|
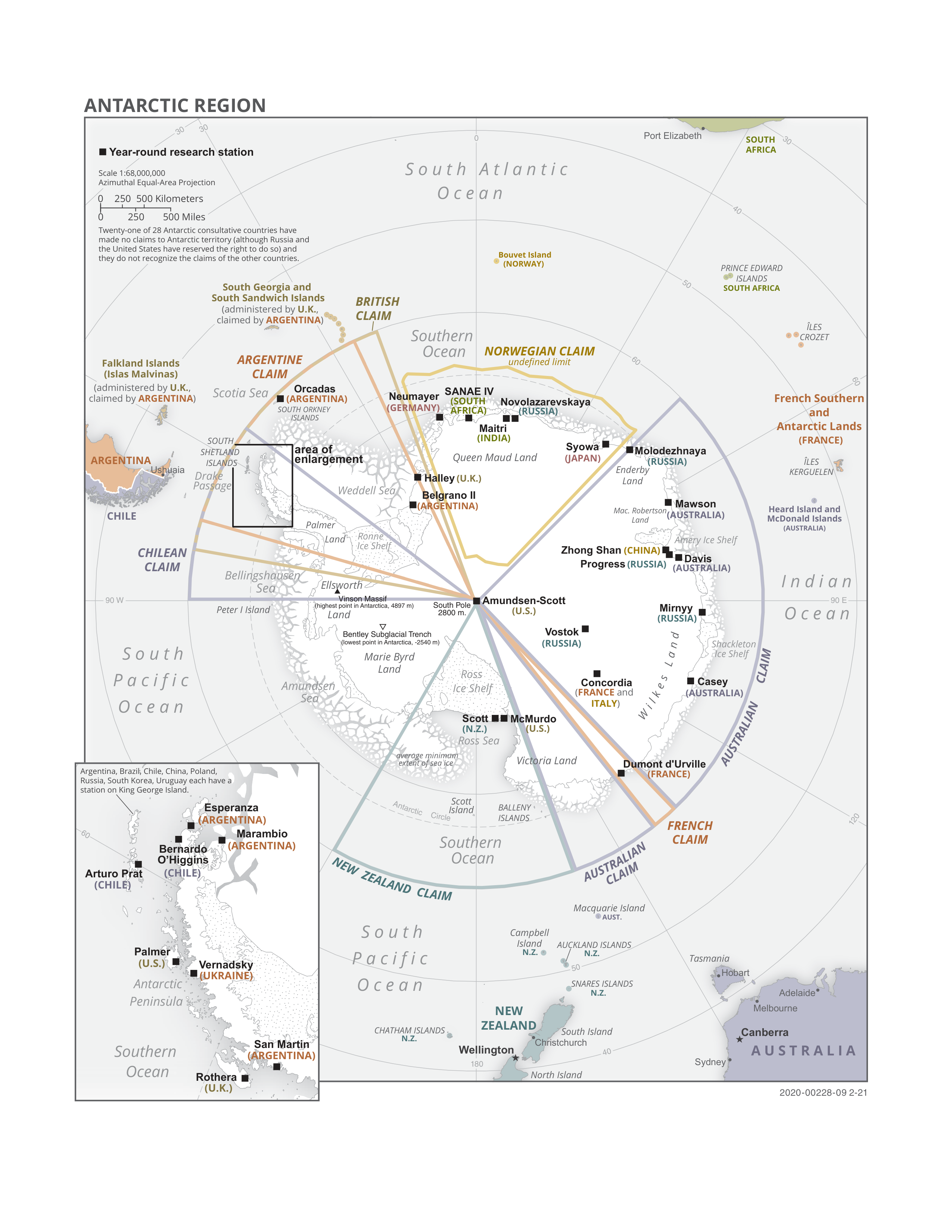
Aldea Island
Aldea Island is the central of the three Bugge Islands, off Wordie Ice Shelf, Fallières Coast, Antarctic Peninsula. The island was named ''Isla Aldea'' by the Chilean Antarctic Expedition, 1947, probably after Sargento Juan de Dios Aldea, of the Chilean Navy, one of the heroes of the naval battle of Iquique, May 21, 1879. See also * Composite Antarctic Gazetteer * List of Antarctic islands south of 60° S * SCAR * Territorial claims in Antarctica Seven sovereign states – Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the United Kingdom – have made eight territorial claims in Antarctica. These countries have tended to place their Antarctic scientific observation and st ... References * Islands of Graham Land Fallières Coast {{FallieresCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bugge Islands
The Bugge Islands are a small group of ice-covered islands lying close off the front of Wordie Ice Shelf and between northwest of Mount Guernsey, off the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. They were first seen from the air and photographed by the British Graham Land Expedition in 1936, and later roughly mapped from the photographs. They were observed in 1947 from the ''Port of Beaumont, Texas'' by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE) under Finn Ronne, who named these islands for his niece, Ruth Bugge, who supplied woolen clothing from Norway for the RARE. The group was also visited by the Chilean Antarctic Expedition, 1947, which named the islands ''Isla Aldea'', ''Isla Eleuterio Ramírez'', ''Isla Latorre'', after heroes of the naval battle of Iquique. From North to South the islands of the group are: *Ramírez Island *Aldea Island Aldea Island is the central of the three Bugge Islands, off Wordie Ice Shelf, Fallières Coast, Antarctic Peninsula. The is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Treaty System
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico , name = Antarctic Treaty System , image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder , image_width = 180px , caption = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty System , type = Condominium , date_drafted = , date_signed = December 1, 1959"Antarctic Treaty" in ''The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 439. , location_signed = Washington, D.C., United States , date_sealed = , date_effective = June 23, 1961 , condition_effective = Ratification of all 12 signatories , date_expiration = , signatories = 12 , parties = 55 , depositor = Federal government of the United States , languages = English, French, Russian, and Spanish , wikisource = Antarctic Treaty The Antarctic Treaty an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wordie Ice Shelf
The Wordie Ice Shelf () was a confluent glacier projecting as an ice shelf into the SE part of Marguerite Bay between Cape Berteaux and Mount Edgell, along the western coast of Antarctic Peninsula. In March 2008, the British Antarctic Survey reported that it appeared ready to break away from the Antarctic Peninsula. By April 2009 it had done so, vanishing completely. Discovered by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill, 1934–37, who named this feature for Sir James Wordie, Honorary Secretary (later President) of the Royal Geographical Society, member of the Discovery Committee, and chairman of the Scott Polar Research Institute. He also had been geologist and Chief of the Scientific Staff of the British expedition, 1914–16, under Ernest Shackleton. See also * List of Antarctic ice shelves This is a list of Antarctic ice shelves. Ice shelves are attached to a large portion of the Antarctic coastline. Their total area is 1,541,700 km2. Names are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fallières Coast
The Fallières Coast is that portion of the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula between the head of Bourgeois Fjord and Cape Jeremy and lies on Marguerite Bay and the Wordie Ice Shelf. On the south it is joined by Rymill Coast, and in the north by Loubet Coast. Fallières Coast was first explored in January 1909 by the French Antarctic Expedition under J.B. Charcot, who named it for Armand Fallières, then President of France The president of France, officially the president of the French Republic (french: Président de la République française), is the executive head of state of France, and the commander-in-chief of the French Armed Forces. As the presidency i .... References Coasts of Graham Land {{FallièresCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Peninsula
The Antarctic Peninsula, known as O'Higgins Land in Chile and Tierra de San Martín in Argentina, and originally as Graham Land in the United Kingdom and the Palmer Peninsula in the United States, is the northernmost part of mainland Antarctica. The Antarctic Peninsula is part of the larger peninsula of West Antarctica, protruding from a line between Cape Adams (Weddell Sea) and a point on the mainland south of the Eklund Islands. Beneath the ice sheet that covers it, the Antarctic Peninsula consists of a string of bedrock islands; these are separated by deep channels whose bottoms lie at depths considerably below current sea level. They are joined by a grounded ice sheet. Tierra del Fuego, the southernmost tip of South America, is about away across the Drake Passage. The Antarctic Peninsula is in area and 80% ice-covered. The marine ecosystem around the western continental shelf of the Antarctic Peninsula (WAP) has been subjected to rapid climate change. Over the past 50 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges delta are called chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental and oceanic. There are also artificial islands, which are man-made. Etymology The word ''island'' derives from Middle English ''iland'', from Old English ''igland'' (from ''ig'' or ''ieg'', similarly meaning 'island' when used independently, and -land carrying its contemporary meaning; cf. Dutch ''eiland'' ("island"), German ''Eiland'' ("small island")). However, the spelling of the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilean Antarctic Expedition
The First Chilean Antarctic Expedition (1947–1948) was an expedition to Antarctica mounted by the Chilean government and military to enforce its territorial claims against British challenges, namely Operation Tabarin. Among other accomplishments the expedition established Base General Bernardo O'Higgins Riquelme on February 18, 1948. Chilean President Gabriel González Videla personally inaugurated the base, thereby becoming the first head of state to set foot on the continent. The inactive research station González Videla Antarctic Base is named in his honor. The O'Higgins Base is still operated by the Chilean Army The Chilean Army ( es, Ejército de Chile) is the land arm of the Military of Chile. This 80,000-person army (9,200 of which are conscripts) is organized into six divisions, a special operations brigade and an air brigade. In recent years, and ..., one of the Antarctic bases with the longest times of continuous operation. The expedition was led by Commodore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juan De Dios Aldea
Juan de Dios Aldea (1853–1879) was a Chilean marine. His remains rest in the crypt of the Monument to the Heroes of the Battle of Iquique, in Valparaíso. Early life He was born to a modest family. He was the son of professor Jose Manuel Aldea and Ursula Fonseca. His childhood was spent in Santiago with his paternal grandparents, Juan de Dios Aldea and Maria Antonieta Contreras. At the age of 8, he enrolled in the Franciscan School of Chillán, directed by his father. Here he distinguished himself with his excellent handwriting and his evident interest for military exercises. Career After living for four years with his aunt, on August 1, 1872, he enrolled as a volunteer soldier in the Financial Commission sent by the Navy's Artillery Battalion; an organization located in Valparaiso which was dependent on the General Command of the Chilean Navy. In this battalion, he also served as a chief. He stayed in the First Company of that battalion for two years. In April 187 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilean Navy
The Chilean Navy ( es, Armada de Chile) is the naval warfare service branch of the Chilean Armed Forces. It is under the Ministry of National Defense. Its headquarters are at Edificio Armada de Chile, Valparaiso. History Origins and the Wars of Independence (1817–1830) The origins of the Chilean Navy date back to 1817, when General Bernardo O'Higgins prophetically declared after the Chilean victory at the Battle of Chacabuco that a hundred such victories would count for nothing if Chile did not gain control of the sea. This led to the development of the Chilean Navy, and the first legal resolutions outlining the organization of the institution were created. Chile's First National Fleet and the Academy for Young Midshipmen, which was the predecessor of the current Naval Academy, were founded, as well as the Marine Corps and the Supply Commissary. The first commander of the Chilean Navy was Manuel Blanco Encalada. Famous British naval commander Lord Cochrane, who former ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Iquique
The Battle of Iquique was a naval engagement that occurred between a Chilean corvette under the command of Arturo Prat Chacón and a Peruvian ironclad under Miguel Grau Seminario on 21 May 1879, during the naval stage of the War of the Pacific, that pitted Chile against Peru and Bolivia. The battle took place off the then-Peruvian port of Iquique. The ironclad sank the Chilean wooden corvette , after four hours of combat, resulting in a Peruvian victory. Background The Bolivian government had threatened to confiscate and to sell the Antofagasta Nitrate & Railway Company, a mining enterprise with Chilean and British investors, by a decree on 1 February 1879. In response, the Chilean government sent a small military force which disembarked and seized control of the port of Antofagasta on 14 February. This event made Bolivian President Hilarión Daza declare war on Chile, and also forced Peru to honor a secret 1873 treaty with Bolivia. Although Peru tried to negotiate and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Composite Antarctic Gazetteer
The Composite Gazetteer of Antarctica (CGA) of the Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) is the authoritative international gazetteer containing all Antarctic toponyms published in national gazetteers, plus basic information about those names and the relevant geographical features. The Gazetteer includes also parts of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) General Bathymetric Chart of the Oceans (GEBCO) gazetteer for under-sea features situated south of 60° south latitude. , the overall content of the CGA amounts to 37,893 geographic names for 19,803 features including some 500 features with two or more entirely different names, contributed by the following sources: {, class="wikitable sortable" ! Country ! Names , - , United States , 13,192 , - , United Kingdom , 5,040 , - , Russia , 4,808 , - , New Zealand , 2,597 , - , Australia , 2,551 , - , Argentina , 2,545 , - , Chile , 1,866 , - , Norway , 1,706 , - , Bulgaria , 1,450 , - , G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |