|
Aicardi–Goutières Syndrome
Aicardi–Goutières syndrome (AGS), which is completely distinct from the similarly named Aicardi syndrome, is a rare, usually early onset childhood, inflammatory disorder most typically affecting the brain and the skin (neurodevelopmental disorder). The majority of affected individuals experience significant intellectual and physical problems, although this is not always the case. The clinical features of AGS can mimic those of ''in utero'' acquired infection, and some characteristics of the condition also overlap with the autoimmune disease systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Following an original description of eight cases in 1984, the condition was first referred to as 'Aicardi–Goutières syndrome' (AGS) in 1992, and the first international meeting on AGS was held in Pavia, Italy, in 2001. AGS can occur due to mutations in any one of a number of different genes, of which nine have been identified to date, namely: ''TREX1'', ''RNASEH2A'', ''RNASEH2B'', ''RNASEH2C'' (which tog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
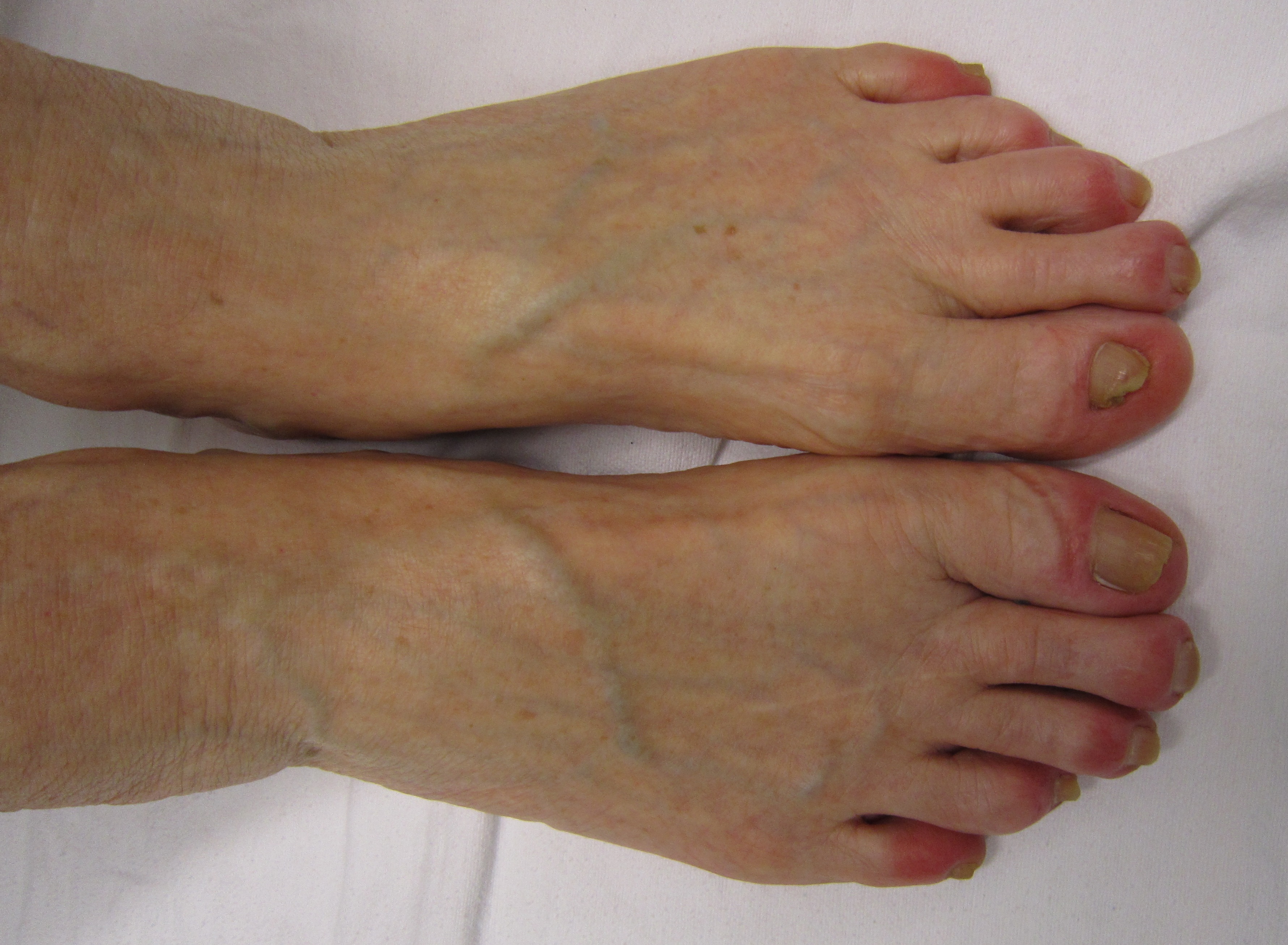
Chilblains
Chilblains, also known as pernio, is a medical condition in which damage occurs to capillary beds in the skin, most often in the hands or feet, when blood perfuses into the nearby tissue resulting in redness, itching, inflammation, and possibly blisters. It occurs most frequently when predisposed individuals, predominantly women, are exposed to cold and humidity. Ulcerated chilblains are referred to as kibes. Temperature-related chilblains can be prevented by keeping the feet and hands warm in cold weather and avoiding exposing these areas to extreme temperature changes. Once the diagnosis of chilblains is made, first-line treatment includes avoiding cold, damp environments and wearing gloves and warm socks. Chilblains can be idiopathic (spontaneous and unrelated to another disease), but similar symptoms may also be a manifestation of another serious medical condition that must be investigated. Related medical conditions include Raynaud syndrome, erythromelalgia, frostbite, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MDA5
MDA5 (melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5) is a RIG-I-like receptor dsRNA helicase Helicases are a class of enzymes thought to be vital to all organisms. Their main function is to unpack an organism's genetic material. Helicases are motor proteins that move directionally along a nucleic acid phosphodiester backbone, separatin ... enzyme that is encoded by the ''IFIH1'' gene in humans. MDA5 is part of the RIG-I-like receptor (RLR) family, which also includes RIG-I and LGP2, and functions as a pattern recognition receptor capable of detecting viruses. It is generally believed that MDA5 recognizes double stranded RNA (dsRNA) over 2000nts in length, however it has been shown that whilst MDA5 can detect and bind to cytoplasmic dsRNA, it is also activated by a high molecular weight RNA complex composed of ssRNA and dsRNA. For many viruses, effective MDA5-mediated antiviral responses are dependent on functionally active LGP2. The signaling cascades in MDA5 is initiated via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endonuclease
Endonucleases are enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a polynucleotide chain. Some, such as deoxyribonuclease I, cut DNA relatively nonspecifically (without regard to sequence), while many, typically called restriction endonucleases or restriction enzymes, cleave only at very specific nucleotide sequences. Endonucleases differ from exonucleases, which cleave the ends of recognition sequences instead of the middle (endo) portion. Some enzymes known as "exo-endonucleases", however, are not limited to either nuclease function, displaying qualities that are both endo- and exo-like. Evidence suggests that endonuclease activity experiences a lag compared to exonuclease activity. Restriction enzymes are endonucleases from eubacteria and archaea that recognize a specific DNA sequence. The nucleotide sequence recognized for cleavage by a restriction enzyme is called the restriction site. Typically, a restriction site will be a palindromic sequence about four to six nucleotides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
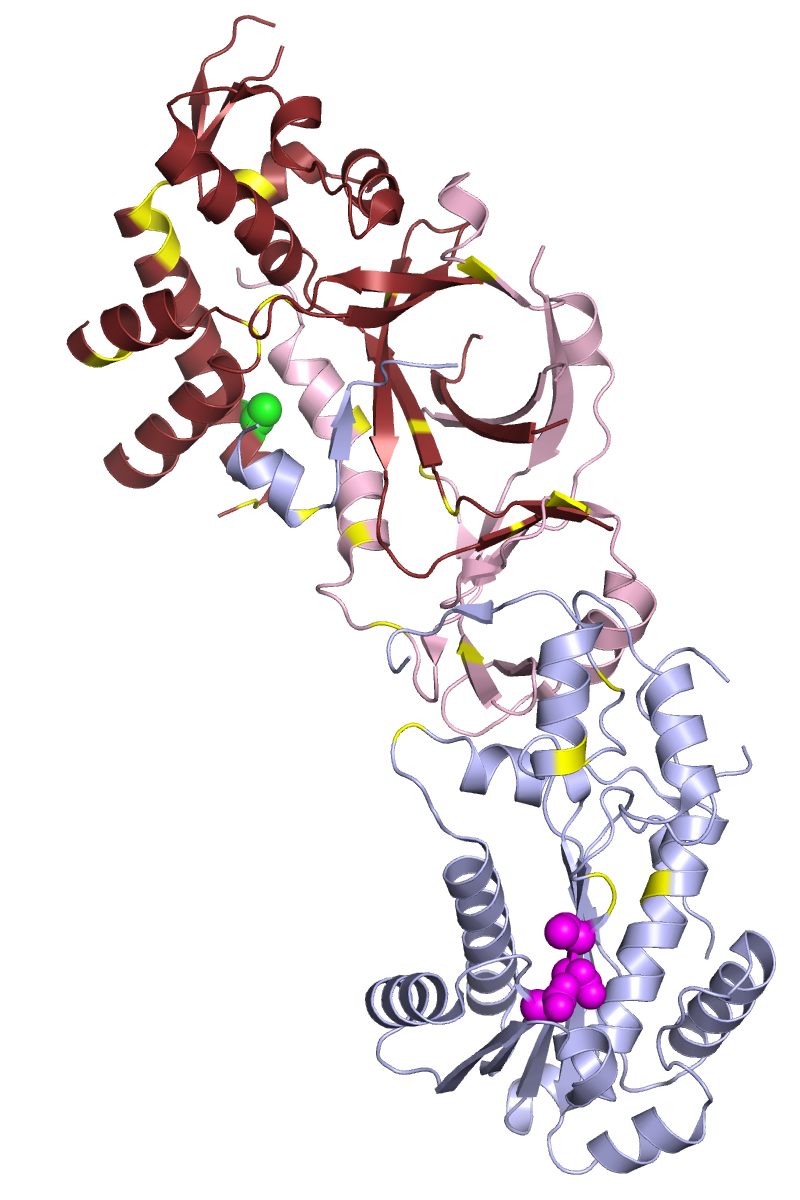
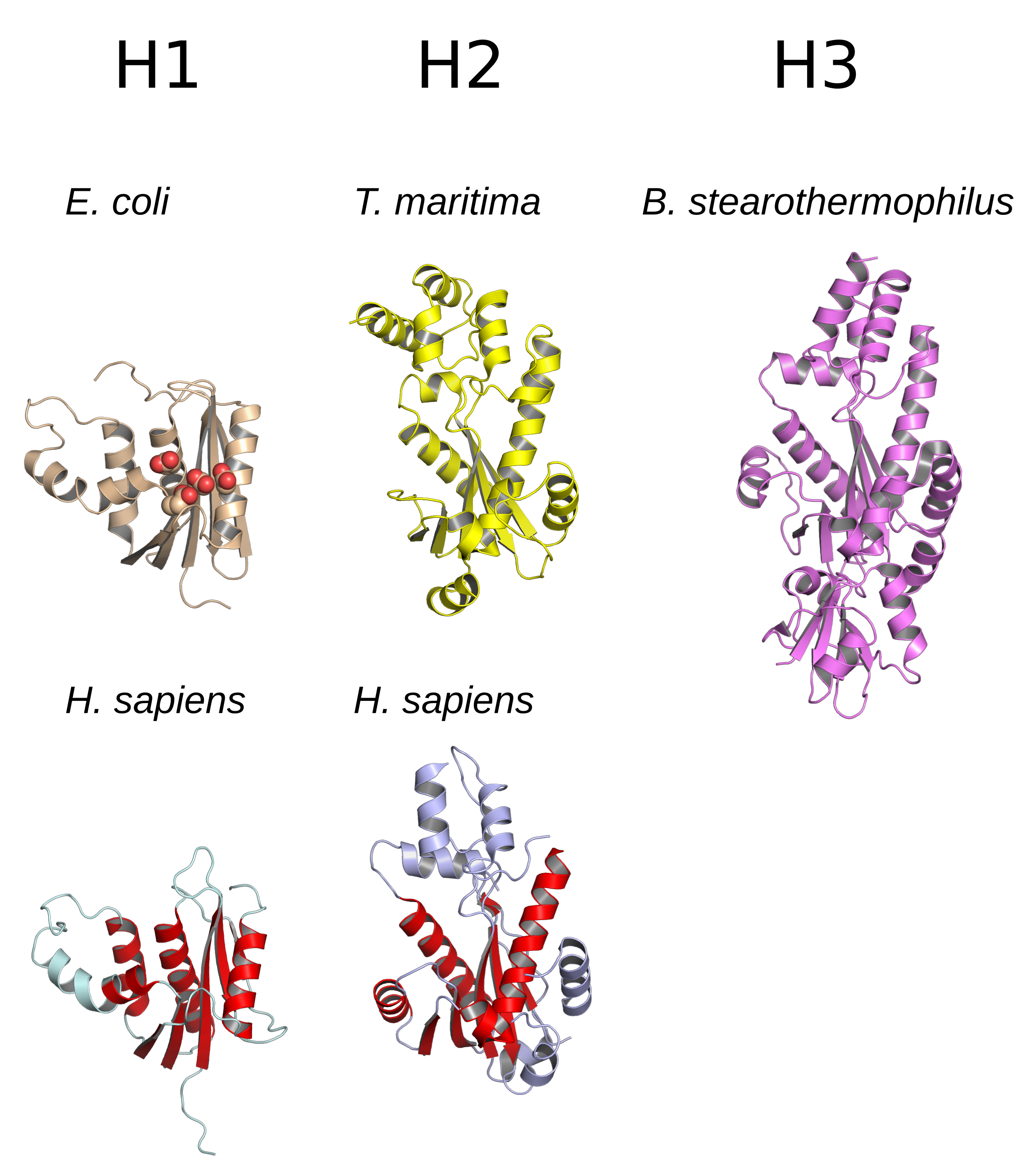
Ribonuclease H
Ribonuclease H (abbreviated RNase H or RNH) is a family of non-sequence-specific endonuclease enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of RNA in an RNA/ DNA substrate via a hydrolytic mechanism. Members of the RNase H family can be found in nearly all organisms, from bacteria to archaea to eukaryotes. The family is divided into evolutionarily related groups with slightly different substrate preferences, broadly designated ribonuclease H1 and H2. The human genome encodes both H1 and H2. Human ribonuclease H2 is a heterotrimeric complex composed of three subunits, mutations in any of which are among the genetic causes of a rare disease known as Aicardi–Goutières syndrome. A third type, closely related to H2, is found only in a few prokaryotes, whereas H1 and H2 occur in all domains of life. Additionally, RNase H1-like retroviral ribonuclease H domains occur in multidomain reverse transcriptase proteins, which are encoded by retroviruses such as HIV and are required for viral repli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exonuclease
Exonucleases are enzymes that work by cleaving nucleotides one at a time from the end (exo) of a polynucleotide chain. A hydrolyzing reaction that breaks phosphodiester bonds at either the 3′ or the 5′ end occurs. Its close relative is the endonuclease, which cleaves phosphodiester bonds in the middle (endo) of a polynucleotide chain. Eukaryotes and prokaryotes have three types of exonucleases involved in the normal turnover of mRNA: 5′ to 3′ exonuclease (Xrn1), which is a dependent decapping protein; 3′ to 5′ exonuclease, an independent protein; and poly(A)-specific 3′ to 5′ exonuclease. In both archaea and eukaryotes, one of the main routes of RNA degradation is performed by the multi-protein exosome complex, which consists largely of 3′ to 5′ exoribonucleases. Significance to polymerase RNA polymerase II is known to be in effect during transcriptional termination; it works with a 5' exonuclease (human gene Xrn2) to degrade the newly formed transcript ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ultimate source o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortical Blindness
Cortical blindness is the total or partial loss of vision in a normal-appearing eye caused by damage to the brain's occipital cortex. Cortical blindness can be acquired or congenital, and may also be transient in certain instances. Acquired cortical blindness is most often caused by loss of blood flow to the occipital cortex from either unilateral or bilateral posterior cerebral artery blockage (ischemic stroke) and by cardiac surgery. In most cases, the complete loss of vision is not permanent and the patient may recover some of their vision (cortical visual impairment). Congenital cortical blindness is most often caused by perinatal ischemic stroke, encephalitis, and meningitis. Rarely, a patient with acquired cortical blindness may have little or no insight that they have lost vision, a phenomenon known as Anton–Babinski syndrome. Cortical blindness and cortical visual impairment (CVI), which refers to the partial loss of vision caused by cortical damage, are both classified a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye remains open, with less common types including closed-angle (narrow angle, acute congestive) glaucoma and normal-tension glaucoma. Open-angle glaucoma develops slowly over time and there is no pain. Peripheral vision may begin to decrease, followed by central vision, resulting in blindness if not treated. Closed-angle glaucoma can present gradually or suddenly. The sudden presentation may involve severe eye pain, blurred vision, mid-dilated pupil, redness of the eye, and nausea. Vision loss from glaucoma, once it has occurred, is permanent. Eyes affected by glaucoma are referred to as being glaucomatous. Risk factors for glaucoma include increasing age, high pressure in the eye, a family history of glaucoma, and use of steroid medication. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Startle Response
In animals, including humans, the startle response is a largely unconscious defensive response to sudden or threatening stimuli, such as sudden noise or sharp movement, and is associated with negative Affect (psychology), affect.Rammirez-Moreno, David. "A computational model for the modulation of the prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex". ''Biological Cybernetics'', 2012, p. 169 Usually the onset of the startle response is a startle reflex reaction. The startle reflex is a brainstem reflectory reaction (reflex) that serves to protect vulnerable parts, such as the back of the neck (whole-body startle) and the eyes (eyeblink) and Fight-or-flight response, facilitates escape from sudden stimuli. It is found across many different species, throughout all stages of life. A variety of responses may occur depending on the affected individual's emotional state, body posture, preparation for execution of a motor task, or other activities. The startle response is implicated in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encephalopathy
Encephalopathy (; from grc, ἐνκέφαλος "brain" + πάθος "suffering") means any disorder or disease of the brain, especially chronic degenerative conditions. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but rather to a syndrome of overall brain dysfunction; this syndrome has many possible organic and inorganic causes. Signs and symptoms The hallmark of encephalopathy is an altered mental state or delirium. Characteristic of the altered mental state is impairment of the cognition, attention, orientation, sleep–wake cycle and consciousness. An altered state of consciousness may range from failure of selective attention to drowsiness. Hypervigilance may be present; with or without: cognitive deficits, headache, epileptic seizures, myoclonus (involuntary twitching of a muscle or group of muscles) or asterixis ("flapping tremor" of the hand when wrist is extended). Depending on the type and severity of encephalopathy, common neurological sym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombocytopaenia
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets, also known as thrombocytes, in the blood. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients and a third of surgical patients. A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets/microliter (μl) of blood. Values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease. One common definition of thrombocytopenia requiring emergency treatment is a platelet count below 50,000/μl. Thrombocytopenia can be contrasted with the conditions associated with an abnormally ''high'' level of platelets in the blood - thrombocythemia (when the cause is unknown), and thrombocytosis (when the cause is known). Signs and symptoms Thrombocytopenia usually has no symptoms and is picked up on a routine complete blood count. Some individuals with thrombocytopenia may experience external bleeding, such as nosebleeds or bleeding gums. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |