|
Ain't Gonna Die Tonight
The word "ain't" is a contraction for ''am not'', ''is not'', ''are not'', ''has not'', ''have not'' in the common English language vernacular. In some dialects ''ain't'' is also used as a contraction of ''do not'', ''does not'' and ''did not''. The development of ''ain't'' for the various forms of ''to be not'', ''to have not'' and ''to do not'' occurred independently, at different times. The usage of ''ain't'' for the forms of ''to be not'' was established by the mid-18th century and for the forms of ''to have not'' by the early 19th century. The usage of ''ain't'' is a continuing subject of controversy in English. ''Ain't'' is commonly used by many speakers in oral and informal settings, especially in certain regions and dialects. Its usage is often highly stigmatized and it can be used by the general public as a marker of low socio-economic or regional status or education level. Its use is generally considered non-standard by dictionaries and style guides except when used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contraction (grammar)
A contraction is a shortened version of the spoken and written forms of a word, syllable, or word group, created by omission of internal letters and sounds. In linguistic analysis, contractions should not be confused with crasis, abbreviations and initialisms (including acronyms), with which they share some semantic and phonetic functions, though all three are connoted by the term "abbreviation" in layman’s terms. Contraction is also distinguished from morphological clipping, where beginnings and endings are omitted. The definition overlaps with the term portmanteau (a linguistic ''blend''), but a distinction can be made between a portmanteau and a contraction by noting that contractions are formed from words that would otherwise appear together in sequence, such as ''do'' and ''not'', whereas a portmanteau word is formed by combining two or more existing words that all relate to a singular concept that the portmanteau describes. English English has a number of con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Country Wife
''The Country Wife'' is a Restoration comedy written by William Wycherley and first performed in 1675. A product of the tolerant early Restoration period, the play reflects an aristocratic and anti-Puritan ideology, and was controversial for its sexual explicitness even in its own time. The title contains a lewd pun with regard to the first syllable of "country". It is based on several plays by Molière, with added features that 1670s London audiences demanded: colloquial prose dialogue in place of Molière's verse, a complicated, fast-paced plot tangle, and many sex jokes. It turns on two indelicate plot devices: a rake's trick of pretending impotence to safely have clandestine affairs with married women, and the arrival in London of an inexperienced young "country wife", with her discovery of the joys of town life, especially the fascinating London men. The implied condition the Rake, Horner, claimed to suffer from was, he said, contracted in France whilst "dealing with co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
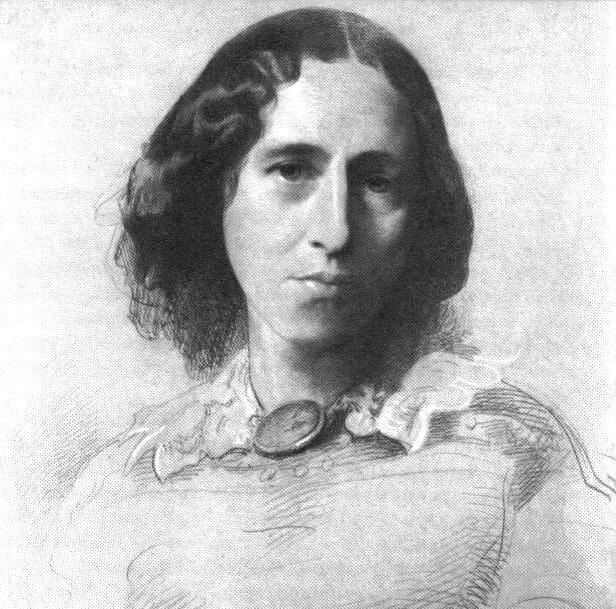
George Eliot
Mary Ann Evans (22 November 1819 – 22 December 1880; alternatively Mary Anne or Marian), known by her pen name George Eliot, was an English novelist, poet, journalist, translator, and one of the leading writers of the Victorian era. She wrote seven novels: ''Adam Bede'' (1859), ''The Mill on the Floss'' (1860), ''Silas Marner'' (1861), ''Romola'' (1862–63), ''Felix Holt, the Radical'' (1866), ''Middlemarch'' (1871–72) and '' Daniel Deronda'' (1876). Like Charles Dickens and Thomas Hardy, she emerged from provincial England; most of her works are set there. Her works are known for their realism, psychological insight, sense of place and detailed depiction of the countryside. ''Middlemarch'' was described by the novelist Virginia Woolf as "one of the few English novels written for grown-up people"Woolf, Virginia. "George Eliot." ''The Common Reader''. New York: Harcourt, Brace, and World, 1925. pp. 166–76. and by Martin Amis and Julian Barnes as the greatest novel in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
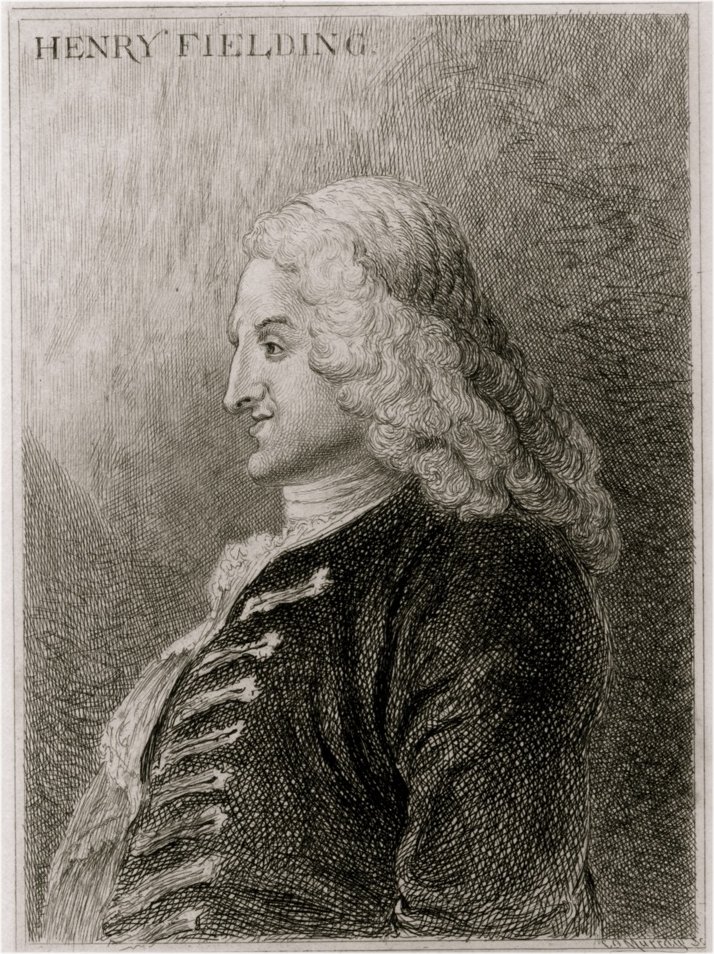
Henry Fielding
Henry Fielding (22 April 1707 – 8 October 1754) was an English novelist, irony writer, and dramatist known for earthy humour and satire. His comic novel '' Tom Jones'' is still widely appreciated. He and Samuel Richardson are seen as founders of the traditional English novel. He also holds a place in the history of law enforcement, having used his authority as a magistrate to found the Bow Street Runners, London's first intermittently funded, full-time police force. Early life Fielding was born 22 April 1707 at Sharpham, Somerset, and educated at Eton College, where he began a lifelong friendship with William Pitt the Elder. His mother died when he was 11. A suit for custody was brought by his grandmother against his charming but irresponsible father, Lt Gen. Edmund Fielding. The settlement placed Henry in his grandmother's care, but he continued to see his father in London. In 1725, Henry tried to abduct his cousin Sarah Andrews (with whom he was infatuated) while she was on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824), known simply as Lord Byron, was an English romantic poet and Peerage of the United Kingdom, peer. He was one of the leading figures of the Romantic movement, and has been regarded as among the greatest of English poets. Among his best-known works are the lengthy Narrative poem, narratives ''Don Juan (poem), Don Juan'' and ''Childe Harold's Pilgrimage''; many of his shorter lyrics in ''Hebrew Melodies'' also became popular. Byron was educated at Trinity College, Cambridge, later traveling extensively across Europe to places such as Italy, where he lived for seven years in Venice, Ravenna, and Pisa after he was forced to flee England due to lynching threats. During his stay in Italy, he frequently visited his friend and fellow poet Percy Bysshe Shelley. Later in life Byron joined the Greek War of Independence fighting the Ottoman Empire and died leading a campaign during that war, for which Greeks rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shibboleth
A shibboleth (; hbo, , šībbōleṯ) is any custom or tradition, usually a choice of phrasing or even a single word, that distinguishes one group of people from another. Shibboleths have been used throughout history in many societies as passwords, simple ways of self-identification, signaling loyalty and affinity, maintaining traditional segregation, or protecting from real or perceived threats. Origin The term originates from the Hebrew word (), which means the part of a plant containing grain, such as the head of a stalk of wheat or rye; or less commonly (but arguably more appropriately) "flood, torrent". The modern use derives from an account in the Hebrew Bible, in which pronunciation of this word was used to distinguish Ephraimites, whose dialect used a differently sounding first consonant. The difference concerns the Hebrew letter ''shin'', which is now pronounced as (as in '' shoe''). In the Book of Judges, chapter 12, after the inhabitants of Gilead under the comma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentence (linguistics)
In linguistics and grammar, a sentence is a linguistic expression, such as the English example "The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog." In traditional grammar, it is typically defined as a string of words that expresses a complete thought, or as a unit consisting of a subject and predicate. In non-functional linguistics it is typically defined as a maximal unit of syntactic structure such as a constituent. In functional linguistics, it is defined as a unit of written texts delimited by graphological features such as upper-case letters and markers such as periods, question marks, and exclamation marks. This notion contrasts with a curve, which is delimited by phonologic features such as pitch and loudness and markers such as pauses; and with a clause, which is a sequence of words that represents some process going on throughout time. A sentence can include words grouped meaningfully to express a statement, question, exclamation, request, command, or suggestion. Typical a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
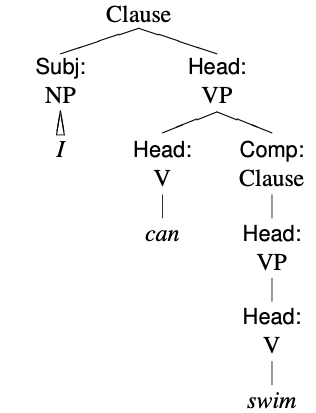
English Auxiliary Verbs
English auxiliary verbs are a small set of English verbs, which include the English modal verbs and a few others. Although definitions vary, as generally conceived an auxiliary lacks inherent semantic meaning but instead modifies the meaning of another verb it accompanies. In English, verb forms are often classed as auxiliary on the basis of certain grammatical properties, particularly as regards their syntax. They also participate in subject–auxiliary inversion and negation (grammar), negation by the simple addition of ''not'' after them. History of the concept In English, the adjective ''auxiliary'' was "formerly applied to any formative or subordinate elements of language, e.g. prefixes, English prepositions, prepositions." As applied to verbs, its conception was originally rather vague and varied significantly. Some historical examples The first English grammar, ''Pamphlet for Grammar'' by William Bullokar, published in 1586, does not use the term "auxiliary", but says, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean English
Caribbean English (CE, CarE) is a set of dialects of the English language which are spoken in the Caribbean and Liberia, most countries on the Caribbean coast of Central America, and Guyana and Suriname on the coast of South America. Caribbean English is influenced by, but is distinct to, the English-based creole languages spoken in the region. Though dialects of Caribbean English vary structurally and phonetically across the region, all are primarily derived from British English and West African languages. In countries with a plurality Indian population, such as Trinidad and Tobago and Guyana, Caribbean English has further been influenced by Hindustani and other South Asian languages. Overview * The daily-used English in the Caribbean has a different set of pronouns, typically ''me, meh'' or ''mi'', ''you, yuh, he, she, it, we, wi'' or ''alawe, wunna'' or ''unu'', and ''dem'' or ''day''. ''I, mi, my, he, she, ih, it, we, wi'' or ''alawe'', ''allayu'' or ''unu'', and '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African-American Vernacular English
African-American Vernacular English (AAVE, ), also referred to as Black (Vernacular) English, Black English Vernacular, or occasionally Ebonics (a colloquial, controversial term), is the variety of English natively spoken, particularly in urban communities, by most working- and middle-class African Americans and some Black Canadians. Having its own unique grammatical, vocabulary, and accent features, AAVE is employed by middle-class Black Americans as the more informal and casual end of a sociolinguistic continuum. However, in formal speaking contexts, speakers tend to switch to more standard English grammar and vocabulary, usually while retaining elements of the nonstandard accent. Despite being widespread throughout the United States, AAVE should not be assumed to be the native dialect of all African Americans. As with most African-American English, African-American Vernacular English shares a large portion of its grammar and phonology with the rural dialects of the Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Our Mutual Friend
''Our Mutual Friend'', written in 1864–1865, is the last novel completed by Charles Dickens and is one of his most sophisticated works, combining savage satire with social analysis. It centres on, in the words of critic J. Hillis Miller, quoting the book's character Bella Wilfer, "money, money, money, and what money can make of life". Most reviewers in the 1860s continued to praise Dickens's skill as a writer in general, but did not review this novel in detail. Some found the plot both too complex and not well laid out. ''The Times'' of London found the first few chapters did not draw the reader into the characters. In the 20th century, however, reviewers began to find much to approve in the later novels of Dickens, including ''Our Mutual Friend''. In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, some reviewers suggested that Dickens was, in fact, experimenting with structure, and that the characters considered somewhat flat and not recognized by the contemporary reviewers were mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)