|
Amarita
Amarita (, es, Amárita ) is a hamlet and ''Concejo (Álava), concejo'' in the municipality of Vitoria-Gasteiz, in Álava province, Basque Country (autonomous community), Basque Country, Spain. It lies along the Santa Engracia river, which empties into the Zadorra near Amarita. History The hamlet was first mentioned in the ' of 1025 with the spelling ''Hamarita''. At the time it belonged to the Alfoz (territory), alfoz of Ubarrundia, together with neighboring settlements. Together with other nearby hamlets, it was transferred to the city of Vitoria in 1332 Alfonso XI of Castile, King Alfonso XI, to which it still belongs. The Basque language was spoken in Amarita until around the seventeenth century. Landmarks Amarita has a church dedicated to Saint Peter. The building dates from the nineteenth century and has a Neoclassical architecture, neoclassic altarpiece. Some elements of the church are older: the tower and the vestry dating from the eighteenth century and the lateral alta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitoria-Gasteiz
es, vitoriano, vitoriana, , population_density_km2 = auto , blank_name_sec1 = Official language(s) , blank_info_sec1 = Spanish, Basque , timezone = CET , utc_offset = +1 , timezone_DST = CEST , utc_offset_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = Postal code , postal_code = 01001–01015 , area_code_type = Dialing code , area_code = , leader_title = Alcalde , leader_name = Gorka Urtaran , leader_party = Basque Nationalist Party , website = , module = , footnotes = Click on the map for a fullscreen view Vitoria-Gasteiz (; ), also alternatively spelled as Vittoria in old English-language sources, is the seat of government and the capital city of the Basque Country and of the province of Álava in northern Spain. It holds the autonomous community's House of Parliament, the headquarters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concejo (Álava)
The ''concejos'' ( eu, kontzejuak, es, concejos) are a type of sub-municipal administrative unit in the province of Álava, Basque Country, Spain. Within the Spanish legal framework, the general name for such sub-municipal units is minor local entity (formally in also known by their acronym ). The existence of ''concejos'' in Álava is documented since the 13th century. Their current status dates from 1984, when a law providing for elections to the ''concejos'' was passed; and from 1995, when their juridical status was clarified. See also * Local government in Spain Local government in Spain refers to the government and administration of what the Constitution calls "local entities", which are primarily municipalities, but also groups of municipalities including provinces, metropolitan areas, comarcas and manc ... Notes References External links ACOA-AKE* {{BasqueCountry-geo-stub Local government in Spain Álava Basque politics __NOTOC__ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euskaltzaindia
Euskaltzaindia (; often translated Royal Academy of the Basque Language) is the official academic language regulatory institution which watches over the Basque language. It conducts research, seeks to protect the language, and establishes standards of use. It is known in Spanish as ''La Real Academia de la Lengua Vasca'' (being under the royal patronage of the Spanish monarchy, like the Real Academia Española) and in French as ''Académie de la Langue Basque''. Creation The Euskaltzaindia was established within the context of the Basque Renaissance (''Eusko Pizkundea'', 1876–1936) in the framework provided by the Congress of Basque Studies held in Oñati in 1918, at a time when the Basque language was being proclaimed as a central cultural value to be protected and promoted. Important figures from the 19th century had already demanded the setting-up of an academy in defence of the language (Ulibarri, 1832; Aizkibel, 1856; d'Abbadie and Duvoisin, 1862; Jose Manterola, 1880 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Peter
) (Simeon, Simon) , birth_date = , birth_place = Bethsaida, Gaulanitis, Syria, Roman Empire , death_date = Between AD 64–68 , death_place = probably Vatican Hill, Rome, Italia, Roman Empire , parents = John (or Jonah; Jona) , occupation = Fisherman, clergyman , feast_day = , venerated = All Christian denominations that venerate saints and in Islam , canonized_date = Pre- Congregation , attributes = Keys of Heaven, Red Martyr, pallium, papal vestments, rooster, man crucified upside down, vested as an Apostle, holding a book or scroll, Cross of Saint Peter , patronage = Patronage list , shrine = St. Peter's Basilica Saint Peter; he, שמעון בר יונה, Šimʿōn bar Yōnāh; ar, سِمعَان بُطرُس, translit=Simʿa̅n Buṭrus; grc-gre, Πέτρος, Petros; cop, Ⲡⲉⲧⲣⲟⲥ, Petros; lat, Petrus; ar, شمعون الصفـا, Sham'un al-Safa, Simon the Pure.; tr, Aziz Petrus (died between AD 64 and 68), also known as Peter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfonso XI Of Castile
Alfonso XI (13 August 131126 March 1350), called the Avenger (''el Justiciero''), was King of Castile and León. He was the son of Ferdinand IV of Castile and his wife Constance of Portugal. Upon his father's death in 1312, several disputes ensued over who would hold regency, which were resolved in 1313. Once Alfonso was declared an adult in 1325, he began a reign that would serve to strengthen royal power. His achievements include the victory in the Battle of Río Salado over Granadans and Marinids and the Castilian control over the Strait of Gibraltar. Life Minority Born on 13 August 1311 in Salamanca, he was the son of King Ferdinand IV of Castile and Constance of Portugal. His father died when Alfonso was one year old. His grandmother, María de Molina, his mother Constance, his granduncle Infante John of Castile, son of King Alfonso X of Castile and uncle Infante Peter of Castile, son of King Sancho IV assumed the regency. His mother died first on 18 November ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfoz (territory)
The geographical term alfoz (plural ''alfoces'') was used in the Iberian Peninsula during the Middle Ages to describe the rural territory, including subordinate hamlets, under the jurisdiction of a corresponding town (''villa'' in Spanish). The ''villa'' and its alfoz, under the authority of the town's local council (''concejo''), sometimes underpinned what was called a ''Comunidad de Villa y Tierra'', an autonomous political division. At the center of this community, the town (or sometimes a city) comprised an urban area and usually boasted of a castle and a fortified wall. By the 12th century, the alfoces had fiscal, judicial and military functions. Furthermore, they lent themselves to the communal use of land for silvopastoral agriculture; however, in the year 1100, monarchs began to allocate portions of land to the Church and the nobility, an act that undermined the very purpose of the alfoz. The alfoz and its villa formed what would later be known as a municipality. The wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auñamendi Encyclopedia
The Auñamendi Encyclopedia is the largest encyclopedia of Basque culture and society, with 120,000 articles and more than 67,000 images. History Founded in 1958 by the Estornés Lasa brothers, Bernardo and Mariano. He began publishing in 1969 with the help of the Auñamendi publishing house. Since 1996, Eusko Ikaskuntza has taken over the task of digitizing, cataloging and putting it on the network. The new encyclopedia is based on the Auñamendi encyclopedia by Bernardo Estornés Lasa, which began in 1933 and whose first and last volumes were released in 1960 and 2008 respectively. There were 58 volumes. The contents of the Auñamendi Encyclopedia are generated by a large group of specialists in different subjects who guarantee the level of quality and scientific rigor of the encyclopedia. All contributions are analyzed and contrasted by the experts at Eusko Ikaskuntza. References External links Auñamendi Encyclopedia {{Authority control Basque culture 1960 non-fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zadorra
The Zadorra is a river tributary of the Ebro in the Basque Country at the north of the Iberian Peninsula. The river flows across province Álava all along (with the exception of Burgos' exclave La Puebla de Arganzon) till it pours into the Ebro near Miranda de Ebro in Burgos' lands. The river's water volume is the largest in Álava, with its basin being the most extensive in the province. Nowadays it provides by means of the Zadorra Reservoir System (comprising reservoirs Uribarri-Ganboa, Urrunaga and Albina) water supply for Vitoria and half of the Basque Autonomous Community. The river rises in the slopes of the Entzia Plateau at the spring known as Los Corrales (municipality of San Millan/Donemiliaga), meandering thereafter across the Alavan Plains to the west (loops around Salvatierra/Agurain) past Vitoria by the north, where it takes a turn to the south heading to the Ebro through La Puebla de Arganzon. Landmarks * The village and iconic castle of Gebara sit by the rive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foral Deputation Of Álava
200px, Foral of Castro Verde - Portugal The word ''foral'' ({{IPA-pt, fuˈɾaɫ, eu, plural: ''forais'') is a noun derived from the Portuguese word ''foro'', ultimately from Latin ''forum'', equivalent to Spanish '' fuero'', Galician ''foro'', Catalan ''fur'' and Basque ''foru''. The ''Carta de Foral'', or simply ''Foral'', was a royal document in Portugal and its former empire, whose purpose was to establish a '' concelho'' (Council) and regulate its administration, borders and privileges. A newly founded town would also need the king's approval through a ''Foral'', in order to be considered one. In this case, the town's administration and privileges would be defined in that document. ''Forais'' were granted between the 12th and the 16th centuries. The ''Foral'' was the basis for municipal foundation, thus the most important event of a city or town's history. It was critical to a successful land settling and an increase in crop yields, by giving more freedom and dignity, vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basque Government
The Basque Government ( eu, Eusko Jaurlaritza, es, Gobierno Vasco) is the governing body of the Basque Autonomous Community of Spain. The head of the Basque government is known as the '' Lehendakari''. The Lehendakari is appointed by the Basque Parliament every four years, after a regional election. Its headquarters are located in the Lakua district of Vitoria-Gasteiz in Álava. The first Basque Government was created after the approval of the first Basque Statute of Autonomy on 1 October 1936, in the midst of the Spanish Civil War. It was headed by José Antonio Aguirre ( EAJ-PNV) and was supported by a coalition of all the parties that fought the Nationalist forces in the Civil War: those comprising the Popular Front ( PSOE, PCE, EAE-ANV and other parties that sided with the Second Spanish Republic). After the defeat of the Republic, the Basque Government survived in exile, chaired by Jesús María Leizaola after the death of Aguirre in 1960. This first Basque Gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
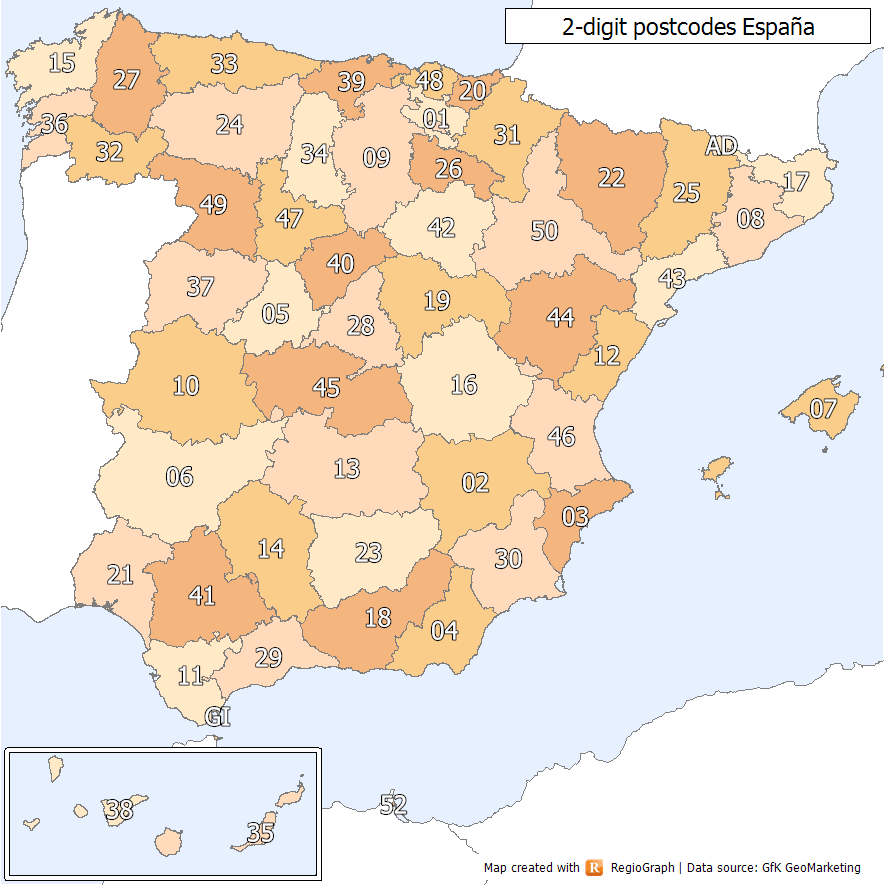
List Of Postal Codes In Spain
Spanish postal codes were introduced on 1 July 1984, when the introduced automated mail sorting. They consist of five numerical digits, where the first two digits, ranging 01 to 52, correspond either to one of the 50 provinces of Spain or to one of the two autonomous cities on the African coast. Two-digit prefixes The first two digits of a Spanish postal code identify the province or autonomous city it belongs to. The numbers were assigned to the 50 provinces of Spain ordered alphabetically at the time of implementation. The official names of some of the provinces have since changed, either to the regional language version of the name (e.g. from the Spanish to the Basque ) or to adopt the name of the autonomous community instead of the provincial capital (e.g. Santander to Cantabria). In these cases, the originally assigned code has been maintained, resulting in some exceptions to the alphabetical order. In addition, Ceuta and Melilla were originally included within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg , image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg , national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond") , national_anthem = (English: "Royal March") , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Madrid , coordinates = , largest_city = Madrid , languages_type = Official language , languages = Spanish , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = , ethnic_groups_ref = , religion = , religion_ref = , religion_year = 2020 , demonym = , government_type = Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Felipe VI , leader_title2 = Prime Minister , leader_name2 = Pedro Sánchez , legislature = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_02.jpg)