|
Alpha Pavonis
Alpha Pavonis (α Pavonis, abbreviated Alpha Pav, α Pav), formally named Peacock , is a binary star in the southern constellation of Pavo, near the border with the constellation Telescopium. Nomenclature ''α Pavonis'' ( Latinised to ''Alpha Pavonis'') is the star's Bayer designation. The historical name ''Peacock'' was assigned by His Majesty's Nautical Almanac Office in the late 1930s during the creation of the Air Almanac, a navigational almanac for the Royal Air Force. Of the fifty-seven stars included in the new almanac, two had no classical names: Alpha Pavonis and Epsilon Carinae. The RAF insisted that all of the stars must have names, so new names were invented. Alpha Pavonis was named "Peacock" ('pavo' is Latin for 'peacock') whilst Epsilon Carinae was called "Avior". In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN's first bulletin of July 2016 included ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavo (constellation)
Pavo is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere, southern sky whose name is Latin for "peafowl, peacock". Pavo first appeared on a 35-cm (14 in) diameter celestial globe published in 1598 in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius and was depicted in Johann Bayer's star atlas ''Uranometria'' of 1603, and was likely conceived by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. French explorer and astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille gave its stars Bayer designations in 1756. The constellations Pavo, Grus (constellation), Grus, Phoenix (constellation), Phoenix and Tucana are collectively known as the "Southern Birds". The constellation's brightest member, Alpha Pavonis, is also known as Peacock and appears as a 1.91-Apparent magnitude, magnitude blue-white star, but is actually a spectroscopic binary. Delta Pavonis is a nearby Sun-like star some 19.9 light-years distant. Six of the star systems in Pavo have been found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Language
Chinese (, especially when referring to written Chinese) is a group of languages spoken natively by the ethnic Han Chinese majority and many minority ethnic groups in Greater China. About 1.3 billion people (or approximately 16% of the world's population) speak a variety of Chinese as their first language. Chinese languages form the Sinitic branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages family. The spoken varieties of Chinese are usually considered by native speakers to be variants of a single language. However, their lack of mutual intelligibility means they are sometimes considered separate languages in a family. Investigation of the historical relationships among the varieties of Chinese is ongoing. Currently, most classifications posit 7 to 13 main regional groups based on phonetic developments from Middle Chinese, of which the most spoken by far is Mandarin (with about 800 million speakers, or 66%), followed by Min (75 million, e.g. Southern Min), Wu (74 million, e.g. Shangh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes the magnetosphere of the Earth, deflecting destructive solar winds. The atmosphere of the Earth consists mostly of nitrogen and oxygen. Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere like carbon dioxide (CO2) trap a part of the energy from the Sun close to the surface. Water vapor is widely present in the atmosphere and forms clouds that cover most of the planet. More solar e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby objects show a larger parallax than farther objects when observed from different positions, so parallax can be used to determine distances. To measure large distances, such as the distance of a planet or a star from Earth, astronomers use the principle of parallax. Here, the term ''parallax'' is the semi-angle of inclination between two sight-lines to the star, as observed when Earth is on opposite sides of the Sun in its orbit. These distances form the lowest rung of what is called "the cosmic distance ladder", the first in a succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects, serving as a basis for other distance measurements in astronomy forming the higher rungs of the ladder. Parallax also affects optical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Pavonis
Gamma Pavonis, Romanization of Greek, Latinized from γ Pavonis, is a star in the southern circumpolar constellation of Pavo (constellation), Pavo. With an apparent visual magnitude of 4.22, it is a fourth-magnitude star and thereby Bortle Dark-Sky Scale, visible to the naked eye. From parallax observations with the Hipparcos satellite, the distance to this star has been estimated at . It is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −30 km/s. Compared to the Sun, this star has a 21% greater mass and a 15% larger radius. It is a brighter star with 152% of the Sun's luminosity, which is it radiating from the outer envelope at an effective temperature of 6,112 K. The stellar classification of F9 V puts it in the class of F-type main sequence stars that generate energy through the nuclear fusion of hydrogen at the core. It is a metal-poor star, which means it has a low abundance of Chemical element, elements heavier than helium. Age estimates range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Pavonis
Epsilon Pavonis, Latinisation of names, Latinized from ε Pavonis, is a single, white-hued star in the constellation Pavo (constellation), Pavo. It can be viewed with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 3.97. The annual stellar parallax, parallax shift of 31.04 milliarcsecond, mas provides a distance estimate of 105 light years from the Sun. This star is a member of the proposed Argus Association, a young moving group of more than 60 stars associated with the IC 2391 cluster. Epsilon Pavonis is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −6.7 km/s. With a stellar classification of A0 Va, Epsilon Pavonis is an ordinary A-type main-sequence star that is generating energy through hydrogen fusion at its stellar core, core. It is just 27 million years old with a projected rotational velocity of 85 km/s. The star has 2.2 times the mass of the Sun and 1.74 the Sun's radius. It is radiating 32 times the Sun's luminosity from its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta Pavonis
Zeta Pavonis, Latinisation of names, Latinized from ζ Pavonis, is an orange-hued star in the southern constellation Pavo (constellation), Pavo. Its apparent magnitude is 4.01, which is bright enough to be faintly visible to the naked eye. The annual stellar parallax, parallax shift of this star is 14.93 milliarcsecond, mas as seen from Earth, which provides a distance estimate of approximately away from the Sun. It is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −16.30. Based upon its motion through space, this star appears to be a member of the Hyades Supercluster. This is an stellar evolution, evolved K-type star, K-type giant star with a stellar classification of K0 III, which indicates it has exhausted the supply of hydrogen at its stellar core, core. The measured angular diameter of this star, after correction for limb darkening, is . At the estimated distance of this star, this yields a physical size of about 19 times the Solar radius, radius of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Pavonis
Beta Pavonis, Latinised from β Pavonis, is a single, white-hued star in the southern constellation of Pavo. It can be seen with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 3.42. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 24.14 mas as seen from Earth, it is located 135 light-years from the Sun. It is moving away from the Sun with a radial velocity of +4 km/s. Beta Pavonis is a member of the Ursa Major Moving Group, a set of stars that share a similar motion through space. Zorec and Royer (2012) list a stellar classification for this star of A5 IV, indicating it is an evolving subgiant star that has consumed the hydrogen at its core and has begun to expand onto the red giant branch. However, Houk (1979) listed a more evolved class of A7 III, suggesting it is already a giant star. It has about 2.3 times the Sun's radius and 2.51 times the mass of the Sun. At the estimated age of 305 million years, the star still has a relatively high rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Pavonis
Delta Pavonis, Latinized from δ Pavonis, is a single star in the southern constellation of Pavo. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.56, making it a fourth-magnitude star that is visible to the naked eye from the southern hemisphere. Parallax measurements yield an estimated distance of from Earth. This makes it one of the nearest bright stars to the Solar System. It is approaching the Sun with a radial velocity of −23.5 km/s, and is predicted to come as close as in around 49,200 years. Observations This object is a subgiant of spectral type G8 IV; it will stop fusing hydrogen at its core relatively soon, starting the process of becoming a red giant. Hence, Delta Pavonis is 24% brighter than the Sun, but the effective temperature of its outer atmosphere is less: 5,571 K. Its mass is 105% of Sol's mass, with a mean radius 120% of Sol's radius. Delta Pavonis's surface convection zone extends downward to about 43.1% of the star's radius, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
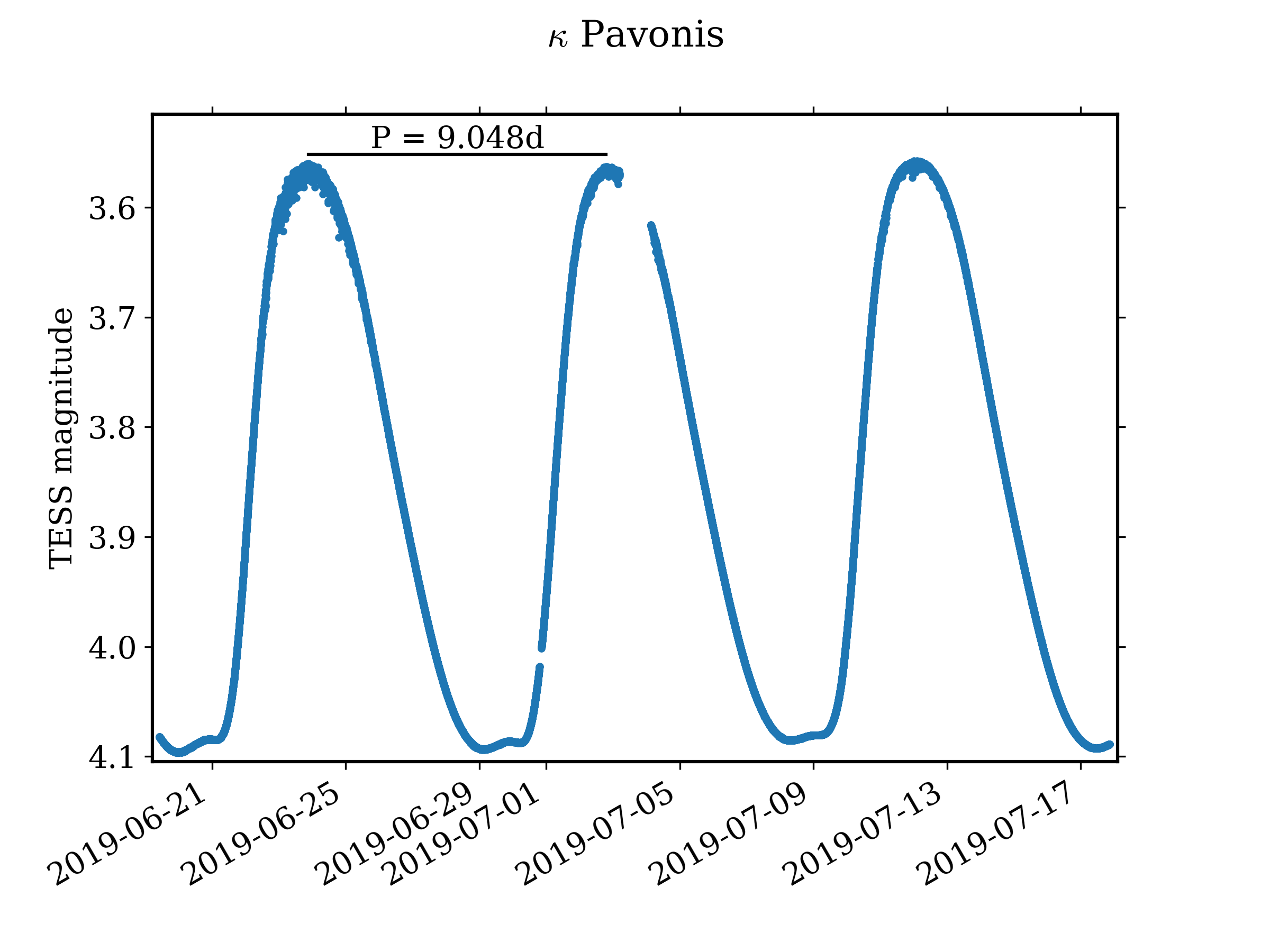
Kappa Pavonis
Kappa Pavonis (κ Pav) is a variable star in the constellation Pavo. It is the brightest W Virginis variable in the sky. Discovery In 1901, κ Pavonis was reported to be a variable star with a magnitude range of 3.8 to 5.2 with a period of 9.0908 days. Further observations revealed radial velocity variations in time with the brightness variations, but this was assumed to indicate a spectroscopic binary system. The brightness variations were then interpreted as eclipses. Less than 10 years later, was κ Pav was listed as a likely Cepheid variable. In 1937 it was used as part of the effort to calibrate the Cepheid distance scale. Only years later were the separate period luminosity relationships for population I and II Cepheid variables identified, and κ Pav was assigned to the type II group. Variability κ Pavonis ranges between apparent magnitudes 3.91 and 4.78, and spectral types F5 to G5, over a period of 9.1 days. It is a W Virginis variable, a type II C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda Pavonis
λ Pavonis, Romanization of Greek, Latinized as Lambda Pavonis, is a single, variable star in the southern constellation of Pavo (constellation), Pavo. It is a blue-white hued star that is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 4.22. This object is located approximately 1,400 light years from the Sun, based upon stellar parallax, parallax. It is a member of the Scorpius–Centaurus association. This is a massive Be star, a rapidly rotating hot blue star which has developed a gas disk around it. It is a Gamma Cassiopeiae variable, γ Cassiopeiae variable or shell star which has occasionally brightened to magnitude 4.0. The stellar classification of B2Ve suggests it is a B-type main-sequence star that is generating energy through stellar core, core hydrogen fusion. This star is spinning rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 190 km/s. This is giving the star an oblate spheroid, oblate shape with an equato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nu Pavonis
ν Pavonis, Latinized as Nu Pavonis, is a possible triple star system in the southern constellation of Pavo (constellation), Pavo. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint star that varies in apparent visual magnitude from 4.60 to 4.64 over a period of 0.85584 days. The system lies approximately 440 light years from the Sun based on stellar parallax, parallax, and is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +17 km/s. It is a possible member of the Wolf 630 group of co-moving stars. This is a single-lined spectroscopic binary system with an orbital period of just 1.71 days in a circular orbit. The unresolved components are close enough that their tidal interaction is significant. The visible component is a slowly pulsating B-type star with a stellar classification of B7III. This implies it is an stellar evolution, evolved giant star, but it is actually more likely to be on the main sequence. An X-ray astronomy, X-ray emission has been detected from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |