|
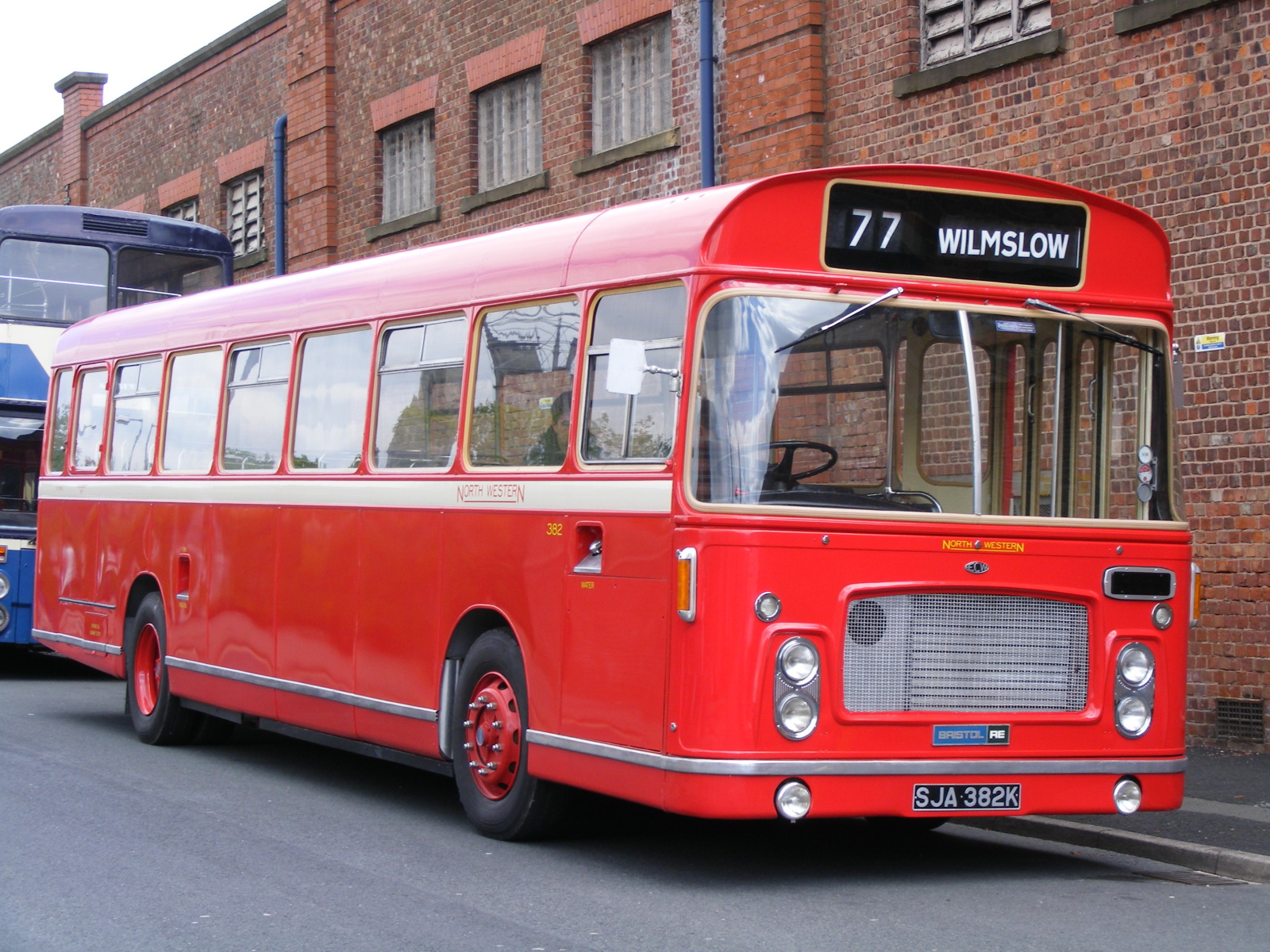
Alexander Y-type
The Alexander Y Type was a long-running design of single-decker bus and single-decker intercity bus bodywork built by Walter Alexander Coachbuilders in Falkirk Falkirk ( gd, An Eaglais Bhreac, sco, Fawkirk) is a large town in the Central Lowlands of Scotland, historically within the county of Stirlingshire. It lies in the Forth Valley, northwest of Edinburgh and northeast of Glasgow. Falkirk had a ..., Scotland. It was built on a wide range of chassis between 1962 and 1983. A small number were built at Alexander's Belfast subsidiary. From 1971 it became the AY Type (with the A signifying alloy construction) or AYS Type (with the S signifying service bus specification), although in common usage all are referred to simply as Y Type. Chassis The majority of Y Type bodies were fitted to Leyland Leopard chassis, and most were built for the Scottish Bus Group and its predecessors. Other customers As can be seen from the table above, SBG was by far the biggest custome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leyland Leopard
The Leyland Leopard was a mid-engined single-decker bus and single-decker coach chassis manufactured by Leyland between 1959 and 1982. History The Leyland Leopard was introduced in 1959. It was developed from the Leyland Tiger Cub, one of the most important changes being the introduction of the larger and more powerful O.600 engine (later-built Leopards were fitted with the 11.1-litre O.680 engine). The Leopard was superseded by the Leyland Tiger. Designation The original 30 ft bus version was coded L1, it was right hand drive with a 16 ft 2in wheelbase and an overall length of 29 ft 4in. The 30 ft coach was the L2 which had the same wheelbase but was an inch shorter overall, the left-hand-drive LHL1 shared the wheelbase but the overall length was 29 ft 2in. All had a swept turning circle of 68 ft. The initial 36 ft models launched at the 1961 Scottish Motor Show at Kelvin Hall all shared an 18 ft 6in wheelbase, the PSU3.1R PSU3.1L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volvo B58
The Volvo B58 was a mid-engined bus chassis manufactured by Volvo in Sweden from 1966 until early 1982. It was succeeded by the B10M. Operators In the United Kingdom, it was sold to many major operators including Wallace Arnold and Park's of Hamilton from 1972. Many of the Volvo B58s in the United Kingdom were built as coaches. One Volvo B58 was rebodied as a double-decker bus with East Lancs Droop Nose double-decker bus body for Skills Coaches. In 1978, Greater Stockholm Transport Authority ordered 250 B58s. Until November 2009, GO Wellington in New Zealand operated 68 Volvo B58 trolleybuses. In Brazil, The Volvo B58 (named the B58E) was built in Curitiba from 1979 to 1998. It was used in city buses, including trolleybuses, and road coaches, in cities like São Paulo, Curitiba, Porto Alegre, Campinas, Sorocaba and Belo Horizonte. Also, in 1992, B58E was Brazil's first bi-articulated chassis, and the first 33 operated in Curitiba as ''Express Line Buses''. In Australia the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercity Buses
InterCity (commonly abbreviated ''IC'' on timetables and tickets) is the classification applied to certain long-distance passenger train services in Europe. Such trains (in contrast to regional, local, or commuter trains) generally call at major stations only. An international variant of the InterCity trains are the EuroCity (EC) trains which consist of high-standard coaches and are run by a variety of operators. History The Inter-City Rapid Transit Company was an Ohio interurban company, which began operations in 1930 as it had purchased its route from the Northern Ohio Traction & Light Company. It remained in operation till 1940. The use of ''Inter-City'' was reborn in the United Kingdom: A daily train of that name was introduced in 1950, running between the cities of London and Birmingham. This usage can claim to be the origin of all later usages worldwide. In 1966 British Rail introduced the brand InterCity for all of its express train routes, and in 1986 the term w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buses Of The United Kingdom
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for charter purposes, or through private ownership. Although the average bus carries between 30 and 100 passengers, some buses have a capacity of up to 300 passengers. The most common type is the single-deck rigid bus, with double-decker and articulated buses carrying larger loads, and midibuses and minibuses carrying smaller loads. Coaches are used for longer-distance services. Many types of buses, such as city transit buses and inter-city coaches, charge a fare. Other types, such as elementary or secondary school buses or shuttle buses within a post-secondary education campus, are free. In many jurisdictions, bus drivers require a special large vehicle licence above and beyond a regular driving licence. Buses may be used for scheduled bus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Dennis Buses
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history. Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Aleksander and Aleksandr. Related names and diminutives include Iskandar, Alec, Alek, Alex, Alexandre, Aleks, Aleksa and Sander; feminine forms include Alexandra, Alexandria, and Sasha. Etymology The name ''Alexander'' originates from the (; 'defending men' or 'protector of men'). It is a compound of the verb (; 'to ward off, avert, defend') and the noun (, genitive: , ; meaning 'man'). It is an example of the widespread motif of Greek names expressing "battle-prowess", in this case the ability to withstand or push back an enemy battle line. The earliest attested form of the name, is the Mycenaean Greek feminine anthroponym , , (/Alexandra/), written in the Linear B syllabic script. Alaksandu, alternatively called ''Alakasandu'' or ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Potteries
First Potteries is a bus company based in Stoke-on-Trent operating services in North Staffordshire, England. It is a part of First Midlands and a subsidiary of FirstGroup. History The company began life as Potteries Motor Traction. As part of the privatisation of the National Bus Company, PMT Limited was created on 12 December 1986 when it was purchased by its management and employees. The team leading PMT's buyout were managing director Mike Moors, traffic manager Steve Ellis, chief engineer Barry Parkinson and company secretary Nigel Barrett. Expansion came quickly for PMT, and it had commenced operations outside its traditional North Staffordshire area a little over six weeks prior to purchase from NBC. On 25 October 1986, the day bus services in the UK were deregulated, a small outstation was established in the neighbouring town of Crewe. This was followed by a venture into Merseyside with the opening of a Red Rider outstation at Moreton on the Wirral Peninsula. A sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Western Road Car Company (1923)
The North Western Road Car Company was a bus company in Stockport, England, formed in 1923 from the existing bus services of the British Automobile Traction Company Limited (itself a subsidiary of the British Electric Traction Company Limited) in Macclesfield. The company operated bus services in five counties (Cheshire, Lancashire, West Riding of Yorkshire, Derbyshire and Staffordshire) through a combination of growth and the acquisition of other bus companies, such as the takeover in 1924 of the Mid-Cheshire Motor Bus Company Limited, which brought new operations in Northwich and Flixton. The company also operated express coach services to London, North Wales and Yorkshire. North Western had garages in: * Altrincham: Oakfield Street * Biddulph: Whalley Street * Buxton: Bridge Street *Castleton, Back Street open till at least 1967 * Glossop: York Street * Macclesfield: Sunderland Street * Manchester: Hulme Hall Road * Matlock: Bakewell Road * Northwich: Chester Way * Oldham: C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Bus Group
The Scottish Bus Group (SBG) was a state-owned group of bus operators covering the whole of mainland Scotland. The origin of the grouping was the operators owned by and including the Scottish Motor Traction company, which were transferred to Scottish Omnibuses after nationalisation in 1948 under control of the British Transport Commission. Highland Omnibuses was added to the group in 1952. A new holding company, Scottish Omnibuses Group (Holdings) was formed in 1961, and this was renamed Scottish Bus GroupCompanies House extract company no SC13181 Scottish Bus Group Limited in 1963. Meanwhile, the group had come under control of the |
Belfast
Belfast ( , ; from ga, Béal Feirste , meaning 'mouth of the sand-bank ford') is the capital and largest city of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan on the east coast. It is the 12th-largest city in the United Kingdom and the second-largest in Ireland. It had a population of 345,418 . By the early 19th century, Belfast was a major port. It played an important role in the Industrial Revolution in Ireland, briefly becoming the biggest linen-producer in the world, earning it the nickname "Linenopolis". By the time it was granted city status in 1888, it was a major centre of Irish linen production, tobacco-processing and rope-making. Shipbuilding was also a key industry; the Harland and Wolff shipyard, which built the , was the world's largest shipyard. Industrialisation, and the resulting inward migration, made Belfast one of Ireland's biggest cities. Following the partition of Ireland in 1921, Belfast became the seat of government for Northern Ireland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coachwork
A coachbuilder or body-maker is someone who manufactures bodies for passenger-carrying vehicles.Construction has always been a skilled trade requiring a relatively lightweight product with sufficient strength. The manufacture of necessarily fragile, but satisfactory wheels by a separate trade, a wheelwright, held together by iron or steel tyres, was always most critical. From about AD 1000 rough vehicle construction was carried out by a ''wainwright'', a wagon-builder. Later names include ''cartwright'' (a carpenter who makes carts, from 1587); ''coachwright''; and ''coachmaker'' (from 1599). Subtrades include ''wheelwright'', ''coachjoiner'', etc. The word ''coachbuilder'' first appeared in 1794. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' 2011 Coachwork is the body of an automobile, bus, horse-drawn carriage, or railway carriage. The word "coach" was derived from the Hungarian town of Kocs. Coachbuilt body is the British English name for the coachbuilder's product. ''Custom body'' is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coach (bus)
A coach (or coach bus/motorcoach) is a type of bus built for longer-distance service, in contrast to transit buses that are typically used within a single metropolitan region. Often used for touring, intercity, and international bus service, coaches are also used for private charter for various purposes. Coaches are also related and fall under a specific category/type of RVs. Deriving the name from horse-drawn carriages and stagecoaches that carried passengers, luggage, and mail, modern motor coaches are almost always high-floor buses, with separate luggage hold mounted below the passenger compartment. In contrast to transit buses, motor coaches typically feature forward-facing seating, with no provision for standing. Other accommodations may include onboard restrooms, televisions, and overhead luggage space. History Background Horse-drawn chariots and carriages ("coaches") were used by the wealthy and powerful where the roads were of a high enough standard from p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_31_March_1989_(2).jpg)


.png)

