|
Am (cuneiform)
The cuneiform sign am, is a common-use sign of the Amarna letters, the ''Epic of Gilgamesh,'' and other cuneiform texts (for example Hittite texts). It is also used as AM. Linguistically, it has the alphabetical usage in texts for ''a'', or ''m'', or syllabically for ''am''. The "a" is replaceable in word formation by any of the 4 vowels: ''a, e, i,'' or ''u''. ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' usage The ''am'' sign usage in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' is as follows: ''am''-(87 times); ''AM''-(4). References * Moran, William L. 1987, 1992. ''The Amarna Letters.'' Johns Hopkins University Press, 1987, 1992. 393 pages.(softcover, ) * Parpola, 1971. ''The Standard Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh'', Parpola, Simo, Neo-Assyrian Text Corpus Project, c 1997, Tablet I thru Tablet XII, Index of Names, Sign List, and Glossary-(pp. 119–145), 165 pages. ---- Image:Amarna_letter-_Royal_Letter_from_Abi-milku_of_Tyre_to_the_king_of_Egypt_MET_DP-211-144.jpg, line drawing, ObverseA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B309ellst
B3, B03, B.III or B-3 may refer to: Military American bombers * Keystone B-3, a biplane bomber of the United States Army Air Corps * Next-Generation Bomber (2018 Bomber), next bomber follow-on to the B-2 stealth bomber program * Long Range Strike Bomber program, successor program to the 2018 Bomber program ** Northrop Grumman B-21, a successor aircraft to the B-1 and B-52 bombers German and Austro-Hungarian aircraft * AEG B.III, a German reconnaissance aircraft * Albatros B.III, a German Idflieg B-class designation aircraft * Aviatik B.III, a 1916 Austro-Hungarian reconnaissance aircraft * Euler B.III, a German Idflieg B-class designation aircraft * Fokker B.III (other), two aircraft models * Halberstadt B.III, a German Idflieg B-class designation aircraft * Kampfgeschwader 54, from its historic ''Geschwaderkennung'' code with the Luftwaffe in World War II * Lohner B.III * LVG B.III, a 1910s German two-seat trainer biplane Submarines * USS ''B-3'' (SS-12), a Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
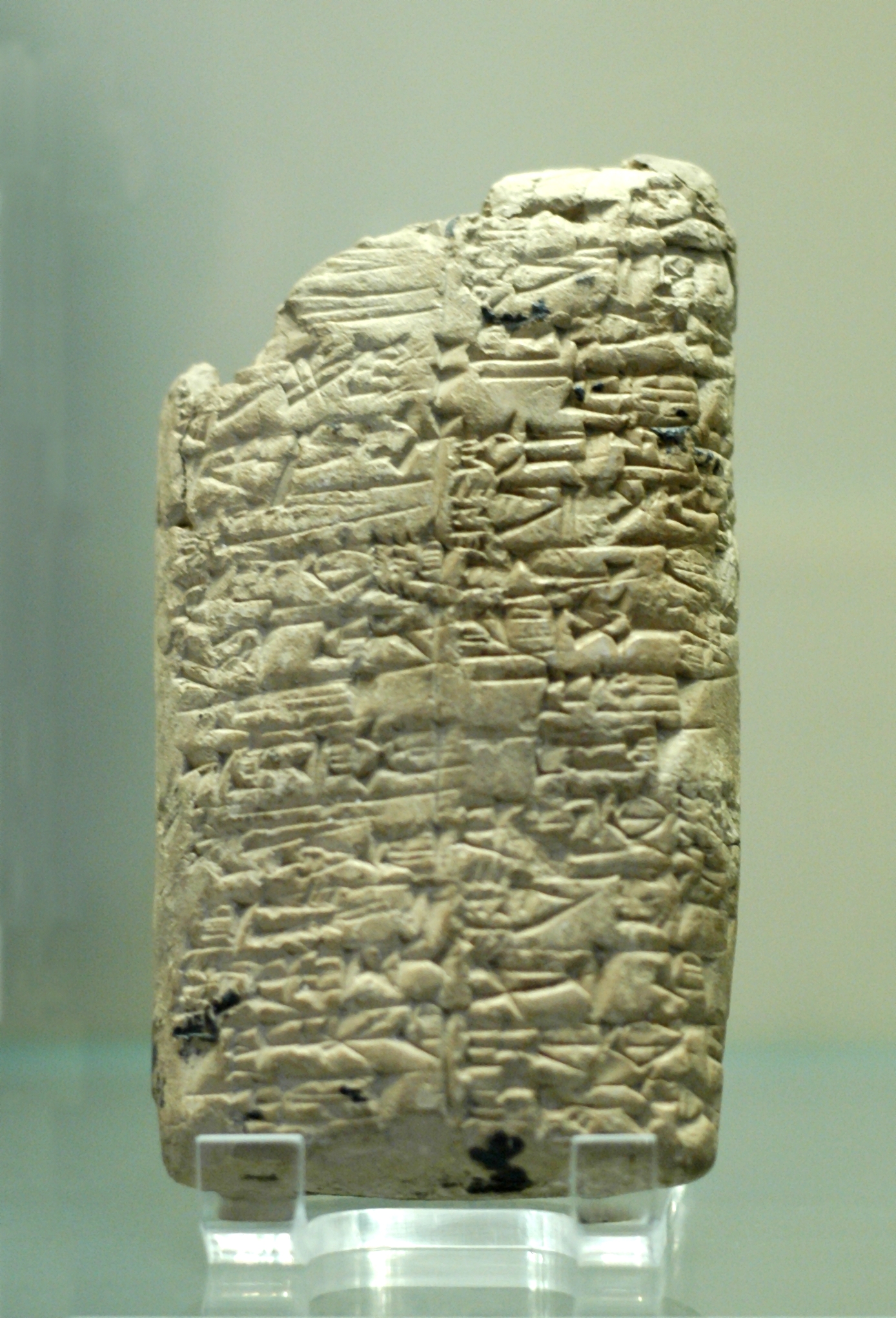
Clay Tablet
In the Ancient Near East, clay tablets (Akkadian ) were used as a writing medium, especially for writing in cuneiform, throughout the Bronze Age and well into the Iron Age. Cuneiform characters were imprinted on a wet clay tablet with a stylus often made of reed ( reed pen). Once written upon, many tablets were dried in the sun or air, remaining fragile. Later, these unfired clay tablets could be soaked in water and recycled into new clean tablets. Other tablets, once written, were either deliberately fired in hot kilns, or inadvertently fired when buildings were burnt down by accident or during conflict, making them hard and durable. Collections of these clay documents made up the first archives. They were at the root of the first libraries. Tens of thousands of written tablets, including many fragments, have been found in the Middle East. Surviving tablet-based documents from the Minoan/ Mycenaean civilizations, are mainly those which were used for accounting. Tablets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letter
The Amarna letters (; sometimes referred to as the Amarna correspondence or Amarna tablets, and cited with the abbreviation EA, for "El Amarna") are an archive, written on clay tablets, primarily consisting of diplomatic correspondence between the Egyptian administration and its representatives in Canaan and Amurru, or neighboring kingdom leaders, during the New Kingdom, spanning a period of no more than thirty years between c. 1360–1332 BC (see here for dates).Moran, p.xxxiv The letters were found in Upper Egypt at el-Amarna, the modern name for the ancient Egyptian capital of ''Akhetaten'', founded by pharaoh Akhenaten (1350s–1330s BC) during the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt. The Amarna letters are unusual in Egyptological research, because they are written not in the language of ancient Egypt, but in cuneiform, the writing system of ancient Mesopotamia. Most are in a variety of Akkadian sometimes characterised as a mixed language, Canaanite-Akkadian; one especially lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letter EA 15
Amarna letter EA 15, titled ''Assyria Joins the International Scene'', is a shorter-length clay tablet Amarna letter from Ashur-uballit I of the '' Land of Assyria'', (line 3 of EA 15). He addresses the Pharaoh in line 1, the ''"King (of) Land Miṣri-(Egypt)"'', thus the use of "Land (of) Assyria". This short letter is synoptic with much information. It discusses the Assyrian messenger's reason for going to Egypt, "to see" the land, and report back to the Assyrian king. The letter speaks of a short history of not sending a messenger, or the two kingdoms talking, for some recent times. Besides the duties of the messenger to see, and report back, a list of "greeting gifts", '' shulmani'', or "peace-gifts" are sent by Ashur-uballit I to the Pharaoh. The letter EA 15: ''Assyria Joins the International Scene'' EA 15, letter one of two from Assyria. (Not a linear, line-by-line translation.) :(Lines 1-6)--Say to the king of the land of E ypt Thus Aššur-ubal it, the king of the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuneiform Line Drawing
Cuneiform is a logo- syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-shaped impressions ( Latin: ) which form its signs. Cuneiform was originally developed to write the Sumerian language of southern Mesopotamia (modern Iraq). Cuneiform is the earliest known writing system. Over the course of its history, cuneiform was adapted to write a number of languages in addition to Sumerian. Akkadian texts are attested from the 24th century BC onward and make up the bulk of the cuneiform record. Akkadian cuneiform was itself adapted to write the Hittite language in the early second millennium BC. The other languages with significant cuneiform corpora are Eblaite, Elamite, Hurrian, Luwian, and Urartian. The Old Persian and Ugaritic alphabets feature cuneiform-style signs; however, they are unrelated to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mari, Syria
Mari (Cuneiform: , ''ma-riki'', modern Tell Hariri; ar, تل حريري) was an ancient Semitic city-state in modern-day Syria. Its remains form a tell 11 kilometers north-west of Abu Kamal on the Euphrates River western bank, some 120 kilometers southeast of Deir ez-Zor. It flourished as a trade center and hegemonic state between 2900 BC and 1759 BC. The city was purposely built in the middle of the Euphrates trade routes between Sumer in the south and the Eblaite kingdom and the Levant in the west. Mari was first abandoned in the middle of the 26th century BC but was rebuilt and became the capital of a hegemonic East Semitic state before 2500 BC. This second Mari engaged in a long war with its rival Ebla and is known for its strong affinity with Sumerian culture. It was destroyed in the 23rd century BC by the Akkadians, who allowed the city to be rebuilt and appointed a military governor ('' Shakkanakku''). The governors became independent with the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claude Schaeffer
Claude may refer to: __NOTOC__ People and fictional characters * Claude (given name), a list of people and fictional characters * Claude (surname), a list of people * Claude Lorrain (c. 1600–1682), French landscape painter, draughtsman and etcher traditionally called just "Claude" in English * Madame Claude, French brothel keeper Fernande Grudet (1923–2015) Places * Claude, Texas, a city * Claude, West Virginia, an unincorporated community Other uses * Allied reporting name of the Mitsubishi A5M Japanese carrier-based fighter aircraft * Claude (alligator) Claude is an albino alligator ('' Alligator mississippiensis'') at the California Academy of Sciences. Claude lacks the pigment melanin, resulting in colorless skin, and he has poor eyesight associated with his albinism. Background Claude was h ..., an albino alligator at the California Academy of Sciences See also * Claude's syndrome, a form of brainstem stroke syndrome {{disambig, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Babylonian
{{disambig ...
Old Babylonian may refer to: *the period of the First Babylonian dynasty (20th to 16th centuries BC) *the historical stage of the Akkadian language of that time See also *Old Assyrian (other) Old Assyrian refers to a period of the Ancient Near East, ca. 20th to 16th centuries BC (the Middle Bronze Age). It may refer to: *The Old Assyrian Empire *The Old Assyrian language *Old Assyrian cuneiform, see Cuneiform script See also * Middle As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giorgio Buccellatti
Giorgio may refer to: * Castel Giorgio, ''comune'' in Umbria, Italy * Giorgio (name), an Italian given name and surname * Giorgio Moroder, or Giorgio, Italian record producer ** ''Giorgio'' (album), an album by Giorgio Moroder * "Giorgio" (song), a song by Lys Assia * Giorgio Bruno, a character from the video game '' Time Crisis 4'' * Giorgio Zott, the main antagonist from the video game '' Time Crisis 3'' * Giorgio Beverly Hills, a prestige fragrance brand See also * Georgios * Georgio (other) Georgio is a variant of George. It may refer to: Mononyms *Georgio (singer) (born 1966), full name Georgio Alentini, born George Allen. American singer, songwriter, and musician *Georgio (rapper) (born 1993), birth name Georges Édouard Nicolo, Fr ... * San Giorgio (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megiddo
Megiddo may refer to: Places and sites in Israel * Tel Megiddo, site of an ancient city in Israel's Jezreel valley * Megiddo Airport, a domestic airport in Israel * Megiddo church (Israel) * Megiddo, Israel, a kibbutz in Israel * Megiddo Junction, a motorway junction in northern Israel USA churches * Megiddo Mission, Rochester, NY * Megiddo Church, Rochester, NY People * Nimrod Megiddo, mathematician and computer scientist Fiction * '' Megiddo: The Omega Code 2'', a 2001 American film * "Megiddo", the 65th chapter and 34th episode of ''That Time I Got Reincarnated as a Slime'' * Prince Megiddo, a character in the Japanese television series '' Kagaku Sentai Dynaman'' * Aradia and Damara Megido, characters from the webcomic ''Homestuck'' Music * ''Megiddo'' (EP), a 1997 EP by Satyricon * ''Megiddo'' (Lauren Hoffman album), 1997 * ''Dawn of Megiddo'', a song from the 1985 album '' To Mega Therion'' by the Swiss metal band Celtic Frost Other uses * Megiddo (battle honou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biridiya
Biridiya was the ruler of Megiddo in the 14th century BC. Biridiya authored five of the Amarna letters correspondence. The name 'Biridiya' is also mentioned in the corpus from the city of 'Kumidu' (letter KL 72:600), the Kamid al lawz. However, the origin of the letter has not been identified, and the content of the letter (request for return of personal property) makes it unlikely it was sent by the King of Megiddo.למלך אדוני: מכתבי אל-עמראנה, כמד, תענך, ומכתבים נוספים מהמאה הארבע-עשרה לפסה"נ (in Hebrew) See also * Hannathon, Biridiya letter EA 245, title: ''"Assignment of Guilt"'' References *Moran, William L. William Lambert Moran (August 11, 1921 – December 19, 2000) was an American Assyriologist. He was born in Chicago, United States. In 1939, Moran joined the Jesuit order. He then attended Loyola University in Chicago, where he received his ... ''The Amarna Letters.'' Johns Hopkins University Pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anson Rainey
Anson Frank Rainey (January 11, 1930 – February 19, 2011) was professor emeritus of ancient Near Eastern cultures and Semitic linguistics at Tel Aviv University. He is known in particular for contributions to the study of the Amarna tablets, the noted administrative letters from the period of Pharaoh Akhenaten's rule during the 18th Dynasty of Egypt.Rollston, C. (2011)Among the last of the titans: Aspects of Professor Anson Rainey's life and legacy (1930–2011)(February 20, 2011); retrieved May 22, 2017 He authored and edited books and articles on the cultures, languages and geography of the Biblical lands. Early life Anson Rainey was born in Dallas, Texas, in 1930. Upon the death of his father that same year, he was left with his maternal grandparents. He attended Brown Military Academy in San Diego, California, from 1943 to 1946. After one semester of study there – as a cadet battalion commander – he served as assistant commandant at Southern California Mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |