|
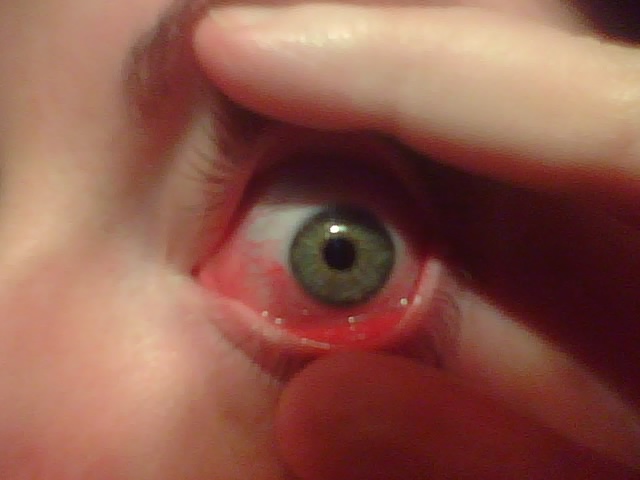
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis (AC) is inflammation of the conjunctiva (the membrane covering the white part of the eye) due to allergy. Although allergens differ among patients, the most common cause is hay fever. Symptoms consist of redness (mainly due to vasodilation of the peripheral small blood vessels), edema (swelling) of the conjunctiva, itching, and increased lacrimation (production of tears). If this is combined with rhinitis, the condition is termed allergic rhinoconjunctivitis (ARC). The symptoms are due to release of histamine and other active substances by mast cells, which stimulate dilation of blood vessels, irritate nerve endings, and increase secretion of tears. Treatment of allergic conjunctivitis is by avoiding the allergen (''e.g.'', avoiding grass in bloom during "hay fever season") and treatment with antihistamines, either topical (in the form of eye drops), or systemic (in the form of tablets). Antihistamines, medications that stabilize mast cells, and nonsteroida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Drop
Eye drops or eyedrops are liquid drops applied directly to the surface of the eye usually in small amounts such as a single drop or a few drops. Eye drops usually contain saline to match the salinity of the eye. Drops containing only saline and sometimes a lubricant are often used as artificial tears to treat dry eyes or simple eye irritation such as itching or redness. Eye drops may also contain one or more medications to treat a wide variety of eye diseases. Depending on the condition being treated, they may contain steroids, antihistamines, sympathomimetics, beta receptor blockers, parasympathomimetics, parasympatholytics, prostaglandins, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antibiotics, antifungals, or topical anesthetics. Eye drops have less of a risk of side effects than do oral medicines, and such risk can be minimized by occluding the lacrimal punctum (i.e. pressing on the inner corner of the eye) for a short while after instilling drops. Prior to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dust Mites
House dust mites (HDM, or simply dust mites) are various species of acariform mites belonging to the family Pyroglyphidae that are found in association with dust in dwellings. They are known for causing allergies. Biology Species The currently known species are: * ''Dermatophagoides farinae'' (American house dust mite) * ''Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus'' (European house dust mite) * '' Dermatophagoides evansi'' * '' Dermatophagoides microceras'' * '' Dermatophagoides halterophilus'' * ''Dermatophagoides siboney'' * ''Dermatophagoides neotropicalis'' * ''Dermatophagoides alexfaini'' * ''Dermatophagoides anisopoda'' * ''Dermatophagoides chirovi'' * ''Dermatophagoides deanei'' * ''Dermatophagoides rwandae'' * ''Dermatophagoides scheremeteroskyi'' * ''Dermatophagoides scheremetewskyi'' * ''Dermatophagoides simplex'' * ''Euroglyphus maynei'' (Mayne's house dust mite) * '' Euroglyphus longior'' * '' Hirstia domicola'' * '' Malayoglyphus carmelitus'' * '' Malayoglyphus intermedius'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoke
Smoke is a suspension of airborne particulates and gases emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwanted by-product of fires (including stoves, candles, internal combustion engines, oil lamps, and fireplaces), but may also be used for pest control ( fumigation), communication ( smoke signals), defensive and offensive capabilities in the military (smoke screen), cooking, or smoking (tobacco, cannabis, etc.). It is used in rituals where incense, sage, or resin is burned to produce a smell for spiritual or magical purposes. It can also be a flavoring agent and preservative. Smoke inhalation is the primary cause of death in victims of indoor fires. The smoke kills by a combination of thermal damage, poisoning and pulmonary irritation caused by carbon monoxide, hydrogen cyanide and other combustion products. Smoke is an aerosol (or mist) of solid particl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types of air pollutants, such as gases (including ammonia, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrous oxides, methane, carbon dioxide and chlorofluorocarbons), particulates (both organic and inorganic), and biological molecules. Air pollution can cause diseases, allergies, and even death to humans; it can also cause harm to other living organisms such as animals and food crops, and may damage the natural environment (for example, climate change, ozone depletion or habitat degradation) or built environment (for example, acid rain). Air pollution can be caused by both human activities and natural phenomena. Air pollution is a significant risk factor for a number of pollution-related diseases, including respiratory infections, heart disease, COPD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmetics
Cosmetics are constituted mixtures of chemical compounds derived from either natural sources, or synthetically created ones. Cosmetics have various purposes. Those designed for personal care and skin care can be used to cleanse or protect the body or skin. Cosmetics designed to enhance or alter one's appearance (makeup) can be used to conceal blemishes, enhance one's natural features (such as the eyebrows and eyelashes), add color to a person's face, or change the appearance of the face entirely to resemble a different person, creature or object. Cosmetics can also be designed to add fragrance to the body. Definition and etymology The word ''cosmetics'' derives from the Greek (), meaning "technique of dress and ornament", from (), "skilled in ordering or arranging" and that from (), meaning "order" and "ornament". Cosmetics are constituted from a mixture of chemical compounds derived from either natural sources, or synthetically created ones. Legal definition T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfumes
Perfume (, ; french: parfum) is a mixture of fragrance, fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds (fragrances), Fixative (perfumery), fixatives and solvents, usually in liquid form, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agreeable scent. The 1939 List of Nobel laureates, Nobel Laureate for Chemistry, Leopold Ružička stated in 1945 that "right from the earliest days of scientific chemistry up to the present time, perfumes have substantially contributed to the development of organic chemistry as regards methods, systematic classification, and theory." Ancient texts and archaeological excavations show the use of perfumes in some of the earliest human civilizations. Modern perfumery began in the late 19th century with the commercial synthesis of aroma compounds such as vanillin or coumarin, which allowed for the composition of perfumes with smells previously unattainable solely from natural aromatics. History The word ''perfume'' derives from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be extracted), enzymes (such as lipase and amylase), antimicrobial agents (such as secretory IgA, and lysozymes). The enzymes found in saliva are essential in beginning the process of digestion of dietary starches and fats. These enzymes also play a role in breaking down food particles entrapped within dental crevices, thus protecting teeth from bacterial decay. Saliva also performs a lubricating function, wetting food and permitting the initiation of swallowing, and protecting the oral mucosa from drying out. Various animal species have special uses for saliva that go beyond predigestion. Some swifts use their gummy saliva to build nests. ''Aerodramus'' nests form the basis of bird's nest soup. Cobras, vipers, and certain other membe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by seed plants. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm cells). Pollen grains have a hard coat made of sporopollenin that protects the gametophytes during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants, or from the male cone to the female cone of gymnosperms. If pollen lands on a compatible pistil or female cone, it germinates, producing a pollen tube that transfers the sperm to the ovule containing the female gametophyte. Individual pollen grains are small enough to require magnification to see detail. The study of pollen is called palynology and is highly useful in paleoecology, paleontology, archaeology, and forensics. Pollen in plants is used for transferring haploid male genetic material from the anther of a single flower to the stigma of another in cross-pollination. In a case of self-pollination, this process takes place from the anth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allergic
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, allergic asthma, and anaphylaxis. Symptoms may include red eyes, an itchy rash, sneezing, coughing, a runny nose, shortness of breath, or swelling. Note: food intolerances and food poisoning are separate conditions. Common allergens include pollen and certain foods. Metals and other substances may also cause such problems. Food, insect stings, and medications are common causes of severe reactions. Their development is due to both genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves immunoglobulin E antibodies (IgE), part of the body's immune system, binding to an allergen and then to a receptor on mast cells or basophils where it triggers the release of inflammatory chemicals such as histamine. Diagnosis is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Of Life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards and concerns". Standard indicators of the quality of life include wealth, employment, the environment, physical and mental health, education, recreation and leisure time, social belonging, religious beliefs, safety, security and freedom. QOL has a wide range of contexts, including the fields of international development, healthcare, politics and employment. Health related QOL (HRQOL) is an evaluation of QOL and its relationship with health. Engaged theory One approach, called engaged theory, outlined in the journal of ''Applied Research in the Quality of Life'', posits four domains in assessing quality of life: ecology, economics, politics and culture. In the domain of culture, for example, it includes the following subdomains of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phlyctenular Keratoconjunctivitis
Phlyctenular keratoconjunctivitis is an inflammatory syndrome caused by a delayed (aka type-IV) hypersensitivity reaction to one or more antigens. The triggering antigen is usually a bacterial protein (particularly from ''Staphylococcus aureus''), but may also be a virus, fungus (particularly ''Candida albicans''), or nematode. Symptoms * Irritation * Discomfort or pain * Foreign-body sensation * Tearing * Blepharospasm * Photophobia * Mucopurulent discharge (rarely) In cases where the cornea is affected, pain and photophobia are more likely, and corneal scarring can occur (potentially impairing vision). Presentation The syndrome is marked by the appearance of characteristic lesions, known as phlyctenules, on the cornea and/or conjunctiva. These usually manifest as small (1 - 3 or 1 - 4 mm) raised nodules, pinkish-white or yellow in color, which may ulcerate (or, more rarely, necrose) and are often surrounded by dilated blood vessels. Corneal lesions are usually triangular in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)