|
Algonquian–Wakashan Languages
Algonquian–Wakashan (also Almosan, Algonkian–Mosan, Algonkin–Wakashan) is a hypothetical language family composed of several established language families that was proposed in 1929. The proposal consists of the following: I. Algic languages, Algic (Algonkin–Ritwan) : A. Algonquian languages, Algonquian (Algonkin) : B. Beothuk language, Beothuk : C. Wiyot language, Wiyot–Yurok language, Yurok (Ritwan) II. Kutenai language, Kutenai (also known as Kootenay; a language isolate) III. Mosan languages, Mosan : A. Wakashan languages, Wakashan : B. Chimakuan languages, Chimakuan : C. Salishan languages, Salishan Kutenai language, Kutenai may possibly be distantly related to the Salishan languages, Salishan family, but this link has not been demonstrated. The Mosan family proposal is also hypothetical and is currently considered undemonstrated, rather appearing to be a Sprachbund. External relationships Joseph Greenberg renamed Sapir's proposal ''Almosan'' and grouped it in an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
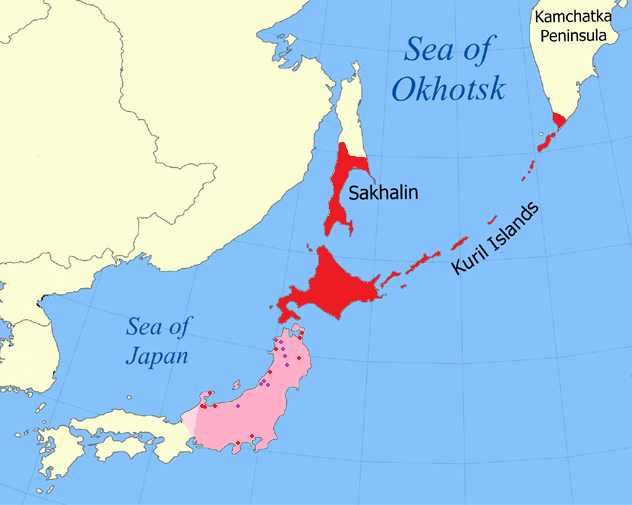
Sakhalin Island
Sakhalin ( rus, Сахали́н, r=Sakhalín, p=səxɐˈlʲin; ja, 樺太 ''Karafuto''; zh, c=, p=Kùyèdǎo, s=库页岛, t=庫頁島; Manchu: ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ, ''Sahaliyan''; Orok: Бугата на̄, ''Bugata nā''; Nivkh: Yh-mif) is the largest island of Russia. It is north of the Japanese archipelago, and is administered as part of the Sakhalin Oblast. Sakhalin is situated in the Pacific Ocean, sandwiched between the Sea of Okhotsk to the east and the Sea of Japan to the west. It is located just off Khabarovsk Krai, and is north of Hokkaido in Japan. The island has a population of roughly 500,000, the majority of which are Russians. The indigenous peoples of the island are the Ainu, Oroks, and Nivkhs, who are now present in very small numbers. The Island's name is derived from the Manchu word ''Sahaliyan'' (ᠰᠠᡥᠠᠯᡳᠶᠠᠨ). Sakhalin was once part of China during the Qing dynasty, although Chinese control was relaxed at times. Sakhalin was lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caddoan
The Caddoan languages are a family of languages native to the Great Plains spoken by tribal groups of the central United States, from present-day North Dakota south to Oklahoma. All Caddoan languages are critically endangered, as the number of speakers has declined markedly due to colonial legacy, lack of support, and other factors. Family division Five languages belong to the Caddoan language family: Kitsai and Wichita have no speakers left. Kitsai stopped being spoken in the 19th century when its members were absorbed into the Wichita tribe. Wichita stopped being spoken in 2016, when the last native speaker of Wichita, Doris McLemore (who left recordings and language materials), died. All of the remaining Caddoan languages spoken today are severely endangered. As of 2007, Caddo is spoken by only 25 people, Pawnee by 10, and Arikara by 10. Caddo and Pawnee are spoken in Oklahoma by small numbers of tribal elders. Arikara is spoken on the Fort Berthold Reservation in North D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JPEG
JPEG ( ) is a commonly used method of lossy compression for digital images, particularly for those images produced by digital photography. The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality. Since its introduction in 1992, JPEG has been the most widely used image compression standard in the world, and the most widely used digital image format, with several billion JPEG images produced every day as of 2015. The term "JPEG" is an acronym for the Joint Photographic Experts Group, which created the standard in 1992. JPEG was largely responsible for the proliferation of digital images and digital photos across the Internet, and later social media. JPEG compression is used in a number of image file formats. JPEG/Exif is the most common image format used by digital cameras and other photographic image capture devices; along with JPEG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mother Tongue (journal)
''Mother Tongue'' is an annual academic journal published by the Association for the Study of Language in Prehistory (ASLIP) that has been published since 1995. Its goal is to encourage international and interdisciplinary information sharing, discussion, and debate among , paleoanthropologists, archaeologists, and historical linguists on questions relating to the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amerind Languages
Amerind is a hypothetical higher-level language family proposed by Joseph Greenberg in 1960 and elaborated by his student Merritt Ruhlen. Greenberg proposed that all of the indigenous languages of the Americas belong to one of three language families, the previously established Eskimo–Aleut and Na–Dene, and with everything else—otherwise classified by specialists as belonging to dozens of independent families—as Amerind. Due to a large number of methodological flaws in the 1987 book ''Language in the Americas'', the relationships he proposed between these languages have been rejected by the majority of historical linguists as spurious.Campbell 1997Adelaar 1989Berman 1992Chafe 1987Matisoff 1990Kimball 1992Mithun 1999Poser 1992Rankin 1992 The term ''Amerind'' is also occasionally used to refer broadly to the various indigenous languages of the Americas without necessarily implying that they are a genealogical group. To avoid ambiguity, the term Amerindian is often used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitaly Shevoroshkin
Vitaly Victorovich Shevoroshkin ( rus, Виталий Викторович Шеворошкин) is an American linguist of Russian origin, specializing in the study of ancient Mediterranean languages. Shevoroshkin was born in 1932 in Georgia (USSR). In the 1960s he tried to decipher Carian inscriptions and proved that their language belonged to the Anatolian languages. In the 1970s he emigrated to the United States. He is now a professor emeritus of Slavic Languages and Literatures and Linguistics at the University of Michigan. Shevoroshkin is also a leader in the study of language in prehistory (paleolinguistics), and in publicizing the recent work of paleolinguists, especially Russians. In 1988 he and Benjamin Stolz organized the First International Interdisciplinary Symposium on Language and Prehistory, at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Forty-six scholars participated as presenters and discussants, sixteen of which were from Russia and other eastern European countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Nikolaev (linguist)
Sergei Lvovich Nikolaev (russian: Серге́й Льво́вич Никола́ев; born 25 December 1954) is a Soviet and Russian linguist, specialist in comparative historical linguistics, Slavic accentology and dialectology. He is the author of a number of books and articles on Indo-European studies, accentology, and Slavic dialectology. Nikolaev is Doctor Nauk in Philological Sciences. He is also a major figure in the Moscow School of Comparative Linguistics. Biography Nikolaev graduated from the philological faculty of Tver State University and Moscow State University. Since 1986, he has worked at the Institute for Slavic and Balkan studies of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Since 1987, he has been the head of regular dialectological expeditions in the area of East Slavic subdialects. In 1992, he received a doctoral degree with a dissertation comprising the totality of his works, and now heads the group of Slavic glottogenesis. Contribution to linguistics Sergei N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chukotko-Kamchatkan Languages
The Chukotko-Kamchatkan or Chukchi–Kamchatkan languages are a language family of extreme northeastern Siberia. Its speakers traditionally were indigenous hunter-gatherers and reindeer-herders. Chukotko-Kamchatkan is endangered. The Kamchatkan branch is moribund, represented only by Western Itelmen, with only 4 or 5 elderly speakers left. The Chukotkan branch had close to 7,000 speakers left (as of 2010, the majority being speakers of Chukchi), with a reported total ethnic population of 25,000. While the family is sometimes grouped typologically and geographically as Paleosiberian, no external genetic relationship has been widely accepted as proven. The most popular such proposals have been for links with Eskimo–Aleut, either alone or in the context of a wider grouping. Alternative names Less commonly encountered names for the family are Chukchian, Chukotian, Chukotan, Kamchukchee and Kamchukotic. Of these, ''Chukchian'' and ''Chukotian'' are ambiguous, since both terms are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgiy Starostin
Georgiy Sergeevich "George" Starostin (russian: Гео́ргий Серге́евич Ста́ростин; born 4 July 1976) is a Russian linguist. He is the son of the late historical linguist Sergei Anatolyevich Starostin (1953–2005), and his work largely continues his father's. He is also known as a self-published music reviewer, author of the ''Only Solitaire Blog''. Research Starostin focuses almost exclusively on maintaining the following of his father's projects: the Evolution of Human Languages project; The Tower of Babel, a publicly searchable online database containing information about many Eurasia's language families; and STARLING, a software package to aid comparative linguists.FAQs of The Tower of Babel project at Starling.rinet.ru Evolution of Human Languages The |
Ilia Peiros
Ilia Peiros (full name: Ilia Iosifovich Peiros, Илья Иосифович Пейрос; born 1948) is a Russian linguist who specializes in the historical linguistics of East Asia. Peiros is a well-known scholar in the Moscow School of Comparative Linguistics, known for its work on long-range comparative linguistics. Peiros is affiliated with the Santa Fe Institute in New Mexico, United States and was also a former faculty member at the University of Melbourne. Education In 1971, Peiros graduated from the Department of Theoretical and Applied Linguistics at Moscow State University. In 1976, he defended his Ph.D. thesis on Sino-Tibetan consonantism. Career In the article "An Austric Macrofamily: some considerations", Peiros proposed that Austro-Tai (comprising Austronesian and Tai-Kadai), Miao-Yao ( Hmong-Mien), and Austroasiatic were all related to each other as part of the Austric language macrofamily. In 1996, together with Sergei Starostin, he published a 6-volume comparati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murray Gell-Mann
Murray Gell-Mann (; September 15, 1929 – May 24, 2019) was an American physicist who received the 1969 Nobel Prize in Physics for his work on the theory of elementary particles. He was the Robert Andrews Millikan Professor of Theoretical Physics Emeritus at the California Institute of Technology, a distinguished fellow and one of the co-founders of the Santa Fe Institute, a professor of physics at the University of New Mexico, and the Presidential Professor of Physics and Medicine at the University of Southern California. Gell-Mann spent several periods at CERN, a nuclear research facility in Switzerland, among others as a John Simon Guggenheim Memorial Foundation fellow in 1972. Early life and education Gell-Mann was born in Lower Manhattan to a family of Jewish immigrants from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, specifically from Czernowitz in present-day Ukraine. His parents were Pauline (née Reichstein) and Arthur Isidore Gell-Mann, who taught English as a second language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)