|
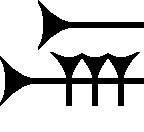
Amarna Letter EA 153
Amarna letter EA 153, titled ''Ships on Hold,'' is a short-length clay tablet letter from Abimilku of the island (at Amarna letters time) of city-state Tyre. EA 153 is approximately tall x wide, (actually 3 1/16 x 2 1/16 inches), and has a missing flaked, lower right corner on its obverse affecting two lines of text. One line repeats ''"...King, Lord-mine...,"'' allowing for only one line of more difficult restoration. The letter shows a high-gloss surface on the clay tablet, and being a short letter, has only 5 to 8/9 cuneiform characters per line. It contains one special cuneiform sign for ''ship'', MÁ, MÁ (ship Sumerogram), a sign used in both the Amarna letters, and the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. Also, the letter's scribe used mostly 'very-short' stroked, and 'fat-and-rounded' cuneiform strokes, instead of the more arrow-shaped, sharp, and linear strokes, . Since on EA 153, there are also distinct, medium-sized wedge strokes, (example ''" be"'' ) as well as L-shaped strok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letter- Royal Letter From Abi-milku Of Tyre To The King Of Egypt MET 24
Amarna (; ar, العمارنة, al-ʿamārnah) is an extensive Egyptian archaeological site containing the remains of what was the capital city of the late Eighteenth Dynasty. The city was established in 1346 BC, built at the direction of the Pharaoh Akhenaten, and abandoned shortly after his death in 1332 BC. The name that the ancient Egyptians used for the city is transliterated in English as Akhetaten or Akhetaton, meaning " the horizon of the Aten".David (1998), p. 125 The site is on the east bank of the Nile River, in what today is the Egyptian province of Minya. It is about south of the city of al-Minya, south of the Egyptian capital, Cairo, and north of Luxor (site of the previous capital, Thebes). The city of Deir Mawas lies directly to its west. On the east side of Amarna there are several modern villages, the chief of which are l-Till in the north and el-Hagg Qandil in the south. Activity in the region flourished from the Amarna Period until the later Roman era. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akhenaten
Akhenaten (pronounced ), also spelled Echnaton, Akhenaton, ( egy, ꜣḫ-n-jtn ''ʾŪḫə-nə-yātəy'', , meaning "Effective for the Aten"), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth Dynasty. Before the fifth year of his reign, he was known as Amenhotep IV ( egy, jmn-ḥtp, links=no, meaning "Amun is satisfied", Hellenized as ''Amenophis IV''). As a pharaoh, Akhenaten is noted for abandoning Egypt's traditional polytheism and introducing Atenism, or worship centered around Aten. The views of Egyptologists differ as to whether the religious policy was absolutely monotheistic, or whether it was monolatry, syncretistic, or henotheistic. This culture shift away from traditional religion was reversed after his death. Akhenaten's monuments were dismantled and hidden, his statues were destroyed, and his name excluded from lists of rulers compiled by later pharaohs. Traditional religious practice was gradually restored, not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARAD (servant Sumerogram)
ARAD, (also ÌR or NITÁ) is the capital letter-(majuscule) Sumerogram for the Akkadian language word ''"ardu"'',Parpola, 1971. ''The Standard Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh'', Glossary, pp. 119-145, p. 121, ardu, for "servant". for ''servant''. It is used especially in the introduction to the Pharaoh: for example ''"To King, Lord-mine (of Gods(pl)-mine, Sun-god-mine), message thus Xxxxxx, "Servant-yours"''-(271). It is also used extensively in Amarna letter texts, the author, usually the "man of a city", (or scribe), where there is a constant reminder that he is a "servant", or "servant-yours"-(of the Pharaoh). Many letters are giving city-state status reports, but many are also requesting help with the Egyptian army troops-(Archers (Egyptian pitati), supplied by the Pharaoh). Epic of Gilgamesh The cuneiform character for ARAD, ÌR, and NITÁ: in the Epic of Gilgamesh is used in the following numbers: ARAD-(2), ÌR-(2), and NITÁ-(2) times. It is used numerous times in the Amar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bi (cuneiform)
The cuneiform bi sign, also pí, and used for other syllabic forms, as well as a sumerogram, is a common use syllabic and alphabetic cuneiform sign used in both the mid-14th century BC Amarna letters and the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. In the Amarna letters, it is sometimes used for the spelling of the archers (Egyptian pitati), 'pí-t(x)-t(x)', an often requested need from the Pharaoh in the vassal state sub-corpus of the letters. As a sumerogram, (capital letter (majuscule)), sign ''bi'' is used for KAŠ, Akkadian language for "šikāru", ''beer''. The following linguistic elements for ''bi'' are used in the Epic: :bé :bi :gaš :kaš :pí :KAŠ, sumerogram: "beer" The ''bi'' sign's usage numbers in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' are as follows: ''bé''-(25 times), ''bi''-(190), ''gaš''-(1), ''kaš''-(12), ''pí''-(2), KAŠ-(1). Amarna letters usage Use of ''pí'', Egyptian archers The archers were part of the Egyptian army, and often requested by the Canaanite vassal city-sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ia (cuneiform)
The cuneiform ia sign 𒅀, is a combined sign, containing i (cuneiform) ligatured with a (cuneiform); it has the common meaning in the suffix form ''-ia'', for the meaning of "-mine". In the Amarna letters, the letters written to the Pharaoh of Egypt (Mizri/Misri in the letters), the Pharaoh is often referenced as "Lord-mine", or especially: ''King-Lord-mine'': "My King, My Lord". In Akkadian, the form is "Šarru-Bēlu-ia"-(King-Lord-mine), since the spelling in some Amarna letters is sometimes ŠÁR- RI for Šarru, (LUGAL = ŠÁR). ''Ia'' is also used in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. It is listed in Parpola's Glossary (Parpola, 1971), for Akkadian language words: meaning ''"mine"'', ''"(to) me"'', and ''"me"'', and one usage for the word "battering ram", ''iašubů''. Amarna letter usage of "ia" Besides the usage of Akkadian language words beginning with ''ia'', the common examples of — ''iāši'', "(to) me", ''iāti'', "me", ''iā'u'', "mine", and ''iānu'', "there is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lí (cuneiform)
The cuneiform sign ni is a common-use sign of the Amarna letters, the ''Epic of Gilgamesh,'' and other cuneiform texts. It has a secondary sub-use in the Amarna letters for addressing the Pharaoh, from the vassal states of Canaan. The address to the Pharaoh is often 'King-Lord-Mine': ''LUGAL, EN-ia'' which has many varieties of expression. "LUGAL" is Akkadian language for "Šarru", English "king", and ''EN'' in Akkadian is ''bēlu'', for "Lord", (thus "King, Lord-Mine"). In some Amarna letters the sub-use of ''ni'' is ''lí'', for spelling "bēlu", '' be-lí'' often . There are other sub-uses of ''ni'' (see ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' usage below). It is also found in some Amarna letters, EA 9, and EA 252, for example where ''ni'' or ''lí'' is scribed in a "flourish" format (an over-lengthened version of the two-horizontals that construct the sign), similar to '' tab'', . In EA 9 especially, there is a 'scribe margin line', both left and right on the clay tablet obverse. For the ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EN (cuneiform)
En (Borger 2003 nr. 164 ; U+12097 𒂗, see also Ensí) is the Sumerian cuneiform for "lord" or "priest". Originally, it seems to have been used to designate a high priest or priestess of a Sumerian city-state's patron-deity – a position that entailed political power as well. It may also have been the original title of the ruler of Uruk. See ''Lugal, ensi and en'' for more details. Deities including En as part of their name include DEnlil, DEnki, DEngurun, and DEnzu. Enheduanna, Akkadian 2285 BC – 2250 BC was the first known holder of the title, "En Priestess." Archaic forms The corresponding Emesal dialect word was UMUN, which may preserve an archaic form of the word. Earlier Emeg̃ir (the standard dialect of Sumerian) forms can be postulated as ''*ewen'' or ''*emen'', eventually dropping the middle consonant and becoming the familiar EN. Amarna letters: bêlu The 1350 BC Amarna letters use EN for bêlu, though not exclusively. The more common spelling is mostly 'be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Na (cuneiform)
The cuneiform na sign is a common, multi-use sign, a syllabic for ''na'', and an alphabetic sign used for ''n'', or ''a''; it is common in both the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' over hundreds of years, and the 1350 BC Amarna letters. In the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' it also has sumerogramic (capital letter (majuscule)) usage for NA. An example usage for ''NA'' in the Epic is for the spelling of ''NA.GAD'', (also '' LÚ.NA.GAD'', and the plural '' LÚ.NA.GAD. MEŠ''), for Akkadian language "nāqidu", ''"herdsman"''. The usage for ''NA'' in herdsman is only for 3 spellings. The commonness of cuneiform ''na'', in the top 25 used signs by Buccellati (Buccellati 1979), (2nd highest usage, exceeded by a: ''a (cuneiform)'') is because of usage for the spelling of ''a-na'' (Akkadian language "ana") -, the common preposition spelling for English language: ''to, for, by, of, at, etc.''. It is also a component for the Akkadian language preposition: ''i-na'' (''ina''), meaning: ''in, into, by, etc.''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A (cuneiform)
The cuneiform sign 𒀀 ( DIŠ, DIŠ OVER DIŠ) for a, and in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' the sumerogram A, Akkadian for ''mû'', "water", which is used in the ''Gilgamesh flood myth'', Chapter XI of the Epic, or other passages. The sign is also used extensively in the Amarna letters. Cuneiform ''a'' is the most common of the four vowels in the Akkadian language, ''a'', ''e'', ''i'', and ''u''. All vowels can be interchangeable, depending on the scribe, though spellings of Akkadian words in dictionaries, will be formalized, and typically: unstressed, a 'long-vowel', or thirdly, a 'combined' vowel (often spelled with two signs (same vowel, ending the first sign, and starting the next sign), thus combined into the single vowel, ''â'', ''ê'', ''î'', or ''û''.). Cuneiform ''a'' is the most common of the four vowels, as can be shown by usage in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', the usage numbers being (ú (u, no. 2) is more common than u, (no. 1), which has additional usages, numera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akkadian Language
Akkadian (, Akkadian: )John Huehnergard & Christopher Woods, "Akkadian and Eblaite", ''The Cambridge Encyclopedia of the World's Ancient Languages''. Ed. Roger D. Woodard (2004, Cambridge) Pages 218-280 is an extinct East Semitic language that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia ( Akkad, Assyria, Isin, Larsa and Babylonia) from the third millennium BC until its gradual replacement by Akkadian-influenced Old Aramaic among Mesopotamians by the 8th century BC. It is the earliest documented Semitic language. It used the cuneiform script, which was originally used to write the unrelated, and also extinct, Sumerian (which is a language isolate). Akkadian is named after the city of Akkad, a major centre of Mesopotamian civilization during the Akkadian Empire (c. 2334–2154 BC). The mutual influence between Sumerian and Akkadian had led scholars to describe the languages as a '' Sprachbund''. Akkadian proper names were first attested in Sumerian texts from around the mid 3rd-mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacuna (manuscripts)
A lacuna ( lacunae or lacunas) is a gap in a manuscript, inscription, text, painting, or musical work. A manuscript, text, or section suffering from gaps is said to be "lacunose" or "lacunulose". Weathering, decay, and other damage to old manuscripts or inscriptions are often responsible for lacunae - words, sentences, or whole passages that are missing or illegible. Palimpsests are particularly vulnerable. To reconstruct the original text, the context must be considered. In papyrology and textual criticism, this may lead to competing reconstructions and interpretations. Published texts that contain lacunae often mark the section where text is missing with a bracketed ellipsis. For example, "This sentence contains 20 words, and ..nouns," or, "Finally, the army arrived at ..and made camp." Notable examples See also * Unfinished work Unfinished may refer to: *Unfinished creative work, a work which a creator either chose not to finish or was prevented from finishing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U (cuneiform)
The cuneiform U sign is found in both the 14th century BC Amarna letters and the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. It can be used for the alphabetic ''u'', instead of the more common 2nd u, (ú). It has two other uses, commonly. It can be used for the number 10 (especially the Amarna letters from Tushratta of Mitanni, or Burna-Buriash II the king of Babylon), but its probable greater use is for the conjunction, ''u'', with any of the conjunction meanings: ''and'', ''but'', ''else'', etc. Of the three u's, by graphemic analysis (Buccellati, 1979), the commonness is as follows: :Ù (cuneiform), conjunction only (but also rare, for alphabetic "u") :ú (cuneiform), alphabetic 'u' :u (cuneiform), alphabetic (minor), 10, conjunction (highest use) Both Ù (cuneiform) and ú are in the top 25 most used signs, but E (cuneiform) and "u (cuneiform)" are not; other vowels (or combination) in the 25 are: a (cuneiform), i (cuneiform), and ia (cuneiform), (which has a secondary use as suffix, ''" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)