|
Algernon Frederick Rous De Horsey
Admiral Sir Algernon Frederick Rous de Horsey (25 July 1827 – 22 October 1922) was a Royal Navy officer, appointed aide-de-camp to Queen Victoria. He distinguished himself in Canada during the Fenian raids, and was thanked in Parliament for suppressing riots in Jamaica. Early life De Horsey was the son of Spencer de Horsey, of Great Glemham Suffolk, and Lady Louise, a daughter of the first Earl of Stradbroke. His only sister was the Countess of Cardigan, whose reminiscences caused a scandal when they were published. Naval career De Horsey joined the Royal Navy in 1840 and served on the coast of Syria later that year. He received the Naval General Service Medal and bar for his service in Syria as well as a medal for his service in Acre given by the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire. Promoted to Lieutenant in July 1846 and to Commander in June 1853, he was given command of the paddle sloop HMS'' Devastation'' that same month and of HMS ''Victor'' from November 1855. Promoted to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiral (United Kingdom)
Admiral is a senior rank of the Royal Navy, which equates to the NATO rank code OF-9, outranked only by the rank of admiral of the fleet. Royal Navy officers holding the ranks of rear admiral, vice admiral and admiral of the fleet are sometimes considered generically to be admirals. The rank of admiral is currently the highest rank to which a serving officer in the Royal Navy can be promoted, admiral of the fleet being in abeyance except for honorary promotions of retired officers and members of the Royal Family. The equivalent rank in the British Army and Royal Marines is general; and in the Royal Air Force, it is air chief marshal. History The first admirals (1224 to 1523) King Henry III of England appointed the first known English Admiral Sir Richard de Lucy on 29 August 1224. De Lucy was followed by Sir Thomas Moulton in 1264, who also held the title of ''Keeper of the Sea and Sea Ports''. Moulton was succeeded by Sir William de Leybourne, (the son of Sir Roger de Leyb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countries this naval rank is termed frigate captain. Commander is also a generic term for an officer commanding any armed forces unit, for example "platoon commander", "brigade commander" and "squadron commander". In the police, terms such as "borough commander" and "incident commander" are used. Commander as a naval and air force rank Commander is a rank used in navies but is very rarely used as a rank in armies. The title, originally "master and commander", originated in the 18th century to describe naval officers who commanded ships of war too large to be commanded by a lieutenant but too small to warrant the assignment of a post-captain and (before about 1770) a sailing master; the commanding officer served as his own master. In practice, these were usually unrated sloops-of-war o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pacocha
The Battle of Pacocha was a naval battle that took place on 29 May 1877 between the rebel-held Peruvian monitor ''Huáscar'' and the British ships and . The vessels did not inflict significant damage on each other, however the battle is notable for seeing the first combat use of the self-propelled torpedo. Background In May 1877, Nicolás de Piérola, former Minister of Finance, initiated an attempt to overthrow then-President Mariano Ignacio Prado. As part of this coup attempt, on 6 May two of his supporters, Colonel Lorranaga and Major Echenique, boarded ''Huáscar'' at the port of Callao while the captain and executive officer were ashore. Officers remaining on the ship were part of the plot and persuaded the crew to join their cause. Now in rebel hands, ''Huáscar'' put to sea with Luis Germán Astete in command. Other Peruvian naval ships present in the port, such as ''Atahualpa'', were in a state of disrepair and unable to pursue. The rebels used the ship to harass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Triumph (1870)
HMS ''Triumph'' was a broadside ironclad battleship of the Victorian era, the sister-ship of . These two ships comprise the ''Swiftsure'' class of 1870. The two sister-ships, which were built side by side by Palmers, were designed and built specifically to serve as flagships on distant stations, primarily with the Pacific squadron. They were powered by a Maudslay horizontal twin-cylinder return connecting-rod engine, and were the last British battleships to be fitted with a hoisting screw. Construction The ship was built by Palmers Shipbuilding and Iron Company, Jarrow, Northumberland. She was launched on 27 September 1870. On 28 November, during fitting out, she was severely damaged by fire. As a result, she was not completed until 8 April 1873. Service history ''Triumph'' was initially commissioned in 1873 for the Channel Fleet, being transferred after a short time to the Mediterranean. On 1 March 1877, she collided with the steamship but was not damaged. She paid of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Shah (1873)
The first HMS ''Shah'' was a 19th-century unarmoured iron hulled, wooden sheathed frigate of Britain's Royal Navy designed by Sir Edward Reed. She was originally to be named HMS ''Blonde'' but was renamed following the visit of the Shah of Persia in 1873. Building Programme The following table gives the build details and purchase cost of the ''Shah'' and the other two iron frigates: ''Inconstant'' and ''Raleigh''. Standard British practice at that time was for these costs to exclude armament and stores. *Date first commissioned. Her complement was 469 officers and men, 46 boys and 87 marines. Armament As of 1888, ''Shah'' was armed with two 9-inch rifled muzzle-loading guns, sixteen 7-inch 6½ ton rifled muzzle-loading guns, eight 5-inch breech-loading guns, three quick-firing guns, twelve machine-guns, and four torpedo launchers. Service career She was only in service for three years. In 1876, she was deployed as flagship of the Royal Navy's Pacific Station unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Repulse (1868)
HMS ''Repulse'' was the last wooden battleship constructed for the Royal Navy. She was laid down as a 90-gun second-rate line-of-battle ship with two decks; having been approved for conversion to a broadside ironclad in 1861, work on her was intentionally delayed until the performance of earlier conversions from wooden hull to ironclad could be assessed. She was therefore eleven years from being laid down to completion, no work at all being undertaken on her between 1861 and 1866. In 1864 Sir Edward Reed had been Chief Constructor for some eighteen months, and was in a position to stipulate the nature of the armament and the disposition of armour which ''Repulse'' should carry when construction should be resumed, which it was in 1866. Guns of 9-inch and 10-inch calibre were already afloat in the Royal Navy, and clearly similar weapons could be carried by potential adversaries. It followed that armour of 4.5 inches thickness, which since had been regarded as adequate, cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuela (ship)
Manuela may refer to: People * Manuela (given name), a Spanish and Portuguese feminine given name * Manuela (singer) (1943–2001), German singer of Schlager songs Film and television * ''Manuela'' (1957 film), a British film directed by Guy Hamilton * ''Manuela'' (1967 film), a Cuban short film directed by Humberto Solás * ''Manuela'' (1976 film), a Spanish film directed by Gonzalo García Pelayo * ''Manuela'' (2006 film), a film directed by Marco Castro * ''Manuela'' (TV series), a 1991 telenovela starring Grecia Colmenares Grecia Dolores Colmenares Mieussens (born December 7, 1962 in Valencia, Venezuela) is a Venezuelan actress. Biography Grecia Dolores Colmenares Mieussens was born on December 7, 1962, in Valencia, Venezuela. She is the daughter of a Venezue ... Music * "Manuela" (Demis Roussos song), 1974 * "Manuela", a song by Julio Iglesias from '' A flor de piel'', 1974 {{disambiguation ja:マヌエラ pl:Manuela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
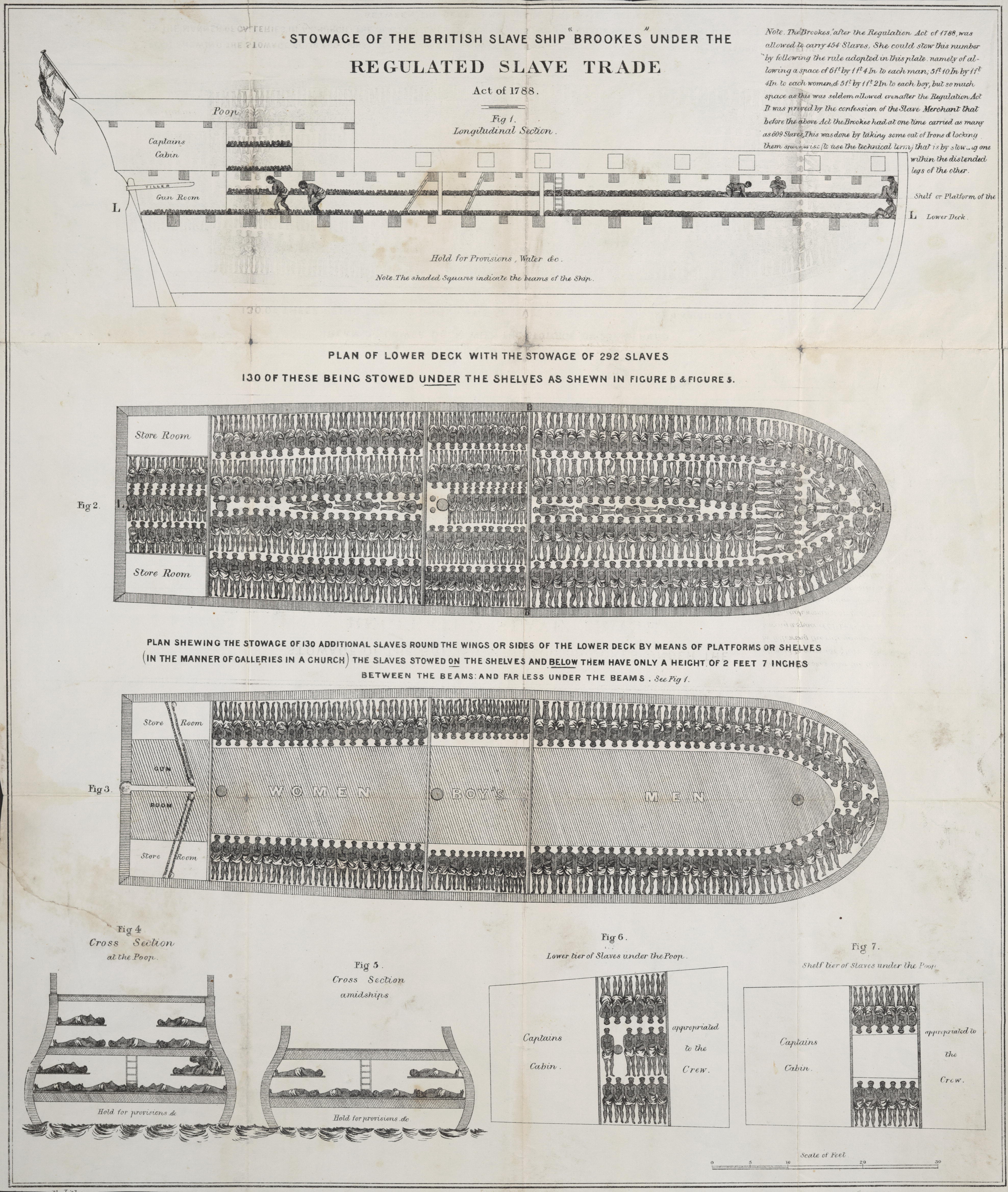
Slave Ship
Slave ships were large cargo ships specially built or converted from the 17th to the 19th century for transporting slaves. Such ships were also known as "Guineamen" because the trade involved human trafficking to and from the Guinea coast in West Africa. Atlantic slave trade In the early 1600s, more than a century after the arrival of Europeans to the Americas, demand for unpaid labor to work plantations made slave-trading a profitable business. The Atlantic slave trade peaked in the last two decades of the 18th century, during and following the Kongo Civil War. To ensure profitability, the owners of the ships divided their hulls into holds with little headroom, so they could transport as many slaves as possible. Unhygienic conditions, dehydration, dysentery and scurvy led to a high mortality rate, on average 15% and up to a third of captives. Often the ships carried hundreds of slaves, who were chained tightly to plank beds. For example, the slave ship ''Henrietta Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamaica Dockyard
Jamaica Dockyard also known as Port Royal Dockyard was a British Royal Navy Dockyard located at Port Royal, Jamaica. It was established 1675 and closed in 1905. The dockyard was initially administered by the Navy Board then later the Board of Admiralty. History In 1675 the British first made use of a wharf at Port Royal and assigned a resident Naval Officer to superintend these facilities;. Following the 1692 earthquake, Port Royal never fully recovered from its preeminent position as a major commercial center. Despite this the dockyard served as the headquarters of the British Royal Navy in the Caribbean. From the eighteenth century until the nineteenth century, various refurbishments and upgrade work were undertaken to improve its docks, facilities fortifications and. From 1735 new wharves and storehouses were built at this time, as well as housing for the officers of the Yard. Over the next thirty years, more facilities were added: cooperages, workshops, sawpits, and accomm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Aboukir (1848)
HMS ''Aboukir'' was a 90-gun second-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy launched in 1848. Career On 6 July 1861, ''Aboukir'' ran aground on Yeusta Skerry. Repairs cost £302. The navy refitted her with Propeller, screw propulsion in 1858 and sold her in 1877. A monument on Southsea seafront commemorates an outbreak of Yellow Fever aboard her between 1873 and 1874. Citations Ships of the line of the Royal Navy 1848 ships Albion-class ships of the line (1842) Ships built in Plymouth, Devon Floating batteries of the Royal Navy Maritime incidents in July 1861 {{UK-line-ship-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamaica Division Of North America And West Indies Station
The Jamaica Division of the North America and West Indies Station was a sub-command of the British Royal Navy's North America and West Indies Station head-quartered at Port Royal dockyard in Jamaica from 1838 to 1905. History In 1830 The Jamaica Station merged with the North American Station to form the North America and West Indies Station. In 1838 the Royal Navy established a sub-command to the Commander-in-Chief, North America and West Indies Station. It was commanded by the Commodore on Jamaica Division of North America and West Indies Station who was responsible for the naval base until March 1905 when the dockyard was closed. In 1951, the Royal Naval Dockyard, Bermuda closed after which the new post of Senior Naval Officer, West Indies (SNOWI) was established as the West Indies Sub-Area Command under the Commander-in-Chief, Home Fleet. The office holder would hold the rank of Commodore. The division primarily consisted of naval vessels assigned to this command but also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commodore (Royal Navy)
Commodore (Cdre) is a rank of the Royal Navy above captain and below rear admiral. It has a NATO ranking code of OF-6. The rank is equivalent to brigadier in the British Army and Royal Marines and to air commodore in the Royal Air Force. Commodore has only been a substantive rank in the Royal Navy since 1997. Until then the term denoted a functional position rather than a formal rank, being the title bestowed on the senior officer of a fleet of at least two naval vessels comprising an independent (usually ad hoc and short-term) command. (In this case, for instance, a lieutenant in substantive rank could be a commodore for the term of the command.) History The rank of commodore was introduced during the 17th century in November 1674 (though not legally established until 1806). In 1684 the navy introduced two classes of commodore, the first known as a ''Commodore Distinction'' and the other a ''Commodore Ordinary''; these would later evolve into commodores first and second cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)