|
Aleutian Arc
The Aleutian Arc is a large volcanic arc in the U.S. state of Alaska. It consists of a number of active and dormant volcanoes that have formed as a result of subduction along the Aleutian Trench. Although taking its name from the Aleutian Islands, this term is a geologic grouping rather than a geographic one, and the Aleutian Arc extends through the Alaska Peninsula following the Aleutian Range to the Aleutian Islands. The Aleutian Arc reflects subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the North American Plate. It extends from the Kamchatka Peninsula in the west to the Gulf of Alaska in the east. Unimak Pass at the southwestern end of the Alaska Peninsula marks the eastward transition from an intra-oceanic in the west to a continental arc in the east. Due to the arcuate geometry of the trench, the relative velocity vector changes from almost trench-normal in the Gulf of Alaska to almost trench-parallel in the west. Along the oceanic part of the subduction zone, convergence varie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of Alaska Volcanoes Cleveland
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Aniakchak
Mount Aniakchak (russian: Аниакчак) is a 3,700-year-old volcanic caldera approximately in diameter, located in the Aleutian Range of Alaska, United States. Although a stratovolcano by composition, the pre-existing mountain collapsed in a major eruption forming the caldera. The area around the volcano is the Aniakchak National Monument and Preserve, maintained by the National Park Service. In November 1967, Aniakchak Caldera was designated as a National Natural Landmark by the National Park Service. Geological history Mount Aniakchak was previously a glacially eroded stratovolcano of andesitic composition, with a pre-caldera volume of . Andesitic material in the volcano included basalt and dacite. The mountain collapsed, forming the present day caldera, during a major eruption of VEI=6, which left evidence in ice cores dated to 1645 BC. which was later moved to 1641 BC in the Greenland Ice Core Chronology 2005 (GICC05) time scale. Recently, McAneney and Baillie have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Dutton
Mount Dutton is a stratovolcano in the Aleutian Range of the U.S. state of Alaska, on the Alaska Peninsula. Geography Dutton lies just short of from King Cove, a fishing headquarters for the locality. Geologic activity Dutton is a highly glaciated volcano. Its summit is composed of a series of lava domes which form a complex stratovolcano. The mountain's recent history is marked by at least avalanche which removed andesitic lava flows and several lava domes from the flank of its body and swiftly cascaded westward and southward towards Belkofski Bay. Between 1984 and 1985, a series of earthquake swarms took place in the volcano's vicinity. Another swarm took place in the summer of 1988. See also *List of volcanoes in the United States A list of volcanoes in the United States and its territories. Alaska American Samoa Arizona California Colorado Hawaii /[./[Https://www.sci.news/geology/puhahonu-shield-volcano-08435.html Puhahonu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Douglas (Alaska)
Mount Douglas is a stratovolcano located south of Kamishak Bay, near the northeasternmost part of the Alaska Peninsula. It lies in the Katmai National Park and Preserve in Kenai Peninsula Borough. The mountain was officially named in 1906 after nearby Cape Douglas based on a 1904 report by USGS geologist G. C. Martin. The Alaska Volcano Observatory currently rates Douglas as Level of Concern Color Code Not Assigned. The volcano has a warm and highly acidic crater lake approximately 160 m (525 ft) wide. In 1982, the lake had a temperature of 21 °C and a pH of 1, and temperatures of 114-118°C were measured in 1991. At the north flank of the volcano unglaciated and relatively uneroded lava flows are found. The last eruption is not known, but probably occurred during the Holocene. __TOC__ See also *List of mountain peaks of North America **List of mountain peaks of the United States ***List of mountain peaks of Alaska *List of Ultras of the United States *List o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devils Desk
Devils Desk is a stratovolcano in Alaska's Katmai National Park, split between the Kodiak Island and Lake and Peninsula boroughs of that U.S. state. Its peak, which is located in Kodiak Island Borough, lies above sea level. It has an elevation of . The age of the volcano is not certain, but a sample from the southwest face of the volcano was dated at 245,000 years old. The edifice represents the neck of a formerly larger stratovolcano, whose flanks have been removed by glacial erosion. The summit is almost encircled by Hook Glacier. See also *List of volcanoes in the United States of America A list of volcanoes in the United States and its territories. Alaska American Samoa Arizona California Colorado Hawaii /[./[Https://www.sci.news/geology/puhahonu-shield-volcano-08435.html Puhahonu ... References External links Devils Desk at the Alaska Volcano Observatory Volcanoes of Kodiak Island Borough, Alaska Volcanoes of Lake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Denison
Mount Denison is a stratovolcano and one of the highest peaks on the Alaska Peninsula. Discovered in 1923 by Harvard professor Kirtley Fletcher Mather, the mountain was named for the geologist's alma mater, Denison University. The mountain's connection to Denison also include its first climbers: all members of the first two ascent teams as well as the group that attempted in 1977 were either students, alumni, or faculty of the university. Mount Denison is located at the end of a volcanic chain in a heavily glaciated and very remote section of Katmai National Park. It is possibly the tallest mountain in the national park, though some sources list Mount Griggs as the highest. Mount Griggs, on the other hand, is much more accessible, being next to the Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes, which can be reached via the road from the national park's visitor center. There is no record of an eruption, but Mount Denison was probably active some time in the last 10,000 years (the Holocene epoch) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Davidof Volcano
Davidof Volcano is a potentially active stratovolcano and caldera remnant in the Aleutian Islands of Alaska, USA, from Anchorage. Located on the eponymous island, Davidof is part of the Rat Islands sub-chain. It is also part of the "Aleutian Krakatau", a group of four islands formed when a stratovolcano caved in during the late Cenozoic. In December 2021, an earthquake swarm was detected on the island, causing the Alaska Volcano Observatory to raise the volcano's alert level to Yellow. Another earthquake swarm, possibly a continuation of the first, was detected in late January 2022. Accessibility Since the island is uninhabited, very little transportation is available. Transport can be found in Adak, albeit that the town is Wood and Kienle, page 20. from the island. Geography and geology Because of the inclusion of Alaska, the United States has the largest number of active volcanoes in the world, many of them geologically young. In Alaska, at least 50 volcanoes, includin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Dana (Alaska)
Mount Dana is a small stratovolcano of the Alaska Peninsula, United States, located northeast of Canoe Bay inlet at the head of Pavlof Bay. It was the source for a major eruption about 3840 years ago that produced a pyroclastic flow that filled valleys south and west of the volcano's crater and reached the sea at Canoe Bay. Geography and geology Dana is northeast of the Canoe Bay inlet, as it sits at the top of Pavlof Bay. It is from Anchorage. The United States has the most active volcanoes in the world, many of them geologically young. In Alaska, at least 50 volcanoes, including those in the Aleutian archipelago, have erupted in historical time. The state accounts for ~80% of the United States' volcanoes, excluding the seamounts in the area, ~8% of world volcanoes, and most of these are located among the Aleutian Islands. The Aleutian Islands arc serves as the northern boundary of the Pacific Ring of Fire, where tectonic activity generates earthquakes and volcanic eruptions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Bay Volcano
Frosty Peak Volcano, also known as Mt. Frosty, Frosty Volcano, or Cold Bay Volcano, is a 6,299 ft (1,920 m) stratovolcano at the southwest end of the Alaska Peninsula in the U.S. state of Alaska. History Frosty Peak is the tallest and most recently formed peak of the volcanic complex. Its exact age is unknown, but it was probably formed in the middle to late Pleistocene, and possibly erupted even more recently. Frosty Peak is the southern cone of the double-coned Frosty Volcano, which formed in the middle Pleistocene some time before the Wisconsin Glaciation. Frosty Volcano itself is located on the northern flank of an even older volcano, the Morzhovoi Volcano. Morzhovoi Volcano was probably formed in the early to middle Pleistocene, and collapsed into a caldera. The highest points that remain from the caldera are called North and South Walrus Peak. See also *List of volcanoes in the United States of America *List_of_stratovolcanoes.html" "title="/[Https://ww ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
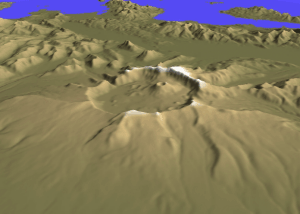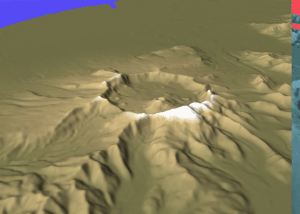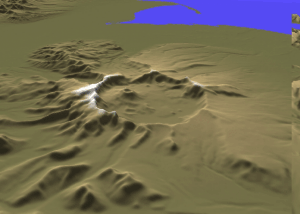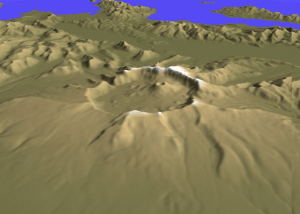
Cleveland Volcano (Alaska)
Mount Cleveland (also known as Cleveland Volcano) is a nearly symmetrical stratovolcano on the western end of Chuginadak Island, which is part of the Islands of Four Mountains just west of Umnak Island in the Fox Islands of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. Mt. Cleveland is high, and one of the most active of the 75 or more volcanoes in the larger Aleutian Arc. Aleutian natives named the island after their fire goddess, Chuginadak, who they believed inhabited the volcano. In 1894 a team from the U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey visited the island and gave Mount Cleveland its current name, after then-president Grover Cleveland. One of the most active volcanoes in the Aleutian Arc, Cleveland has erupted at least 22 times in the last 230 years. A VEI 3 eruption in 1944 produced the arc's only known volcanic fatality. Most recently Mount Cleveland has erupted three times in 2009, twice in 2010, once in 2011 and in 2016 and 2017. The volcano's remoteness limits opportunities f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Chiginagak
Chiginagak Volcano is a stratovolcano on the Alaska Peninsula, located about 15 km NW of Chiginagak Bay. Eruptive history An unglaciated lava flow and an overlying pyroclastic-flow deposit extending east from the summit are the most recent products of Chiginagak. They most likely originated from a lava dome at 1687m on the SE flank, 1 km from the summit of the volcano. Brief ash eruptions were reported in July 1971 and August 1998. Fumarolic activity occurs at 1600m elevation on the NE flank of the volcano, and two areas of hot-spring travertine deposition are located at the NW base of the volcano near Volcano Creek. A wide and deep acidified summit crater lake at Chiginagak formed after November 2004 and before May 2005. In early May 2005, a catastrophic release of acidic water from the lake, with an accompanying acidic aerosol component, drained and flooded indecision and volcano creeks with acidic water, traveled 27 km downstream and flowed into the Mother Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Carlisle
Mount Carlisle is a stratovolcano in Alaska which forms part of the 5 mile (8 km) wide Carlisle Island, one of the Islands of Four Mountains which, in turn, form part of the central Aleutian Islands. Despite its modest summit elevation, a small glacier exists high on the western slopes just below the rim of the summit crater. A few historical eruptions of Carlisle have been recorded, but its proximity to several other neighboring volcanoes means that there has been some confusion in the older records as to which of the volcanoes was erupting. As the area is extremely remote, distant observations of volcanic plumes cannot be verified for certain. __TOC__ See also *List of mountain peaks of North America **List of mountain peaks of the United States ***List of mountain peaks of Alaska *List of Ultras of the United States *List of volcanoes in the United States A list of volcanoes in the United States and its territories. Alaska American Samoa Arizona Californ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)