|
Alexander Gusev (scientist)
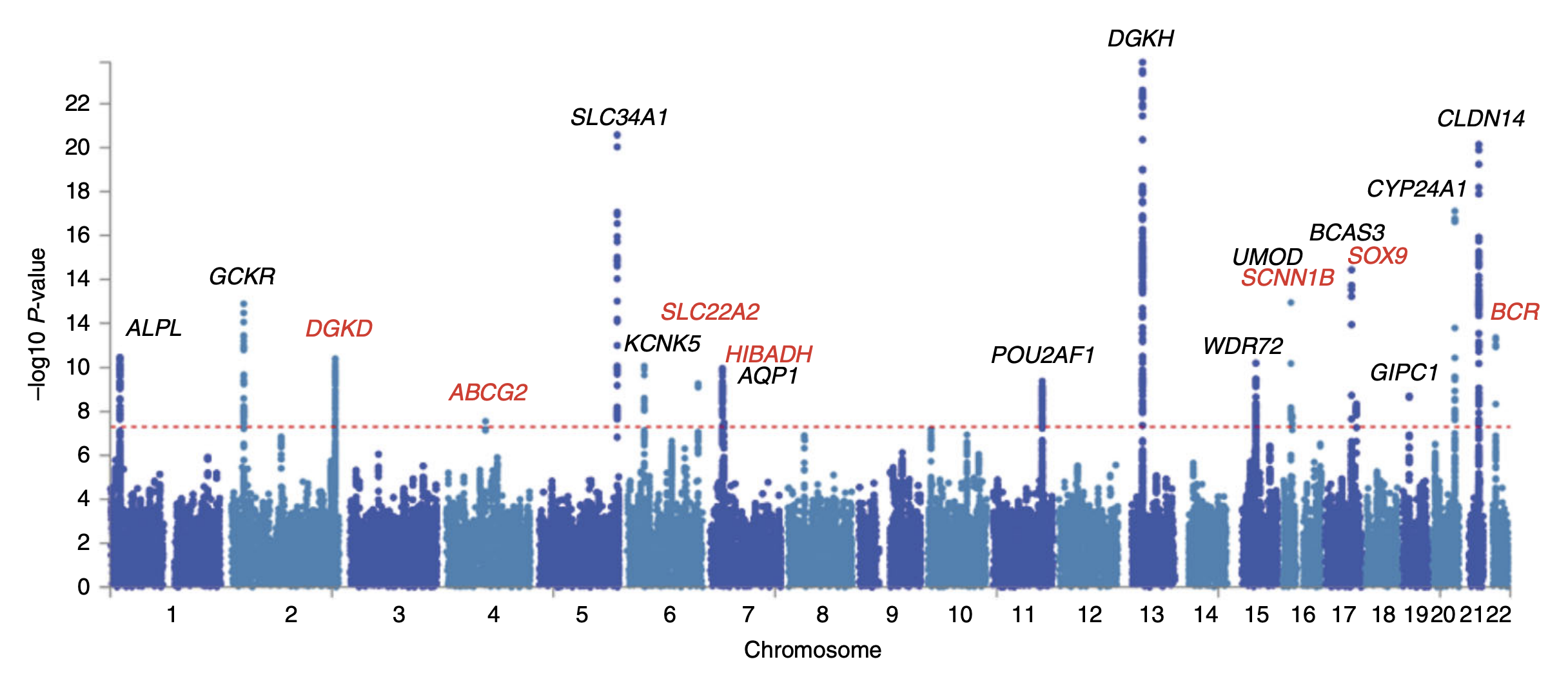
Alexander (Sasha) Gusev is a computational biologist and an Assistant Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School. Research and career Alexander Gusev has developed computational methods that use genetic data to decipher disease mechanisms. For example, he has identified 34 new genes associated with increased risk of earliest-stage ovarian cancer. He has developed computational methods that integrate molecular data to facilitate functional interpretation of findings from genome-wide association studies. He has contributed to the development of the transcriptome-wide association study approach to mapping disease-associated genes. In addition, he studies the interactions between germline In biology and genetics, the germline is the population of a multicellular organism's cells that pass on their genetic material to the progeny (offspring). In other words, they are the cells that form the egg, sperm and the fertilised egg. They ... (host) and somatic events (tumor) - which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Genetics
Statistical genetics is a scientific field concerned with the development and application of statistical methods for drawing inferences from genetic data. The term is most commonly used in the context of human genetics. Research in statistical genetics generally involves developing theory or methodology to support research in one of three related areas: *population genetics - Study of evolutionary processes affecting genetic variation between organisms *genetic epidemiology - Studying effects of genes on diseases *quantitative genetics - Studying the effects of genes on 'normal' phenotypes Statistical geneticists tend to collaborate closely with geneticists, molecular biologists, clinicians and bioinformaticians. Statistical genetics is a type of computational biology Computational biology refers to the use of data analysis, mathematical modeling and computational simulations to understand biological systems and relationships. An intersection of computer science, biology, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germline
In biology and genetics, the germline is the population of a multicellular organism's cells that pass on their genetic material to the progeny (offspring). In other words, they are the cells that form the egg, sperm and the fertilised egg. They are usually differentiated to perform this function and segregated in a specific place away from other bodily cells. As a rule, this passing-on happens via a process of sexual reproduction; typically it is a process that includes systematic changes to the genetic material, changes that arise during recombination, meiosis and fertilization for example. However, there are many exceptions across multicellular organisms, including processes and concepts such as various forms of apomixis, autogamy, automixis, cloning or parthenogenesis. The cells of the germline are called germ cells. For example, gametes such as a sperm and an egg are germ cells. So are the cells that divide to produce gametes, called gametocytes, the cells that produce thos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard Medical School People
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and one of the most prestigious and highly ranked universities in the world. The university is composed of ten academic faculties plus Harvard Radcliffe Institute. The Faculty of Arts and Sciences offers study in a wide range of undergraduate and graduate academic disciplines, and other faculties offer only graduate degrees, including professional degrees. Harvard has three main campuses: the Cambridge campus centered on Harvard Yard; an adjoining campus immediately across Charles River in the Allston neighborhood of Boston; and the medical campus in Boston's Longwood Medical Area. Harvard's endowment is valued at $50.9 billion, making it the wealthiest academic institution in the world. Endowment inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia University Alumni
Columbia may refer to: * Columbia (personification), the historical female national personification of the United States, and a poetic name for America Places North America Natural features * Columbia Plateau, a geologic and geographic region in the U.S. Pacific Northwest * Columbia River, in Canada and the United States ** Columbia Bar, a sandbar in the estuary of the Columbia River ** Columbia Country, the region of British Columbia encompassing the northern portion of that river's upper reaches ***Columbia Valley, a region within the Columbia Country ** Columbia Lake, a lake at the head of the Columbia River *** Columbia Wetlands, a protected area near Columbia Lake ** Columbia Slough, along the Columbia watercourse near Portland, Oregon * Glacial Lake Columbia, a proglacial lake in Washington state * Columbia Icefield, in the Canadian Rockies * Columbia Island (District of Columbia), in the Potomac River * Columbia Island (New York), in Long Island Sound Populated places * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Geneticists
Statistics (from German: ''Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample to the population as a whole. An experim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geneticists
A geneticist is a biologist or physician who studies genetics, the science of genes, heredity, and variation of organisms. A geneticist can be employed as a scientist or a lecturer. Geneticists may perform general research on genetic processes or develop genetic technologies to aid in the pharmaceutical or and agriculture industries. Some geneticists perform experiments in model organisms such as ''Drosophila'', ''C. elegans'', zebrafish, rodents or humans and analyze data to interpret the inheritance of biological traits. A basic science geneticist is a scientist who usually has earned a PhD in genetics and undertakes research and/or lectures in the field. A medical geneticist is a physician who has been trained in medical genetics as a specialization and evaluates, diagnoses, and manages patients with hereditary conditions or congenital malformations; and provides genetic risk calculations and mutation analysis. Education Geneticists participate in courses from many are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precision Medicine
Precision, precise or precisely may refer to: Science, and technology, and mathematics Mathematics and computing (general) * Accuracy and precision, measurement deviation from true value and its scatter * Significant figures, the number of digits that carry real information about a measurement * Precision and recall, in information retrieval: the proportion of relevant documents returned * Precision (computer science), a measure of the detail in which a quantity is expressed * Precision (statistics), a model parameter or a quantification of precision Computing products * Dell Precision, a line of Dell workstations * Precision Architecture, former name for PA-RISC, a reduced instruction set architecture developed by Hewlett-Packard * Ubuntu 12.04 "Precise Pangolin", Canonical's sixteenth release of Ubuntu Companies * Precision Air, an airline based in Tanzania * Precision Castparts Corp., a casting company based in Portland, Oregon, in the United States * Precision Drilling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatic Mutation
A somatic mutation is a change in the DNA sequence of a somatic cell of a multicellular organism with dedicated reproductive cells; that is, any mutation that occurs in a cell other than a gamete, germ cell, or gametocyte. Unlike germline mutations, which can be passed on to the descendants of an organism, somatic mutations are not usually transmitted to descendants. This distinction is blurred in plants, which lack a dedicated germline, and in those animals that can reproduce asexually through mechanisms such as budding, as in members of the cnidarian genus ''Hydra''. While somatic mutations are not passed down to an organism's offspring, somatic mutations will be present in all descendants of a cell within the same organism. Many cancers are the result of accumulated somatic mutations. Fraction of cells affected The term somatic generally refers to the cells of the body, in contrast to the reproductive (germline) cells, which give rise to the egg or sperm. For example, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcriptome-wide Association Study
Transcriptome-wide association study (TWAS) is a statistical genetics methodology to improve detection power and provide functional annotation for genetic associations with phenotypes by integrating single-nucleotide polymorphism to trait (SNP-trait) associations from genome-wide association studies with SNP-based prediction models of gene expression. The approach was presented by Eric R. Gamazon et al. and Alexander Gusev et al. in the journal ''Nature Genetics''. This methodology has been widely adopted, having received 2057 citations (as of December 24, 2021) according to Google Scholar. See also * Genome-wide association study * Functional genomics * Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project * Epigenome-wide association study An epigenome-wide association study (EWAS) is an examination of a genome-wide set of quantifiable epigenetic marks, such as DNA methylation, in different individuals to derive associations between epigenetic variation and a particular identifiable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncogenomics
Oncogenomics is a sub-field of genomics that characterizes cancer-associated genes. It focuses on genomic, epigenomic and transcript alterations in cancer. Cancer is a genetic disease caused by accumulation of DNA mutations and epigenetic alterations leading to unrestrained cell proliferation and neoplasm formation. The goal of oncogenomics is to identify new oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes that may provide new insights into cancer diagnosis, predicting clinical outcome of cancers and new targets for cancer therapies. The success of targeted cancer therapies such as Gleevec, Herceptin and Avastin raised the hope for oncogenomics to elucidate new targets for cancer treatment. Besides understanding the underlying genetic mechanisms that initiate or drive cancer progression, oncogenomics targets personalized cancer treatment. Cancer develops due to DNA mutations and epigenetic alterations that accumulate randomly. Identifying and targeting the mutations in an individual patien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome-wide Association Study
In genomics, a genome-wide association study (GWA study, or GWAS), also known as whole genome association study (WGA study, or WGAS), is an observational study of a genome-wide set of Single-nucleotide polymorphism, genetic variants in different individuals to see if any variant is associated with a trait. GWA studies typically focus on associations between single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and traits like major human diseases, but can equally be applied to any other genetic variants and any other organisms. When applied to human data, GWA studies compare the DNA of participants having varying phenotypes for a particular trait or disease. These participants may be people with a disease (cases) and similar people without the disease (controls), or they may be people with different phenotypes for a particular trait, for example blood pressure. This approach is known as phenotype-first, in which the participants are classified first by their clinical manifestation(s), as oppose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itsik Pe'er
Itsik Pe'er is a computational biologist and a Full Professor in the Department of Computer Science at Columbia University. Research and career Pe'er has created computational tools for the analysis of high-throughput DNA sequence data. In particular, he has developed an approach to map copy number variation from whole exome sequencing data. He has published approaches to quantify hidden relatedness and infer population structure using DNA data. He has conducted studies on the genetics of complex traits in Ashkenazi Jews, historically a relatively isolated population enabling identification of genetic risk factors for common disorders in all populations. He is generating a comprehensive resource of genetic variants in the population for precision public health. Selected publications * Estimation of the multiple testing burden for genomewide association studies of nearly all common variants. I Pe'er, R Yelensky, D Altshuler, MJ Daly ''Genetic Epidemiology''. 32(4):381-5. doi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |