|
Akrillai
Akrillai ( grc, Ἄκριλλαι) and Akrilla ( grc, Ἄκριλλα), Acrillae (in Latin) was an ancient Greek colony located in the modern province of Ragusa, Sicily, Italy, where the town of Chiaramonte Gulfi stands today. The ruins of the old colony can be found in the ''contrada'' (quarter) Piano del Conte-Morana and Piano Grillo. A necropolis dating from the 6th-5th century BC has been identified in the ''contrada'' Paraspola-Pirruna. The name appears in different forms among different authors: Akrilla, Akrille; in ancient sources: Akrillaiu; the name is variously written by Latin writers Acrilla and Acrille. History Hellenic era The city was founded by the Corinthian and Syracusan colonists at the same time of Kamarina (598 BC), overlooking the Valley of the Hipparis to establish their power against the city of Gela, founded by a Cretan-Rhodian effort. Akrillai was also a road-station on the route from Syracuse to Gela and Akragas. By passing via Akrai and Kasmenai, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiaramonte Gulfi
Chiaramonte Gulfi ( Sicilian: ''Ciaramunti'') is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Ragusa, Sicily, southern Italy. Geography Chiaramonte Gulfi is located on a hill-top north of Ragusa at an altitude of above sea level. The highest point is on Monte Arcibessi at . Its hamlets ( ''frazioni'') are the villages of Piano dell'Acqua, Roccazzo and Sperlinga. The town is also called '' Balcony of Sicily'' for its panoramic position, with views over the ''Valley of the Ippari'' and its towns (Comiso, Vittoria, Acate) and all the way to the Mediterranean Sea if looking south, as far as Mount Etna in direction north and to the Erean Mountains with Caltagirone if looking west. History In the area numerous archeological sites from the Bronze Age and Iron Age have been found, as well as ruins dating to the Greek Archaic era and Hellenistic era. Also Roman, Byzantine and medieval testimonies can be found. The city was founded by the Greek colonists from Syracuse in the 7th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corrado Melfi
Corrado Melfi, Baron of St. John (Chiaramonte Gulfi, January 16, 1850 - January 9, 1940) was an Italian historian and archaeologist. At the end of the 19th century he discovered the archeological site of Akrillai and the minor site of Scornavacche, not far from Akrillai. In 1912 he gave large accounts of his discoveries in his ''Cenni storici su Chiaramonte Gulfi''. The findings of excavations are housed in the Hyblean Archaeological Museum of Ragusa and in the Archeological Museum of Syracuse Syracuse may refer to: Places Italy *Syracuse, Sicily, or spelled as ''Siracusa'' *Province of Syracuse United States *Syracuse, New York **East Syracuse, New York **North Syracuse, New York *Syracuse, Indiana * Syracuse, Kansas *Syracuse, Miss ....N. Bonacasa, ''Commemorazione di Antonino Di Vita'', Rend. Mor. Acc. Lincei s.9 volume 23, 299-313 (2012). References Archaeologists from Sicily 1850 births 1940 deaths People from Ragusa, Sicily Writers from the Province of Ragusa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casmene
Casmenae or Kasmenai ( grc, Κασμέναι, Casmene in Italian) was an ancient Greek colony located on the Hyblaean Mountains, founded in 644 BC by the Syracusans at a strategic position for the control of central Sicily. It was also intended as a military forward-position on the ''Via Selinuntina'' road that connected Syracuse to ''Akragas'' (modern-day Agrigento) - also on that road were Gela and Akrillai to Casmenae's west and Akrai to its east. Destroyed by the Romans in 212 BC, Casmenae was abandoned during the 3rd century BC and never inhabited again. The site was discovered by the Sicilian archeologist Paolo Orsi during the first half of the 20th century, after he had identified the most probably site at Monte Casale in Buscemi at above sea level, on an extinct volcano near Monte Lauro, from Giarratana and from Palazzolo Acreide. Remains of the defensive walls, long, are still visible along with the base of one of the temples and some dwellings. Historical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirillo
The Dirillo, or Acate, is a river in Sicily which springs from the Hyblaean Mountains and flows through the areas of Vizzini, Licodia Eubea, Mazzarrone, Chiaramonte Gulfi, Acate, Vittoria, Gela. It enters the Strait of Sicily south-east of the town of Gela. As the largest river in the area it is sometimes known as the ''Fiume Grande''. The river was known in antiquity as the Achates ( grc, Ἀχάτης). It was noted by Silius Italicus for the remarkable clearness of its waters. Theophrastus in his treatise ''On Stones'' (ca. 315 B.C.) indicates that the name of the gemstone ''achates'' (agate) was based on the source of such stones from this river. Pliny the Elder makes the same connection in his ''Naturalis Historia'' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syracuse, Sicily
Syracuse ( ; it, Siracusa ; scn, Sarausa ), ; grc-att, wikt:Συράκουσαι, Συράκουσαι, Syrákousai, ; grc-dor, wikt:Συράκοσαι, Συράκοσαι, Syrā́kosai, ; grc-x-medieval, Συρακοῦσαι, Syrakoûsai, ; el, label=Modern Greek language, Modern Greek, Συρακούσες, Syrakoúses, . is a historic city on the Italy, Italian island of Sicily, the capital of the Italian province of Syracuse. The city is notable for its rich Greek and Roman history, Greek culture, culture, amphitheatres, architecture, and as the birthplace of the pre-eminent mathematician and engineer Archimedes. This 2,700-year-old city played a key role in ancient times, when it was one of the major powers of the Mediterranean world. Syracuse is located in the southeast corner of the island of Sicily, next to the Gulf of Syracuse beside the Ionian Sea. It is situated in a drastic rise of land with depths being close to the city offshore although the city itself is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
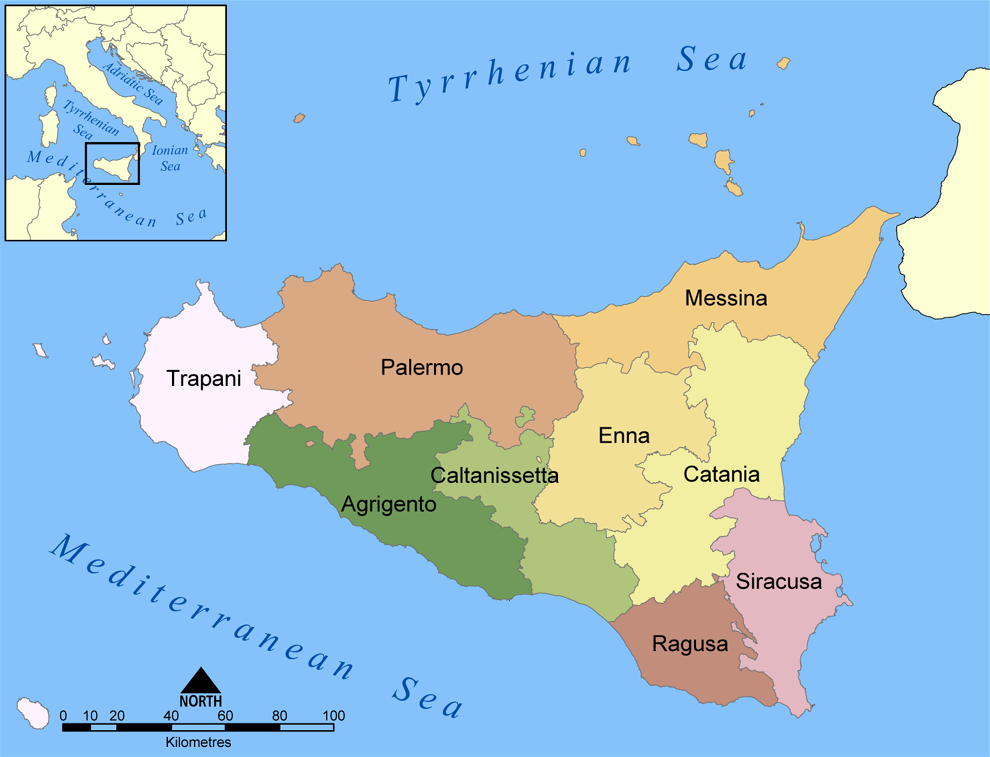
Province Of Ragusa
The Province of Ragusa ( it, Provincia di Ragusa; Sicilian: ''Pruvincia 'i Rausa'') was a province in the autonomous region of Sicily in southern Italy, located in the south-east of the island. Following the abolition of the Sicilian provinces, it was replaced in 2015 by the Free municipal consortium of Ragusa. Its capital is the city of Ragusa, which is the most southerly provincial capital in Italy. Geography From Scoglitti to Pozzallo, the Ragusan coastline is approximately long. Along the Ragusan coast are many fishing villages such as Kaukana, Punta Secca, Marina di Ragusa and Marina di Modica. The Hyblaean Mountains are dominating the north of the province and its highest peaks are Monte Lauro, Monte Casale and Monte Arcibessi. The rivers of the province are the Irminio, Dirillo and Ippari and the only lake in the province is the Lago di Santa Rosalia along the course of the Irminio river. The skyline of Ragusa is punctuated by the towers, domes and cupolas of the many ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire, Rome's control rapidly expanded during this period—from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean world. Roman society under the Republic was primarily a cultural mix of Latin and Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Roman Pantheon. Its political organization developed, at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by a senate. The top magistrates were the two consuls, who had an extensive range of executive, legislative, judicial, military, and religious powers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
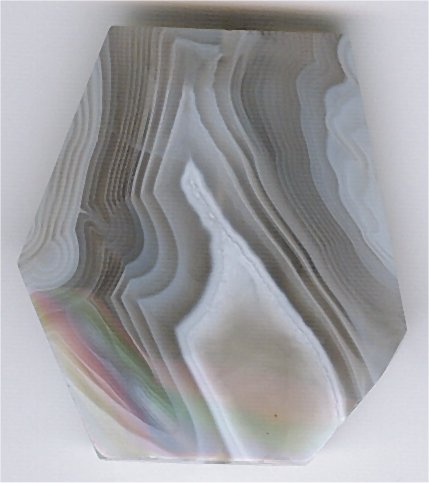
Agate
Agate () is a common rock formation, consisting of chalcedony and quartz as its primary components, with a wide variety of colors. Agates are primarily formed within volcanic and metamorphic rocks. The ornamental use of agate was common in Ancient Greece, in assorted jewelry and in the seal stones of Greek warriors, while bead necklaces with pierced and polished agate date back to the 3rd millennium BCE in the Indus Valley civilisation. Etymology The stone was given its name by Theophrastus, a Greek philosopher and naturalist, who discovered the stone along the shore line of the Dirillo River or Achates ( grc, Ἀχάτης) in Sicily, sometime between the 4th and 3rd centuries BCE. Formation and properties Agate minerals have the tendency to form on or within pre-existing rocks, creating difficulties in accurately determining their time of formation. Their host rocks have been dated to have formed as early as the Archean Eon. Agates are most commonly found as nodules wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perseus Project
The Perseus Project is a digital library project of Tufts University, which assembles digital collections of humanities resources. Version 4.0 is also known as the "Perseus Hopper", and it is hosted by the Department of Classical Studies. The project is mirrored by the Max Planck Society in Berlin, Germany, as well as by the University of Chicago. History The project was founded in 1987 to collect and present materials for the study of ancient Greece. It has published two CD-ROMs and established the Perseus Digital Library on the World Wide Web in 1995. The project has expanded its original scope; current collections cover Greco-Roman classics and the English Renaissance. Other materials, such as the papers of Edwin Bolles and the history of Tufts University, have been moved into the Tufts Digital Library. The editor-in-chief of the project is Gregory R. Crane, the Tufts Winnick Family Chair in Technology and Entrepreneurship. He has held that position since the founding of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titus Livius
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in 753 BC through the reign of Augustus in Livy's own lifetime. He was on familiar terms with members of the Julio-Claudian dynasty and a friend of Augustus, whose young grandnephew, the future emperor Claudius, he exhorted to take up the writing of history. Life Livy was born in Patavium in northern Italy, now modern Padua, probably in 59 BC. At the time of his birth, his home city of Patavium was the second wealthiest on the Italian peninsula, and the largest in the province of Cisalpine Gaul (northern Italy). Cisalpine Gaul was merged in Italy proper during his lifetime and its inhabitants were given Roman citizenship by Julius Caesar. In his works, Livy often expressed his deep affection and pride for Patavium, and the city was well kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asad Ibn Al-Furat
Asad Ibn Al-Furat ( ar, أسد بن الفرات; c.759 – c.828) was a jurist and theologian in Ifriqiya, who played an important role in the Arab conquest of Sicily. His family, originally from Harran in Mesopotamia, emigrated with him to Ifriqiya. Asad studied in Medina with Malik ibn Anas, the founder of the Malikite school, and in Kufa with a disciple of Abu Hanifa, the founder of the Hanafite tradition. He collected his views on religious law in the Asadiyya, which had great influence in Ifriqiya. After his return to Ifriqiya he became a judge in Kairouan, where he soon came into conflict with the Emir Ziyadat Allah I (817-838) after criticising his luxurious and impious lifestyle. In order to get rid of this unwelcome critic, Ziyadat appointed Asad the leader of an expedition to Byzantine Sicily. In 827 Asad landed with a force of Arabs in Sicily and following a defeat of Byzantine troops proceeded to besiege Syracuse. However, the city could not be taken and Asad soon d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western List of islands in the Indian Ocean, Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Arabs in Turkey, Turkey, Arab Indonesians, Indonesia, and Iranian Arabs, Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both Arab identity, carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |