|
Albert II, Duke Of Brunswick-Grubenhagen
Albert II, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg (german: Albrecht II., Herzog zu Braunschweig-Lüneburg; 1 November 1419 – 15 August 1485), was a Prince of Grubenhagen; he reigned from 1440 until his death in 1485. Albert II was the third son of Duke Eric I and Elizabeth of Brunswick-Göttingen, a daughter of Otto the Bad, Duke of Brunswick-Göttingen. He was a grandson of the Duke Albert I, was still a minor when his father died on 27 May 1427. His first cousin once removed, Duke Otto the Younger of Grubenhagen-Osterode served until 1440 as regent for Albert II and his brothers Henry III and Ernest II. After 1440, the three brothers, following the Grubenhagen tradition, ruled jointly until Henry died in 1464. After the death of Henry III, Ernest II joined the clergy and Albert II became sole ruler and regent for Henry III's son, Henry IV. Albert II was repeatedly involved in feuds. For example, in 1477, Duke William IV the Younger of Göttingen got into a dispute wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Guelph
The House of Welf (also Guelf or Guelph) is a European dynasty that has included many German and British monarchs from the 11th to 20th century and Emperor Ivan VI of Russia in the 18th century. The originally Franconian family from the Meuse-Moselle area was closely related to the imperial family of the Carolingians. Origins The (Younger) House of Welf is the older branch of the House of Este, a dynasty whose earliest known members lived in Veneto and Lombardy in the late 9th/early 10th century, sometimes called Welf-Este. The first member was Welf I, Duke of Bavaria, also known as Welf IV. He inherited the property of the Elder House of Welf when his maternal uncle Welf III, Duke of Carinthia and Verona, the last male Welf of the Elder House, died in 1055. Welf IV was the son of Welf III's sister Kunigunde of Altdorf and her husband Albert Azzo II, Margrave of Milan. In 1070, Welf IV became Duke of Bavaria. Welf II, Duke of Bavaria married Countess Matilda of Tuscany, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
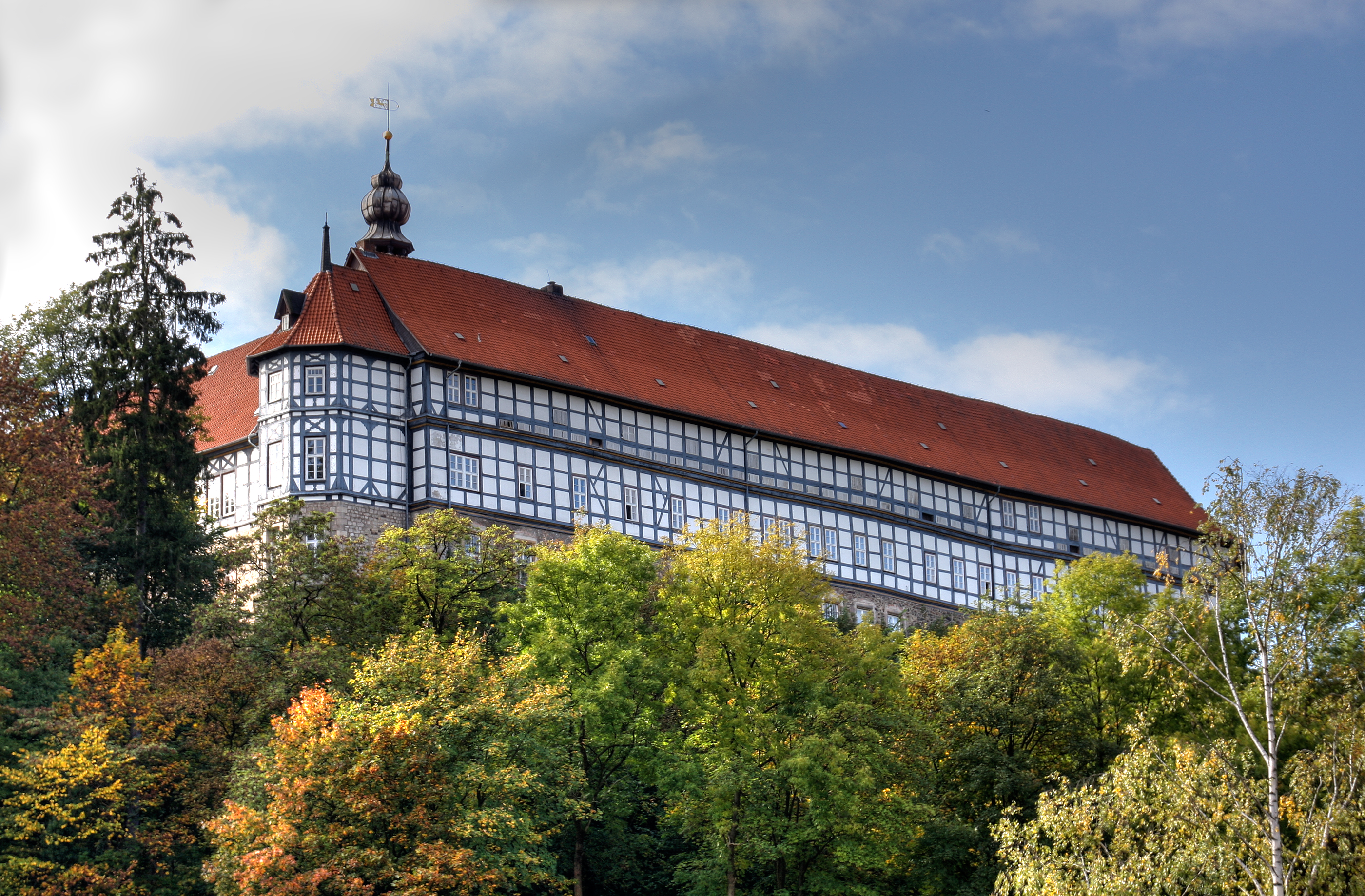
Herzberg Castle
Herzberg Castle (german: Schloss Herzberg) is a German ''schloss'' in Herzberg am Harz in the district of Göttingen in the state of Lower Saxony. The present-day, quadrangular building has its origins in the 11th century as a medieval '' castle''. After a fire in 1510 it was rebuilt as a ''schloss'' and is one of the few in Lower Saxony that was constructed as a timber-framed building. Because it belonged to the House of Welf for 700 years it is also known as the Welf Castle of Herzberg (''Welfenschloss Herzberg''). Geography Herzberg Castle stands on a wooded eminence () immediately above and west of the centre of the town of Herzberg am Harz, which lies on the southwestern edge of the Harz Mountains. A stretch of the River Sieber runs past the castle to the north. Architecture The present castle is an enclosed four-winged building with a rectangular courtyard (40 x 58 m) and was rebuilt after a serious fire in November 1510. Since the new castle was completed in 152 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernhard III, Prince Of Anhalt-Bernburg
Bernhard III, Prince of Anhalt-Bernburg (died 20 August 1348) was a German prince of the House of Ascania and ruler of the principality of Anhalt-Bernburg. He was the eldest son of Bernhard II, Prince of Anhalt-Bernburg, by his wife Helene, daughter of Wizlaw II, Prince of Rügen. Life Bernhard succeeded his father as ruler of Anhalt-Bernburg after his death in 1323. His two younger brothers renounced their rights in order to become priests, which left Bernhard as sole ruler of Bernburg. Along with his princely title, he also used the styles "Count of Askanien" and "Lord of Bernburg". Marriages and children In 1328 Bernhard married Agnes (c. 1310 – 4 January 1338), daughter of Rudolph I, Elector of Saxony and Duke of Saxe-Wittenberg. Her paternal grandmother and namesake Agnes of Habsburg was a daughter of Rudolph I, King of the Romans. The spouses were third cousins: Agnes's great-grandfather Albert I, Duke of Saxony, was a brother of Henry I, Count of Anhalt, Bernhard's g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnus The Pious, Duke Of Brunswick-Lüneburg
Magnus, meaning "Great" in Latin, was used as cognomen of Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus in the first century BC. The best-known use of the name during the Roman Empire is for the fourth-century Western Roman Emperor Magnus Maximus. The name gained wider popularity in the Middle Ages among various European people who lived in Stykkishólmur in their royal houses, being introduced to them upon being converted to the Latin-speaking Catholic Christianity. This was especially the case with Scandinavian royalty and nobility. As a Scandinavian forename, it was extracted from the Frankish ruler Charlemagne's Latin name "Carolus Magnus" and re-analyzed as Old Norse ''magn-hús'' = "power house". People Given name Kings of Hungary * Géza I (1074–1077), also known by his baptismal name Magnus. Kings of Denmark * Magnus the Good (1042–1047), also Magnus I of Norway King of Livonia * Magnus, Duke of Holstein (1540–1583) King of Mann and the Isles * Magnús Óláfsson (died 1265) Ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry I, Duke Of Brunswick-Grubenhagen
Henry I (August 1267 – 7 September 1322), Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg, called the Admirable (german: Heinrich der Wunderliche, la, Henricus Mirabilis), a member of the House of Welf, was the first ruler of the Principality of Grubenhagen from 1291 until his death. Life He was the eldest son of the Brunswick duke Albert the Tall and his second wife Adelaide, daughter of Margrave Boniface II of Montferrat. His father had ruled the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg jointly with his brother John, until both divided their territory in 1269. Albert went on to rule the Principality of Wolfenbüttel until his death in 1279. Henry first ruled the Brunswick principality of Wolfenbüttel jointly with his younger brothers Albert II the Fat and William. In 1291 they again divided the territory; Henry received the part that came to be known as Principality of Grubenhagen. It included the cities of Einbeck, half of Hamelin, Clausthal, Amelungsborn, Duderstadt, Herzberg, and Osterode. Henr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William VII Of Jülich, 1st Duke Of Berg
William II ( – 25 June 1408) was born in Jülich, as the son of Gerhard VI of Jülich, Count of Berg and Ravensberg, and Margaret, daughter and heiress of Otto IV, Count of Ravensberg, and Margaret of Berg.Walther Möller, ''Stammtafeln westdeutscher Adelsgeschlechter im Mittelalter'' (Darmstadt, 1922, reprint Verlag Degener & Co., 1995), Vol. 1, page 14. Upon his father's death in 1360, William became Count of Berg and Ravensberg, a title that his father had gained by marrying the heiress of Berg and Ravensberg. In 1380, King Wenzel elevated him to the rank of Duke, thus becoming the first Duke of Berg. William fought the counties of Mark and Cleves to prevent them from combining but in 1397 he was taken prisoner in the battle of Kleverhamm. He lost Remagen, Kaiserwerth and Sinzig to his nephew Adolf IV, Count of Kleve-Mark and due to these losses, his sons turned against him and imprisoned him in 1403/04. He ultimately forced them to submit and later supported his broth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest I, Duke Of Brunswick-Göttingen
Duke Ernest I of Brunswick-Göttingen ( – 24 April 1367John Morby, ''Dynasties of the World: a chronological and genealogical handbook'', Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1989, p. 132 viewed on 20 August 2006) was a member of the Guelph dynasty and was Duke of Brunswick-Göttingen from 1344 until his death. Life Ernest was a son of Duke Albert II of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel-Göttingen and his wife, Rixa of Werle. In the division of 1286, his father had received the Principality of Göttingen and in 1292, he inherited Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel from his childless brother William I. After his father's death in 1318, Ernest's older brother Otto the Mild, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Otto the Mild took up government. After Otto died childless in 1344, Ernest and his older brother Magnus I, Duke of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, Magnus I divided the Duchy. Ernest received the Principality of Göttingen The Principality of Göttingen (german: Fürstentum Göttingen) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnus II, Duke Of Brunswick-Lüneburg
Magnus (c. 1324 – 25 July 1373), called Magnus with the Necklace ( lat, Magnus Torquatus) or Magnus II, was Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg, ruling the Brunswick-Lüneburg principalities of Wolfenbüttel (colloquially also called Brunswick) and, temporarily, Lüneburg. Biography Magnus was the son of Magnus the Pious, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg (Wolfenbüttel). In 1362 Magnus and his brother Louis I, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg helped their brother Prince-Archbishop Albert II of Bremen to assert himself against the incumbent diocesan administrator Morris of Oldenburg, who claimed the see for himself. Magnus, Louis and the latter's father-in-law William II, Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg (Celle), and their troops beleaguered Morris in the prince-archiepiscopal castle in Vörde and forced him to sign his resignation. After the death of his brother Louis in 1367, Magnus became the designated heir of both ducal principalities, Wolfenbüttel and Celle (colloquially also Lüneburg). W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernest I, Duke Of Brunswick-Grubenhagen
Ernest I of Brunswick-Grubenhagen (german: Ernst I., Fürst von Braunschweig-Grubenhagen ; – 9 March 1361) was Prince of Brunswick-Grubenhagen. Life He was the son of Henry I, the Admirable and his wife Agnes, née Countess of Meissen. Henry the Admirable founded the Principality of Grubenhagen in 1291, after the Guelph princes had divided their inheritance. Ernest originally intended to follow a spiritual career, but after his father's death, he and his brothers Henry II and William jointly ruled the principality. Grubenhagen was rather smaller than the other Guelph principalities. Because Henry the Admirable had many children (eight sons and eight daughters), it was difficult to supply all the descendants in style. His eldest son Henry II could therefore not take the undivided sovereignty over the principality. In 1324, Henry concluded an extensive pact with his brothers Ernest and William under which the territory should be governed jointly, but shortly afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
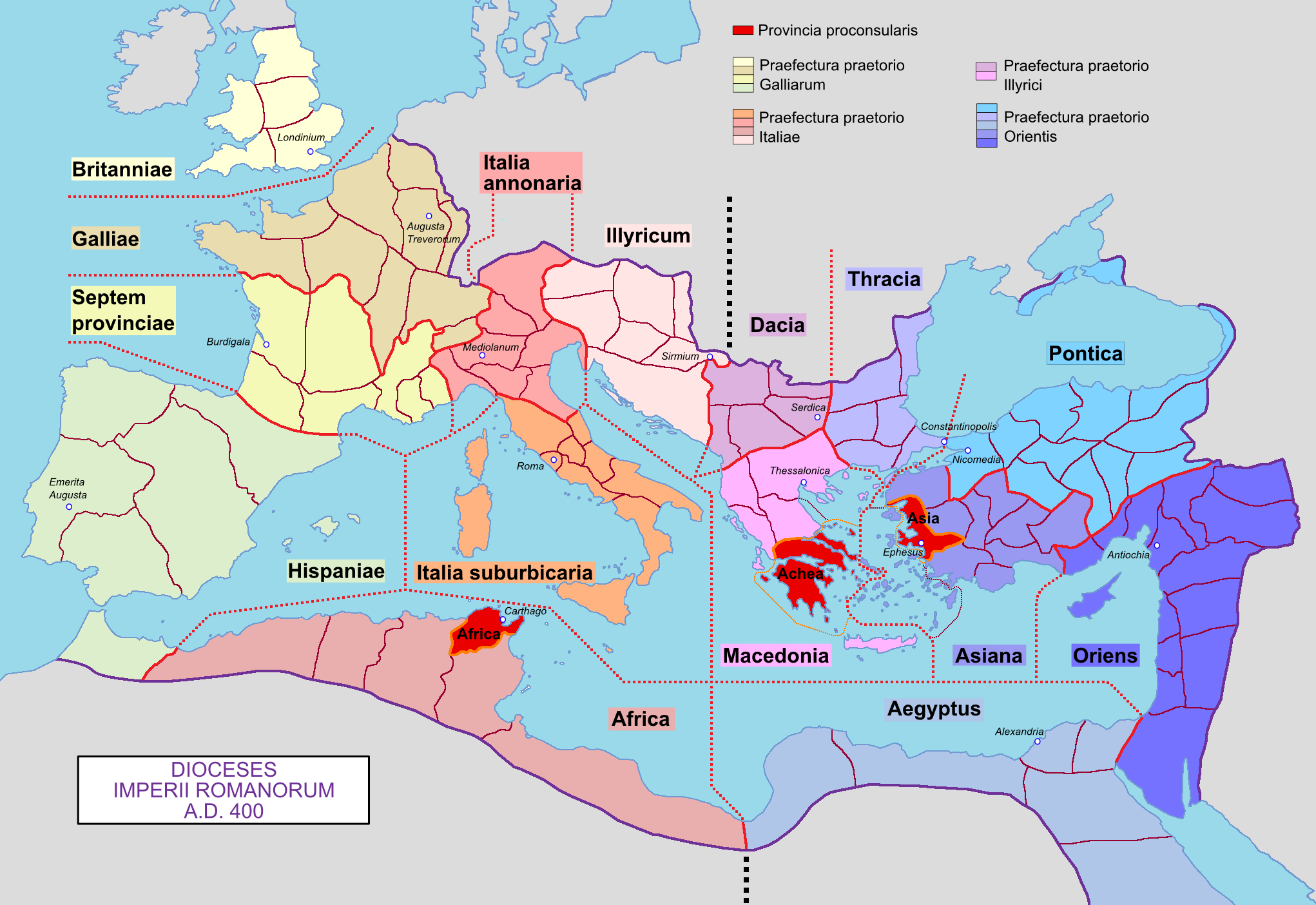
Diocese Of Münster
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into dioceses based on the civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situation must have hardly survived Julian, 361–363. Episcopal courts are not heard of again in the East until 398 and in the West in 408. The quality of these courts was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archdiocese Of Paderborn
The Archdiocese of Paderborn is an archdiocese of the Latin Rite of the Roman Catholic Church in Germany; its seat is Paderborn."Archdiocese of Paderborn" ''''. David M. Cheney. Retrieved February 29, 2016"Metropolitan Archdiocese of Paderborn" ''GCatholic.org''. Gabriel Chow. Retrieved February 29, 2016 It was a from its foundation in 799 until 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Osnabrück
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop. History In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associated in a larger unit, the diocese (Latin ''dioecesis'', from the Greek term διοίκησις, meaning "administration"). Christianity was given legal status in 313 with the Edict of Milan. Churches began to organize themselves into dioceses based on the civil dioceses, not on the larger regional imperial districts. These dioceses were often smaller than the provinces. Christianity was declared the Empire's official religion by Theodosius I in 380. Constantine I in 318 gave litigants the right to have court cases transferred from the civil courts to the bishops. This situation must have hardly survived Julian, 361–363. Episcopal courts are not heard of again in the East until 398 and in the West in 408. The quality of these courts was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |