|
Algaculture
Algaculture is a form of aquaculture involving the farming of species of algae. The majority of algae that are intentionally cultivated fall into the category of microalgae (also referred to as phytoplankton, microphytes, or planktonic algae). Macroalgae, commonly known as seaweed, also have many commercial and industrial uses, but due to their size and the specific requirements of the environment in which they need to grow, they do not lend themselves as readily to cultivation (this may change, however, with the advent of newer seaweed cultivators, which are basically algae scrubbers using upflowing air bubbles in small containers). Commercial and industrial algae cultivation has numerous uses, including production of nutraceuticals such as omega-3 fatty acids (as algal oil) or natural food colorants and dyes, food, fertilizers, bioplastics, chemical feedstock (raw material), protein-rich animal/aquaculture feed, pharmaceuticals, and algal fuel, and can also be used as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioeconomy
Biobased economy, bioeconomy or biotechonomy is economic activity involving the use of biotechnology and biomass in the production of goods, services, or energy. The terms are widely used by regional development agencies, national and international organizations, and biotechnology companies. They are closely linked to the evolution of the biotechnology industry and the capacity to study, understand, and manipulate genetic material that has been possible due to scientific research and technological development. This includes the application of scientific and technological developments to agriculture, health, chemical, and energy industries. The terms bioeconomy (BE) and bio-based economy (BBE) are sometimes used interchangeably. However, it is worth to distinguish them: the biobased economy takes into consideration the production of non-food goods, whilst bioeconomy covers both bio-based economy and the production and use of food and feed. More than 60 countries and regions have bioec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
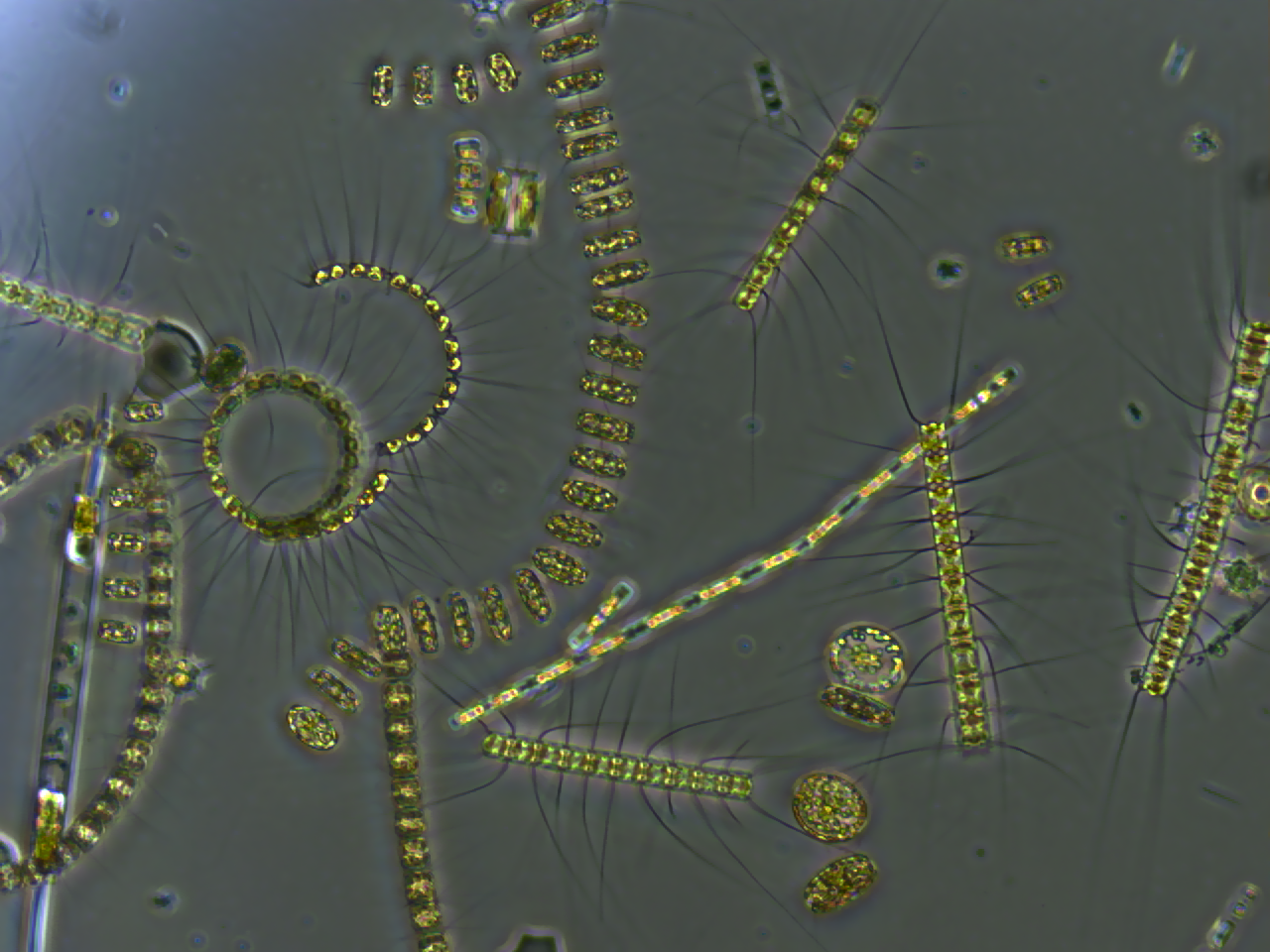
Algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) are any of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms. The name is an informal term for a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as '' Chlorella'', '' Prototheca'' and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to in length. Most are aquatic and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the '' Charophyta'', a division of green algae which includes, for example, '' Spirogyra'' and stoneworts. Algae that are carried by water are plankton, specifically phytoplankton. Algae constitute a polyphyletic group since they do not include a common ancestor, and although their plastids seem to have a single ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as do trees and other plants on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers ( euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half of the oxygen production, despi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planktonic Algae
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as do trees and other plants on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers ( euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half of the oxygen production, desp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. lotus). Aquaculture involves cultivating freshwater, brackish water and saltwater populations under controlled or semi-natural conditions, and can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is the harvesting of wild fish. Mariculture, commonly known as marine farming, refers specifically to aquaculture practiced in seawater habitats and lagoons, opposed to in freshwater aquaculture. Pisciculture is a type of aquaculture that consists of fish farming to obtain fish products as food. Aquaculture can also be defined as the breeding, growing, and harvesting of fish and other aquatic plants, also known as farming in water. It is an environmental source of food and commercial product which help to improve healthier habitats and used to reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algae Scrubber
An algae scrubber is a water filtering device (not to be confused with a scrubber pad used to clean glass) which uses light to grow algae; in this process, undesirable chemicals are removed from the water. Algae scrubbers allow saltwater, freshwater and pond hobbyists to operate their tanks using natural filtration in the form of primary production, much like oceans and lakes. Concepts An algae scrubber filters water by moving water rapidly over a rough, highly illuminated surface, which causes algae to start growing in large amounts. As the algae grow, they consume nutrients such as nitrate, phosphate, nitrite, ammonia, ammonium and even metals such as copper from the water. These nutrients are normally a problem in aquariums and ponds because they cause nuisance algae to grow, and also because they cause sickness and/or other problems in aquarium fish, invertebrates and corals. An algae scrubber allows algae to grow, but the algae grow inside the filter instead of in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustainable Food System
A sustainable food system is a type of food system that provides healthy food to people and creates sustainable environmental, economic and social systems that surround food. Sustainable food systems start with the development of sustainable agricultural practices, development of more sustainable food distribution systems, creation of sustainable diets and reduction of food waste throughout the system. Sustainable food systems have been argued to be central to many or all 17 Sustainable Development Goals. Moving to sustainable food systems, including via shifting consumption to sustainable diets, is an important component of addressing the causes of climate change and adapting to it. A 2020 review conducted for the European Union found that up to 37% of global greenhouse gas emissions could be attributed to the food system, including crop and livestock production, transportation, changing land use (including deforestation) and food loss and waste. Reduction of meat producti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algal Fuel
Algae fuel, algal biofuel, or algal oil is an alternative to liquid fossil fuels that uses algae as its source of energy-rich oils. Also, algae fuels are an alternative to commonly known biofuel sources, such as corn and sugarcane. When made from seaweed (macroalgae) it can be known as seaweed fuel or seaweed oil. It is also carbon negative unless the dead plant matter is burned, as the energy (stored as hydrogen gas) is produced by solar photosynthesis and comes from the sun. The emissions from burning the hydrogen make up only water and air. Several companies and government agencies are funding efforts to reduce capital and operating costs and make algae fuel production commercially viable. Like fossil fuel, algae fuel releases when burnt, but unlike fossil fuel, algae fuel and other biofuels only release recently removed from the atmosphere via photosynthesis as the algae or plant grew. The energy crisis and the world food crisis have ignited interest in algaculture (farmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of ''Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as kelps provide essential nursery habitat for fisheries and other marine species and thus protect food sources; other species, such as planktonic algae, play a vital role in capturing carbon, producing at least 50% of Earth's oxygen. Natural seaweed ecosystems are sometimes under threat from human activity. For example, mechanical dredging of kelp destroys the resource and dependent fisheries. Other forces also threaten some seaweed ecosystems; a wasting disease in predators of purple urchins has led to a urchin population surge which destroyed large kelp forest regions off the coast of California. Humans have a long history of cultivating seaweeds for their uses. In recent years, seaweed farming has become a global agricultural practice, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroalgae
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of ''Rhodophyta'' (red), ''Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as kelps provide essential nursery habitat for fisheries and other marine species and thus protect food sources; other species, such as planktonic algae, play a vital role in capturing carbon, producing at least 50% of Earth's oxygen. Natural seaweed ecosystems are sometimes under threat from human activity. For example, mechanical dredging of kelp destroys the resource and dependent fisheries. Other forces also threaten some seaweed ecosystems; a wasting disease in predators of purple urchins has led to a urchin population surge which destroyed large kelp forest regions off the coast of California. Humans have a long history of cultivating seaweeds for their uses. In recent years, seaweed farming has become a global agricultural practice, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerated Waters
Aerated water is, correctly speaking, water to which air is added. The term is, however, frequently applied to carbonated water. Purpose of aeration Sulfur compounds dissolved in water are not necessarily dangerous, but can give the water a bad taste or foul smell. These compounds can be removed in several ways, the most effective being by exposure to chlorine gas. However, aeration can also be effective if the amount of sulfur in the water is relatively low. During aeration, water is pumped into a non-pressurized tank and agitated. This physically removes many of the sulfur compounds, which are then vented. Exposure to oxygen in the air also oxidizes some of the compounds, creating atomic sulfur which can be filtered from the water. Aeration is also an effective means of removing radon from water. Small tanks and ponds for keeping aquatic animals such as fish or lobsters often rely on aeration to maintain sufficient level of oxygenation in the water. This can be achieved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. The larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments, but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for resources with the adult population. Animals in the larval stage will consume food to fuel their transition into the adult form. In some organisms like polychaetes and barnacles, adults are im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |