * Albatross Books, a German publishing house that produced the first modern mass market paperback books * Albatros Literaturpreis, a literary award * "L'albatros" (poem) ("The Albatross"), 1859 poem by Charles Baudelaire * ''The Albatross'', a 1971 novella by Susan Hill * ''The Albatross'', the fictional propeller-sustained airship in Jules Verne's novel ''Robur the Conqueror'' * ''Albatross'' (novel), a 2019 novel by Terry Fallis Film and television * Films Albatros Films Albatros was a French film production company established in 1922. It was formed by a group of White Russian exiles who had been forced to flee following the 1917 Russian Revolution and subsequent Russian Civil War. Initially the firm's pe ..., a French film productio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigadier General
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed to a field command, a brigadier general is typically in command of a brigade consisting of around 4,000 troops (four battalions). Variants Brigadier general Brigadier general (Brig. Gen.) is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries, usually sitting between the ranks of colonel and major general. When appointed to a field command, a brigadier general is typically in command of a brigade consisting of around 4,000 troops (four battalions). In some countries, this rank is given the name of ''brigadier'', which is usually equivalent to ''brigadier general'' in the armies of nations that use the rank. The rank can be traced back to the militaries of Europe where a "brigadier general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major (rank)
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators, major is one rank above captain, and one rank below lieutenant colonel. It is considered the most junior of the field officer ranks. Background Majors are typically assigned as specialised executive or operations officers for battalion-sized units of 300 to 1,200 soldiers while in some nations, like Germany, majors are often in command of a company. When used in hyphenated or combined fashion, the term can also imply seniority at other levels of rank, including ''general-major'' or ''major general'', denoting a low-level general officer, and ''sergeant major'', denoting the most senior non-commissioned officer (NCO) of a military unit. The term ''major'' can also be used with a hyphen to denote the leader of a military band such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Relations
Public relations (PR) is the practice of managing and disseminating information from an individual or an organization (such as a business, government agency, or a nonprofit organization) to the public in order to influence their perception. Public relations and publicity differ in that PR is controlled internally, whereas publicity is not controlled and contributed by external parties. Public relations may include an organization or individual gaining exposure to their audiences using topics of public interest and news items that do not require direct payment. The exposure mostly is media-based. This differentiates it from advertising as a form of marketing communications. Public relations aims to create or obtain coverage for clients for free, also known as earned media, rather than paying for marketing or advertising also known as paid media. But in the early 21st century, advertising is also a part of broader PR activities. An example of good public relations would be ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pfalz Flugzeugwerke
Pfalz Flugzeugwerke was a World War I German aircraft manufacturer, located at the Speyer airfield in the Palatinate (German: Pfalz). They are best known for their series of fighters, notably the Pfalz D.III and Pfalz D.XII. The company went bankrupt after the Armistice, when the French occupation forces confiscated all of the equipment, but the factory was re-used by various other companies until re-forming in 1997. Today they are a parts manufacturer referred to as PFW. Early history Pfalz was the brainchild of Alfred Eversbusch, son of a foundry owner in Neustadt an der Weinstraße. It appears that he had built his own aircraft between 1912 and 1913, although the exact origin of the design is unclear. On June 3, 1913, the Pfalz company was registered, consisting of Alfred, his brother Ernst, and his brother-in-law Willy Sabersky-Müssigbrodt, as well as several investors: Richard and Eugen Kahn, and August Kahn (unrelated). They initially proposed to build designs from A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albatros Flugzeugwerke
Albatros Flugzeugwerke GmbH was a German aircraft manufacturer best known for supplying the German airforces during World War I. The company was based in Johannisthal, Berlin, where it was founded by Walter Huth and Otto Wiener on December 20, 1909. The company (and its subsidiary, Ostdeutsche Albatros Werke (OAW)) produced some of the most capable fighter aircraft of World War I, notably the Albatros D.III and Albatros D.V, both designed by Robert Thelen for the firm. The works continued to operate until 1931, when it was merged into Focke-Wulf. History The company was founded in Berlin-Johannisthal the end of 1909 by Enno Walther Huth as Albatros Werke AG. The first aircraft the company produced was a French Antoinette monoplane, which they built under licence. They then produced several versions of the Etrich Taube monoplane, as well the Doppeltaube biplane which used the same basic planform. A variety of other biplanes, with more conventional wing planforms were also b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fokker D
Fokker was a Dutch aircraft manufacturer named after its founder, Anthony Fokker. The company operated under several different names. It was founded in 1912 in Berlin, Germany, and became famous for its fighter aircraft in World War I. In 1919 the company moved its operations to the Netherlands. During its most successful period in the 1920s and 1930s, it dominated the civil aviation market. Fokker went into bankruptcy in 1996, and its operations were sold to competitors. History Fokker in Germany At age 20, while studying in Germany, Anthony Fokker built his initial aircraft, the ''Spin'' (Spider)—the first Dutch-built plane to fly in his home country. Taking advantage of better opportunities in Germany, he moved to Berlin, where in 1912, he founded his first company, Fokker Aeroplanbau, later moving to the Görries suburb just southwest of Schwerin (at ), where the current company was founded, as Fokker Aviatik GmbH, on 12 February 1912. World War I Fokker capitalized o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montecelio
Guidonia Montecelio (), commonly known as Guidonia, is a town and ''comune'' in the Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, Lazio, central Italy. Geography The municipality of Guidonia Montecelio, formed by the main towns of Guidonia and Montecelio, lies to the north-east of Rome, some kilometres from the Grande Raccordo Anulare - a ring-shaped motorway which forms a circle around the capital. The terrain of Guidonia Montecelio is mainly flat, and the community lies in between the Via Nomentana and the Via Tiburtina. It borders with Fonte Nuova, Marcellina, Palombara Sabina, Rome, San Polo dei Cavalieri, Sant'Angelo Romano and Tivoli. The hamlets (''frazioni'') are Albuccione, Bivio di Guidonia, Colle Fiorito, Colleverde, La Botte, Marco Simone, Montecelio, Pichini, Setteville, Setteville Nord, Villalba and Villanova. History Montecelio was founded in 998 as a fortified ''castrum'' (''Castrum Monticellorum''). In 1915 the ''Regio Esercito'' (Italian Royal Army) built a major milita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willy Coppens
Willy Omer François Jean baron Coppens de Houthulst (6 July 1892 – 21 December 1986) was Belgium's leading fighter ace and the champion "balloon buster" of World War I. He was credited with 37 confirmed victories and six probables. Early life Coppens was born in Watermael-Boitsfort, son of Omer Coppens, a Belgian impressionistic painter who studied in the Royal Academy of Ghent. He was conscripted into the army in 1912, to serve with the ''Premiere Regiment Grenadiers''. World War I In 1914, following the German invasion of Belgium, Coppens transferred to The Motor Machine Gun Corps. On 6 September 1915, he signed up for flight training in the Compagnie des Aviateurs. Ultimately, due to insufficiencies in Belgian training, he took eight weeks of leave to train to fly. He and 39 other Belgians learned to fly on their own expense in Britain. He received his pilot's certificate on 9 December 1915. After this training in Britain he had further training at the Farman Scho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuselage
The fuselage (; from the French ''fuselé'' "spindle-shaped") is an aircraft's main body section. It holds crew, passengers, or cargo. In single-engine aircraft, it will usually contain an engine as well, although in some amphibious aircraft the single engine is mounted on a pylon attached to the fuselage, which in turn is used as a floating hull. The fuselage also serves to position the control and stabilization surfaces in specific relationships to lifting surfaces, which is required for aircraft stability and maneuverability. Types of structures Truss structure This type of structure is still in use in many lightweight aircraft using welded steel tube trusses. A box truss fuselage structure can also be built out of wood—often covered with plywood. Simple box structures may be rounded by the addition of supported lightweight stringers, allowing the fabric covering to form a more aerodynamic shape, or one more pleasing to the eye. Geodesic construction Geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |