|
Alpha Sagittarii
Alpha Sagittarii (α Sagittarii, abbreviated Alpha Sgr, α Sgr), also named Rukbat , is a star in the constellation of Sagittarius. Properties Alpha Sagittarii is a blue, class B dwarf star. It does not appear particularly bright in the sky to the naked eye, with a visual apparent magnitude of +3.97. The star has an effective temperature about twice that of the Sun and is nearly three times as massive, with a luminosity in visible wavelengths about 117 times that of the Sun. Based on an excess emission of infrared radiation, it may have a debris disk, much like Vega. It is a single-lined spectroscopic binary system. The ROSAT All Sky Survey discovered that Alpha Sagittarii is emitting an excess flux of X-rays, which is not expected to originate from a star of this spectral class. The most likely explanation is that the companion is an active pre-main sequence star or else a star that has just reached the main sequence. Nomenclature ''α Sagittarii'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
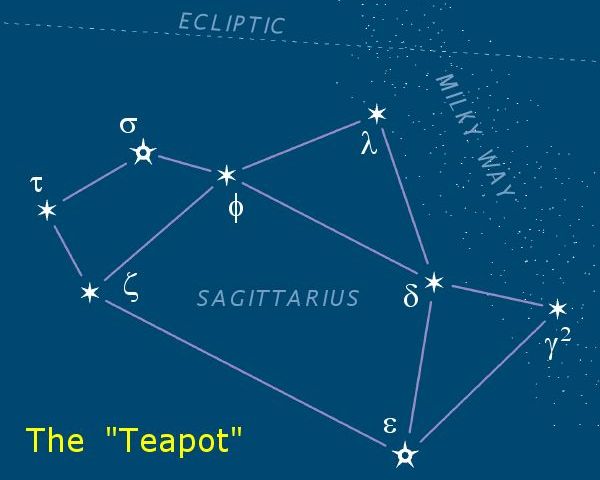
Sagittarius (constellation)
Sagittarius is one of the constellations of the zodiac and is located in the Southern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Its old astronomical symbol is (♐︎). Its name is Latin for "archer". Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur pulling back a bow. It lies between Scorpius and Ophiuchus to the west and Capricornus and Microscopium to the east. The center of the Milky Way lies in the westernmost part of Sagittarius (see Sagittarius A). Visualizations As seen from the northern hemisphere, the constellation's brighter stars form an easily recognizable asterism known as "the Teapot". The stars δ Sgr (Kaus Media), ε Sgr (Kaus Australis), ζ Sgr (Ascella), and φ Sgr form the body of the pot; λ Sgr (Kaus Borealis) is the point of the lid; γ2 Sgr (Alnasl) is the tip of the spout; and σ Sgr (Nunki) and τ Sgr the handle. These same sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arabs, Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as First language, mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rogue Planet
A rogue planet (also termed a free-floating planet (FFP), interstellar, nomad, orphan, starless, unbound or wandering planet) is an interstellar object of planetary-mass, therefore smaller than fusors (stars and brown dwarfs) and without a host planetary system. Such objects have been ejected from the planetary system in which they formed or have never been gravitationally bound to any star or brown dwarf. The Milky Way alone may have billions to trillions of rogue planets, a range the upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will likely be able to narrow down. Some planetary-mass objects may have formed in a similar way to stars, and the International Astronomical Union has proposed that such objects be called sub-brown dwarfs. A possible example is Cha 110913−773444, which may have been ejected and become a rogue planet, or formed on its own to become a sub-brown dwarf. Astronomers have used the Herschel Space Observatory and the Very Large Telescope to observe a very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oort Cloud
The Oort cloud (), sometimes called the Öpik–Oort cloud, first described in 1950 by the Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, is a theoretical concept of a cloud of predominantly icy planetesimals proposed to surround the Sun at distances ranging from 2,000 to 200,000 AU (0.03 to 3.2 light-years).The Oort cloud's outer limit is difficult to define as it varies over the millennia as different stars pass the Sun and thus is subject to variation. Estimates of its distance range from 50,000 to 200,000 au. It is divided into two regions: a disc-shaped inner Oort cloud (or Hills cloud) and a spherical outer Oort cloud. Both regions lie beyond the heliosphere and are in interstellar space. The Kuiper belt, the scattered disc and the detached objects, the other three reservoirs of trans-Neptunian objects, are less than one thousandth as far from the Sun as the Oort cloud. The outer limit of the Oort cloud defines the cosmographic boundary of the Solar System and the extent of the Sun's Hill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragonriders Of Pern
''Dragonriders of Pern'' is a science fantasy series written primarily by American author Anne McCaffrey, who initiated it in 1967. Beginning in 2003, her middle child Todd McCaffrey has written Pern novels, both solo and jointly with Anne. The series (as of 2022) comprises 24 novels and two collections of short stories. The two novellas included in the first novel, ''Dragonflight'', made McCaffrey the first woman to win a Hugo Award for writing fiction as well as the first to win a Nebula Award.''Publishers Weekly'' review of Robin Roberts, ''Anne McCaffrey: A Life with Dragons'' (2007)Quoted by Amazon.com Retrieved 2011-07-16. Overview Humans have colonized the planet Pern in the Rukbat star system, but have lost much of their technology and history (including their origin on Earth) due to periodic onslaughts of Thread, a mycorrhizoid spore that voraciously consumes all organic material, including humans and their crops, given the opportunity. Thread comes from the Red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anne McCaffrey
Anne Inez McCaffrey (1 April 1926 – 21 November 2011) was an American-Irish writer known for the ''Dragonriders of Pern'' science fiction series. She was the first woman to win a Hugo Award for fiction (Best Novella, ''Weyr Search'', 1968) and the first to win a Nebula Award (Best Novella, ''Dragonrider'', 1969). Her 1978 novel ''The White Dragon (novel), The White Dragon'' became one of the first science-fiction books to appear on the New York Times Best Seller list, ''New York Times'' Best Seller list. In 2005 the Science Fiction and Fantasy Writers of America named McCaffrey its 22nd SFWA Grand Master, Grand Master, an annual award to living writers of fantasy and science fiction. She was inducted by the EMP Museum#Science Fiction and Fantasy Hall of Fame, Science Fiction Hall of Fame on 17 June 2006. She also received the Robert A. Heinlein Award for her work in 2007. Life and career Anne McCaffrey was born in Cambridge, Massachusetts, the second of three children ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Star Names
Chinese star names (Chinese: , ''xīng míng'') are named according to ancient Chinese astronomy and astrology. The sky is divided into star mansions (, ''xīng xiù'', also translated as "lodges") and asterisms (, ''xīng guān''). The system of 283 asterisms under Three Enclosures and Twenty-eight Mansions was established by Chen Zhuo of the Three Kingdoms period, who synthesized ancient constellations and the asterisms created by early astronomers Shi Shen, Gan De and Wuxian. Since the Han and Jin Dynasties, stars have been given reference numbers within their asterisms in a system similar to the Bayer or Flamsteed designations, so that individual stars can be identified. For example, Deneb (α Cyg) is referred to as (''Tiān Jīn Sì'', the Fourth Star of Celestial Ford). In the Qing Dynasty, Chinese knowledge of the sky was improved by the arrival of European star charts. ''Yixiang Kaocheng'', compiled in mid-18th century by then deputy Minister of Rites Ignaz Kögler, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta2 Sagittarii
Beta² Sagittarii (β² Sagittarii, abbreviated Beta² Sgr, β² Sgr) is a star in the zodiac constellation of Sagittarius. It is visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of +4.29. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 24.31 mas as seen from Earth, it is located 134 light-years from the Sun. Based upon variations in its proper motion, this is a probable astrometric binary system. As such, its two components would be designated Beta² Sagittarii A (officially named Arkab Posterior , the traditional name of the system) and B. Nomenclature ''β² Sagittarii'' ( Latinised to ''Beta² Sagittarii'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the two components as ''Beta² Sagittarii A'' and ''B'' derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta1 Sagittarii
Beta1 Sagittarii, Latinized from β1 Sagittarii, is a binary star system in the zodiac constellation of Sagittarius, next to the southern constellation border with Telescopium. The brighter primary is named Arkab Prior , the traditional name of the system. It is visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of +4.01. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 10.40 mas as seen from Earth, it is located roughly 310 light-years from the Sun. At Beta¹ Sagittarii's distance, the visual magnitude is diminished by an extinction factor of 0.17 due to interstellar dust. The pair of stars that constitute this system have an angular separation of 28.3 arc seconds, with an estimated physical separation of about 3,290 AU. The primary, Beta1 Sagittarii A, is a B-type main sequence star with a stellar classification of B9 V. It is about 95% of the way through its lifespan on the main sequence. The star has around 3.7 times the mass o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterism (astronomy)
An asterism is an observed pattern or group of stars in the sky. Asterisms can be any identified pattern or group of stars, and therefore are a more general concept than the formally defined 88 constellations. Constellations are based on asterisms, but unlike asterisms, constellations outline and today completely divide the sky and all its celestial objects into regions around their central asterisms. For example, the asterism known as the Big Dipper comprises the seven brightest stars in the constellation Ursa Major. Another is the asterism of the Southern Cross, within the constellation of Crux. Asterisms range from simple shapes of just a few stars to more complex collections of many stars covering large portions of the sky. The stars themselves may be bright naked-eye objects or fainter, even telescopic, but they are generally all of a similar brightness to each other. The larger brighter asterisms are useful for people who are familiarizing themselves with the night sky. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipper (Chinese Constellation)
The Dipper mansion (斗宿, pinyin: Dǒu Xiù) is one of the Twenty-eight mansions of the Chinese constellations. It is one of the northern mansions of the Black Tortoise. In Taoism, it is known as the "Six Stars of the Southern Dipper" (南斗六星, Nándǒu liù xīng), in contrast to the Big Dipper The Big Dipper ( US, Canada) or the Plough ( UK, Ireland) is a large asterism consisting of seven bright stars of the constellation Ursa Major; six of them are of second magnitude and one, Megrez (δ), of third magnitude. Four define a "bowl" ... north to this mansion. Asterisms Stars * ζ Sgr * τ Sgr * σ Sgr * φ Sgr * λ Sgr * μ Sgr {{DEFAULTSORT:Dipper (Chinese Constellation) Chinese constellations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Astronomy
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions have been found on oracle bones unearthed at Anyang, dating back to the mid-Shang dynasty. The core of the "mansion" (宿 ''xiù'') system also took shape around this period, by the time of King Wu Ding (1250–1192 BCE). Detailed records of astronomical observations began during the Warring States period (fourth century BCE) and flourished from the Han period onward. Chinese astronomy was equatorial, centered on close observation of circumpolar stars, and was based on different principles from those in traditional Western astronomy, where heliacal risings and settings of zodiac constellations formed the basic ecliptic framework. Joseph Needham has described the ancient Chinese as the most persistent and accurate obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |