|
Altdorf Forest
The Altdorf Forest (german: Altdorfer Wald) is a forested, low mountain ridge between Aulendorf and Vogt in the county of Ravensburg in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It is up to high. The forest has an area of about 82 km² and is thus the largest contiguous forest in Upper Swabia. It is divided into state, municipal and private forests, of which the aristocratic House of Waldburg-Wolfegg owns the largest area. References Landscape fact file by the – Altdorfer Wald [Baidu] |
Aulendorf
Aulendorf () is a town in the district of Ravensburg, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is situated southwest of Biberach an der Riß, and north of Ravensburg. Aulendorf exists of the town itself along with the incorporated villages Tannhausen, Bloenried and Zollenreute. Aulendorf is well known in Upper Swabia for its catholic all-day high school "Studienkolleg St. Johann" founded by the Styler Missionaries. It was once the capital of the historic German statelet of Königsegg. Transport Aulendorf is a local train hub for three lines: * Herbertingen–Aulendorf railway * Allgäu Railway (Württemberg), Allgäu railway * Southern Railway (Württemberg), Southern railway Culture and attractions Aulendorf is located on the Upper Swabian Baroque Route and the ''Schwäbische Bäderstrasse''. Museums * The adventure parcours ''Medialer Erlebnisparcours'' tells the history about the castle ''Schloss Aulendorf'' * The museum ''Bürgermuseum'' presents the history of the town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private Forest
A private forest (also private woodland or private wood) is a forest that is not owned by municipal authorities (such as a corporate forest), church authorities or the state (e.g. a state forest or national forest). It can refer to woodland owned by a natural or juridical person or a partnership. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, private forests are defined as forests owned by individuals, families, communities, private co-operatives, corporations and other business entities, religious and private educational institutions, pension or investment funds, NGOs, nature conservation associations and other private institutions. Currently, 22 percent f the world’s forestsare privately owned. Globally, the share of publicly owned forests has decreased since 1990 and the area of forest under private ownership has increased. Categories In forestry terms, private forest may be divided into various sub-categories. For example, in Germany private for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forests And Woodlands Of Baden-Württemberg
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines a forest as, "Land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a canopy cover of more than 10 percent, or trees able to reach these thresholds ''in situ''. It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban use." Using this definition, '' Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020'' (FRA 2020) found that forests covered , or approximately 31 percent of the world's land area in 2020. Forests are the predominant terrestrial ecosystem of Earth, and are found around the globe. More than half of the world's forests are found in only five countries (Brazil, Canada, China, Russia, and the United States). The largest share of forests (45 percent) are in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Baden-Württemberg
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and the environment (environmental geography). Geographic regions and sub-regions are mostly described by their imprecisely defined, and sometimes transitory boundaries, except in human geography, where jurisdiction areas such as national borders are defined in law. Apart from the global continental regions, there are also hydrospheric and atmospheric regions that cover the oceans, and discrete climates above the land and water masses of the planet. The land and water global regions are divided into subregions geographically bounded by large geological features that influence large-scale ecologies, such as plains and features. As a way of describing spatial areas, the concept of regions is important and widely used among the many branches of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerhard Taddey
Gerhard is a name of Germanic origin and may refer to: Given name * Gerhard (bishop of Passau) (fl. 932–946), German prelate * Gerhard III, Count of Holstein-Rendsburg (1292–1340), German prince, regent of Denmark * Gerhard Barkhorn (1919–1983), German World War II flying ace * Gerhard Berger (born 1959), Austrian racing driver * Gerhard Boldt (1918–1981), German soldier and writer * Gerhard de Beer (born 1994), South African football player * Gerhard Diephuis (1817–1892), Dutch jurist * Gerhard Domagk (1895–1964), German pathologist and bacteriologist and Nobel Laureate * Gerhard Dorn (c.1530–1584), Flemish philosopher, translator, alchemist, physician and bibliophile * Gerhard Ertl (born 1936), German physicist and Nobel Laureate * Gerhard Fieseler (1896–1987), German World War I flying ace * Gerhard Flesch (1909–1948), German Nazi Gestapo and SS officer executed for war crimes * Gerhard Gentzen (1909–1945), German mathematician and logician * Gerhard Armauer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundesamt Für Naturschutz
The German Federal Agency for Nature Conservation (german: Bundesamt für Naturschutz, ''BfN'') is the German government's scientific authority with responsibility for national and international nature conservation. BfN is one of the government's departmental research agencies and reports to the German Environment Ministry (BMU). The Agency provides the German Environment Ministry with professional and scientific assistance in all nature conservation and land management issues and in international cooperation activities. BfN furthers its objectives by carrying out related scientific research and is also in charge of a number of funding programmes. BfN additionally performs important enforcement work under international agreements on species conservation and nature conservation, the Antarctic Treaty, and the German Genetic Engineering Act. Application areas of BfN The diversity of species, habitats and landscapes is critical to human survival. Safeguarding this diversity for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waldburg-Wolfegg
Waldburg-Wolfegg was a County ruled by the House of Waldburg, located in southeastern Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Waldburg-Wolfegg was a partition of Waldburg-Wolfegg-Zeil and was repartitioned in 1667, creating Waldburg-Waldsee Waldburg-Waldsee was a County and later Principality within Holy Roman Empire, ruled by the House of Waldburg, located in southeastern Baden-Württemberg, Germany, around Bad Waldsee. Waldburg-Waldsee was a partition of Waldburg-Wolfegg. ..., which annexed Waldburg-Wolfegg in 1798 and became the principality of Waldburg-Wolfegg and Waldsee. Counts of Waldburg-Wolfegg * Maximilian Franz Eusebius, 1667–81 * Ferdinand Louis, 1681–1735 * Joseph Franz, 1735–74 * Ferdinand, 1774–79 * Josef Alois, 1779–91 * Karl Eberhard Wunibald, 1791–98 1589 establishments in the Holy Roman Empire {{Germany-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipal Forest
A municipal forest or municipal woodland is a forest or wood owned by a town or city. Such woods often have a higher density of leisure facilities like play parks, restaurants and cafes, bridleways, cycle paths and footpaths. Unlike an urban forest, which is located largely or entirely within an urban area and may be privately owned, a municipal forest is publicly owned and may well be outside the city or town to which it belongs. Most urban forests will be municipal forests, but many municipal forests are non-urban. Europe Germany In Germany municipal forests are usually corporate forests in accordance with Section 3 of the Federal Forest Act (§ 3 ''Bundeswaldgesetz''). Among the best known municipal forests in Germany are the Tiergarten (210 ha) in Berlin, the Berlin City Forest (28,500 ha) which includes the Grunewald (ca. 3,000 ha) and Köpenick Forest (ca. 6,500 ha), the Frankfurt City Forest (3,866 ha), the Dresden Heath (6,133 ha) and the Ros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vogt (municipality)
During the Middle Ages, an (sometimes given as modern English: advocate; German: ; French: ) was an office-holder who was legally delegated to perform some of the secular responsibilities of a major feudal lord, or for an institution such as an abbey. Many such positions developed, especially in the Holy Roman Empire. Typically, these evolved to include responsibility for aspects of the daily management of agricultural lands, villages and cities. In some regions, advocates were governors of large provinces, sometimes distinguished by terms such as (in German). While the term was eventually used to refer to many types of governorship and advocacy, one of the earliest and most important types of was the church advocate (). These were originally lay lords, who not only helped defend religious institutions in the secular world, but were also responsible for exercising lordly responsibilities within the church's lands, such as the handling of legal cases which might require the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Forest
A state forest or national forest is a forest that is administered or protected by some agency of a sovereign or federated state, or territory. Background The precise application of the terms vary by jurisdiction. For example: * In Australia, a state forest is a forest that is protected by state laws, rather than by the Government of Australia. * In Austria, the state forests are managed by the * In Brazil, a national forest is a protected area for sustainablility * In Canada, provinces administer provincial forests * In France, a national forest is a forest owned by the French state * In Germany, state forests are either federal forest called the ''Bundesforst'', which is controlled by the Institute for Federal Real Estate (''Bundesforstverwaltung''), or forest of the ''Länder'' called ''Landesforste'' * In Iceland, forests managed by the Icelandic Forest Service are classified as national forests. * In New Zealand, a state forest is a forest that is controlled by the Min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
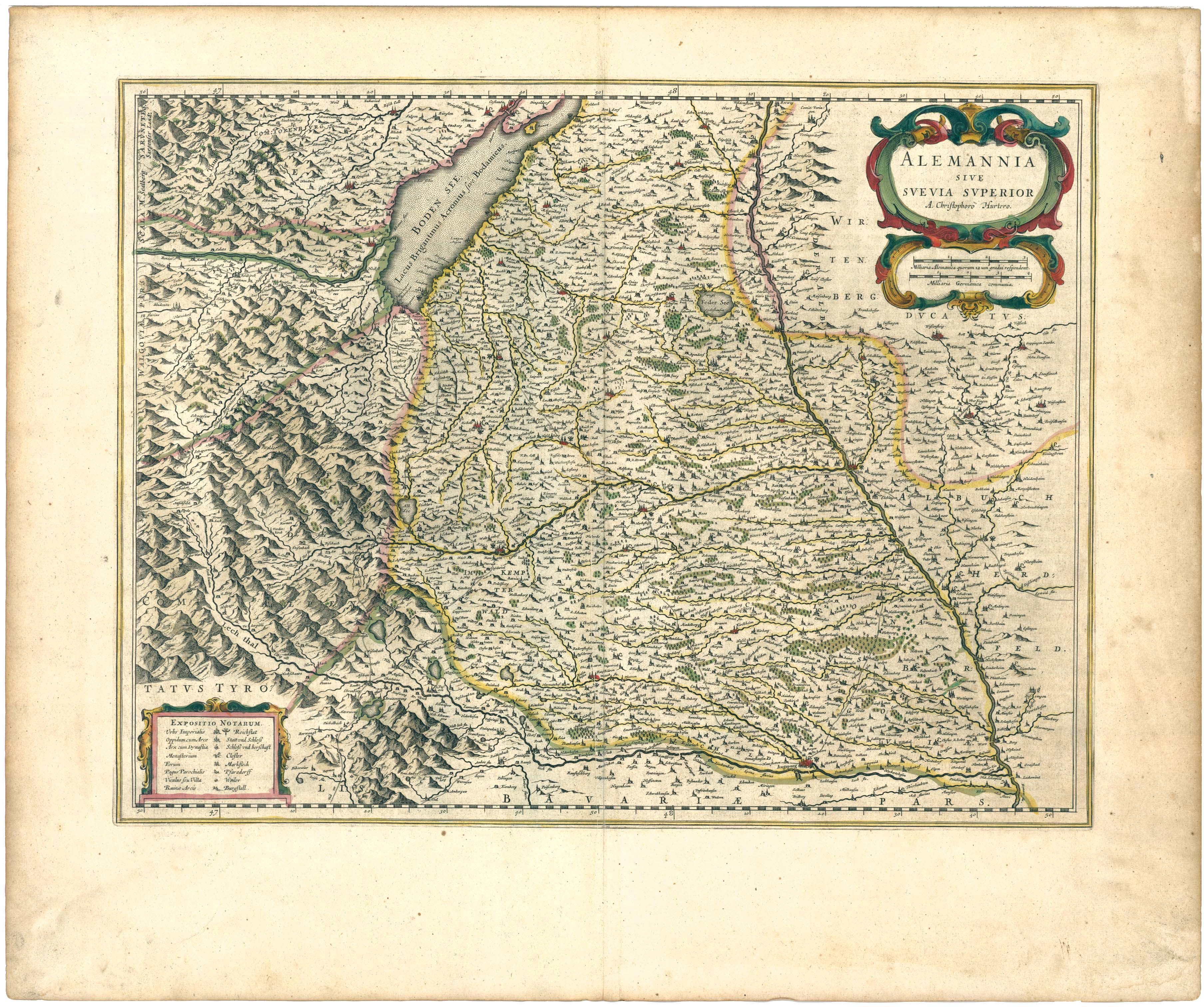
Upper Swabia
Upper Swabia (german: Oberschwaben or ) is a region in Germany in the federal states of Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria.''Brockhaus Enzyklopädie.'' 19. Auflage. Band 16, 1991, p. 72. The name refers to the area between the Swabian Jura, Lake Constance and the Lech. Its counterpart is Lower Swabia (''Niederschwaben''), the region around Heilbronn. Geography The region of Upper Swabia is situated in the central south of Germany consisting of the south-east of Baden-Württemberg and the south-west bavarian Swabia region and lies on the Iller-Lech Plateau, also known as the Upper Swabian Plain, one of the natural regions of Germany. The landscape of Upper Swabia was formed by retreating glaciers after the Riss glaciation, leaving behind a large number of shallows which quickly filled up with water. This led to the large quantity of lakes in Upper Swabia. The landscape of Upper Swabia is quite hilly rising from approximately 458 metres above sea level in the va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |