|
Alveolar Capillary Dysplasia
Alveolar capillary dysplasia (ACD) is a rare, congenital diffuse lung disease characterized by abnormal blood vessels in the lungs that cause highly elevated pulmonary blood pressure and an inability to effectively oxygenate and remove carbon dioxide from the blood. ACD typically presents in newborn babies within hours of birth as rapid and labored breathing, blue-colored lips or skin, quickly leading to respiratory failure and death. Atypical forms of ACD have been reported with initially milder symptoms and survival of many months before the onset of respiratory failure or lung transplantation. Most cases of ACD are caused by mutations affecting the gene ''FOXF1'' or its nearby enhancer region. Exactly how these mutations lead to abnormal lung development is unknown. Abnormal lung development is characterized by thickened alveolar interstitium, misplacement of pulmonary capillaries away from the alveolar surface, and fewer capillaries overall. This results in poor gas exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanosis
Cyanosis is the change of body tissue color to a bluish-purple hue as a result of having decreased amounts of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Body tissues that show cyanosis are usually in locations where the skin is thinner, including the mucous membranes, lips, nail beds, and ear lobes. Some medications containing amiodarone or silver, Mongolian spots, large birth marks, and the consumption of food products with blue or purple dyes can also result in the bluish skin tissue discoloration and may be mistaken for cyanosis. Cyanosis is further classified into central cyanosis vs. peripheral cyanosis. Pathophysiology The mechanism behind cyanosis is different depending on whether it is central or peripheral. Central cyanosis Central cyanosis is caused by a decrease in arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) and begins to show once the concentration of deoxyhemoglobin in the blood reaches a concentration of ≥ 5.0 g/dL (≥ 3.1 mmol/L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breathing
Breathing (or ventilation) is the process of moving air into and from the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen. All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellular respiration, which extracts energy from the reaction of oxygen with molecules derived from food and produces carbon dioxide as a waste product. Breathing, or "external respiration", brings air into the lungs where gas exchange takes place in the alveoli through diffusion. The body's circulatory system transports these gases to and from the cells, where "cellular respiration" takes place. The breathing of all vertebrates with lungs consists of repetitive cycles of inhalation and exhalation through a highly branched system of tubes or airways which lead from the nose to the alveoli. The number of respiratory cycles per minute is the breathing or respiratory rate, and is one of the four primary vital signs of life. Under normal conditions t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasodilators
Vasodilation is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasoconstriction, which is the narrowing of blood vessels. When blood vessels dilate, the flow of blood is increased due to a decrease in vascular resistance and increase in cardiac output. Therefore, dilation of arterial blood vessels (mainly the arterioles) decreases blood pressure. The response may be intrinsic (due to local processes in the surrounding tissue) or extrinsic (due to hormones or the nervous system). In addition, the response may be localized to a specific organ (depending on the metabolic needs of a particular tissue, as during strenuous exercise), or it may be systemic (seen throughout the entire systemic circulation). Endogenous substances and drugs that cause vasodilation are termed vasodilators. Such vasoactivity is necessary for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move air into and out of the lungs, with the main goal of helping the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide. Mechanical ventilation is used for many reasons, including to protect the airway due to mechanical or neurologic cause, to ensure adequate oxygenation, or to remove excess carbon dioxide from the lungs. Various healthcare providers are involved with the use of mechanical ventilation and people who require ventilators are typically monitored in an intensive care unit. Mechanical ventilation is termed invasive if it involves an instrument to create an airway that is placed inside the trachea. This is done through an endotracheal tube or nasotracheal tube. For non-invasive ventilation in people who are conscious, face or nasal mask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autopsy
An autopsy (post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death or to evaluate any disease or injury that may be present for research or educational purposes. (The term "necropsy" is generally reserved for non-human animals). Autopsies are usually performed by a specialized medical doctor called a pathologist. In most cases, a medical examiner or coroner can determine the cause of death. However, only a small portion of deaths require an autopsy to be performed, under certain circumstances. Purposes of performance Autopsies are performed for either legal or medical purposes. Autopsies can be performed when any of the following information is desired: * Determine if death was natural or unnatural * Injury source and extent on the corpse * Manner of death must be determined * Post mortem interval * Determining the deceas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions. History T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisible to the eye unless aided by a microscope. There are many types of microscopes, and they may be grouped in different ways. One way is to describe the method an instrument uses to interact with a sample and produce images, either by sending a beam of light or electrons through a sample in its optical path, by detecting photon emissions from a sample, or by scanning across and a short distance from the surface of a sample using a probe. The most common microscope (and the first to be invented) is the optical microscope, which uses lenses to refract visible light that passed through a thinly sectioned sample to produce an observable image. Other major types of microscopes are the fluorescence microscope, electron microscope (both the transmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Alveolus
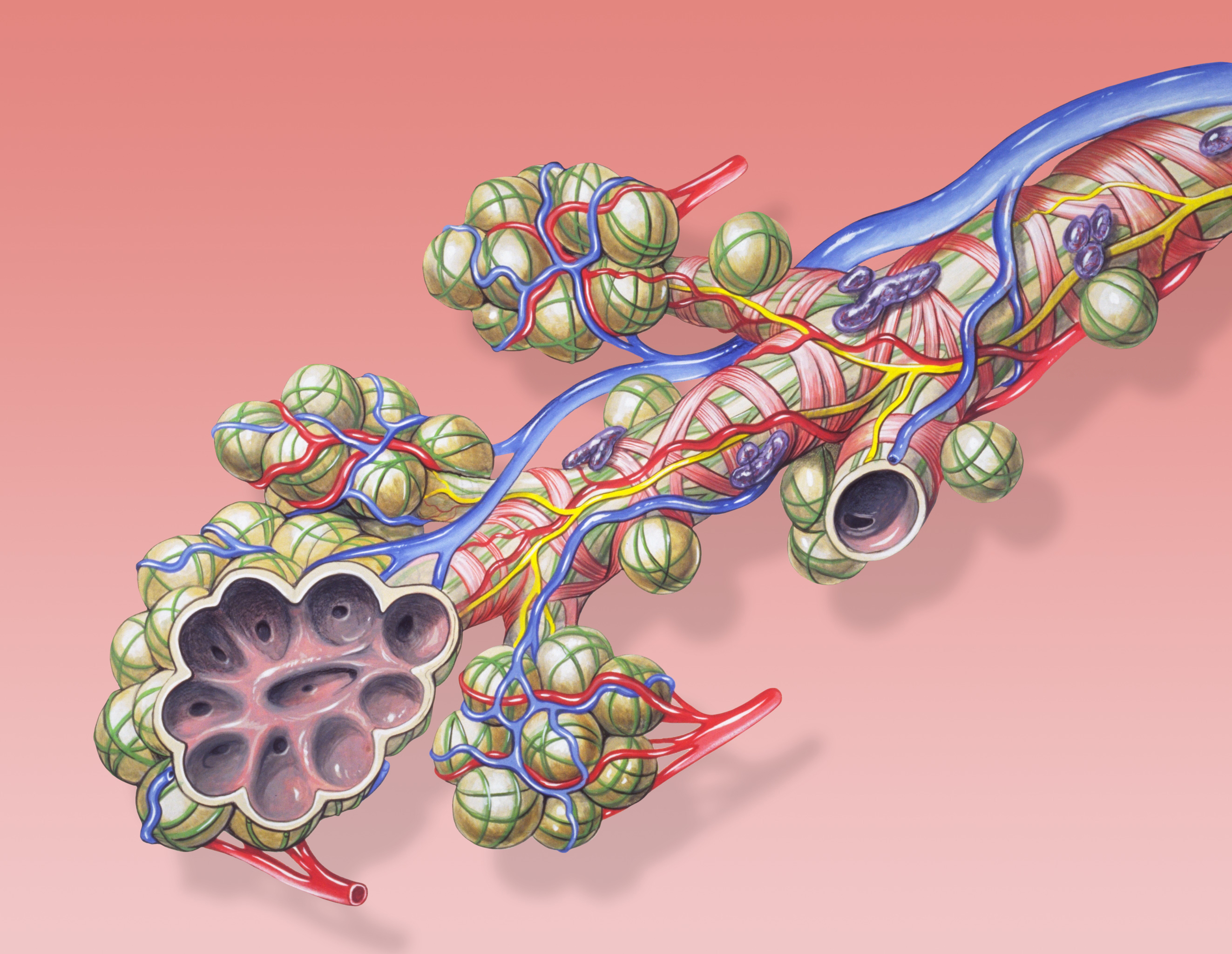
A pulmonary alveolus (plural: alveoli, from Latin ''alveolus'', "little cavity"), also known as an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide. Alveoli make up the functional tissue of the mammalian lungs known as the lung parenchyma, which takes up 90 percent of the total lung volume. Alveoli are first located in the respiratory bronchioles that mark the beginning of the respiratory zone. They are located sparsely in these bronchioles, line the walls of the alveolar ducts, and are more numerous in the blind-ended alveolar sacs. The acini are the basic units of respiration, with gas exchange taking place in all the alveoli present. The alveolar membrane is the gas exchange surface, surrounded by a network of capillaries. Across the membrane oxygen is diffused into the capillaries and carbon dioxide released from the capillaries into the alveoli to be breathed out. Alveoli are pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enhancer (genetics)
In genetics, an enhancer is a short (50–1500 bp) region of DNA that can be bound by proteins ( activators) to increase the likelihood that transcription of a particular gene will occur. These proteins are usually referred to as transcription factors. Enhancers are ''cis''-acting. They can be located up to 1 Mbp (1,000,000 bp) away from the gene, upstream or downstream from the start site. There are hundreds of thousands of enhancers in the human genome. They are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. The first discovery of a eukaryotic enhancer was in the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene in 1983. This enhancer, located in the large intron, provided an explanation for the transcriptional activation of rearranged Vh gene promoters while unrearranged Vh promoters remained inactive. Locations In eukaryotic cells the structure of the chromatin complex of DNA is folded in a way that functionally mimics the supercoiled state characteristic of prokaryotic DNA, so although the en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultimate source o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung Transplantation
Lung transplantation, or pulmonary transplantation, is a surgical procedure in which one or both lungs are replaced by lungs from a donor. Donor lungs can be retrieved from a living or deceased donor. A living donor can only donate one lung lobe. With some lung diseases, a recipient may only need to receive a single lung. With other lung diseases such as cystic fibrosis, it is imperative that a recipient receive two lungs. While lung transplants carry certain associated risks, they can also extend life expectancy and enhance the quality of life for those with end stage pulmonary disease. Qualifying conditions Lung transplantation is the therapeutic measure of last resort for patients with end-stage lung disease who have exhausted all other available treatments without improvement. A variety of conditions may make such surgery necessary. As of 2005, the most common reasons for lung transplantation in the United States were: * 27% chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |