|
Agésilas
''Agésilas'' is a play written by Pierre Corneille and published in 1666. It was first performed in April 1666 at the Hôtel de Bourgogne. Characters * Agésilas, king of Sparta *Lysander, famous Spartan captain *Cotys, king of Paphlagonia *Spitridate, Persian high lord *Mandane, sister of Spitridate *Elpinice, daughter of Lysander *Aglatide, daughter of Lysander *Xénoclès, lieutenant of Agésilas *Cléon, Greek orator from Halicarnassus Plot The action takes places in Ephesus. Lysander has promised to marry his daughters Elpinice and Aglatide to Cotys and Spitridate respectively but he needs the agreement of Agésilas. Cotys and Spitridate quickly realize that this arrangement doesn't suit them. In effect, Spitridate and Elpinice have fallen in love with each other, and the same is true of Cotys and Mandane. Cotys agrees to give Elpinice to Spitridate if Spitridate will give him Mandane in return. However, Spitridate is wary of this because he's afraid of offending Lysander. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Corneille
Pierre Corneille (; 6 June 1606 – 1 October 1684) was a French tragedian. He is generally considered one of the three great seventeenth-century French dramatists, along with Molière and Racine. As a young man, he earned the valuable patronage of Cardinal Richelieu, who was trying to promote classical tragedy along formal lines, but later quarrelled with him, especially over his best-known play, ''Le Cid'', about a medieval Spanish warrior, which was denounced by the newly formed ''Académie française'' for breaching the unities. He continued to write well-received tragedies for nearly forty years. Biography Early years Corneille was born in Rouen, Normandy, France, to Marthe Le Pesant and Pierre Corneille, a distinguished lawyer. His younger brother, Thomas Corneille, also became a noted playwright. He was given a rigorous Jesuit education at the ''Collège de Bourbon'' (Lycée Pierre-Corneille since 1873), where acting on the stage was part of the training. At 18 he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hôtel De Bourgogne (theatre)
Hôtel de Bourgogne was a theatre, built in 1548 for the first authorized theatre troupe in Paris, the Confrérie de la Passion. It was located on the rue Mauconseil (now the rue Étienne Marcel in the 2nd arrondissement of Paris), on a site that had been part of the residence of the Dukes of Burgundy (the former Hôtel de Bourgogne). The most important French theatre until the 1630s, it continued to be used until 1783,Forman 2010, p. 134 ("Hôtel de Bourgogne"). after which it was converted to a leather market and eventually totally demolished. The Confrérie performed farce and secular dramas, but lacking great success, began renting the theatre to itinerant acting companies, including Italian ''commedia dell'arte'' troupes, who introduced the characters Harlequin and Pantalone, as well as burlesque. In 1628, a French company, the Comédiens du Roi, became permanently established and performed many of the classics of French theatre, including ''Andromaque'' and ''Phèdre'' by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agesilaus II
Agesilaus II (; grc-gre, Ἀγησίλαος ; c. 442 – 358 BC) was king of Sparta from c. 399 to 358 BC. Generally considered the most important king in the history of Sparta, Agesilaus was the main actor during the period of Spartan hegemony that followed the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC). Although brave in combat, Agesilaus lacked the diplomatic skills to preserve Sparta's position, especially against the rising power of Thebes, which reduced Sparta to a secondary power after its victory at Leuctra in 371 BC. Despite the traditional secrecy fostered by the Spartiates, the reign of Agesilaus is particularly well-known thanks to the works of his friend Xenophon, who wrote a large history of Greece (the '' Hellenica'') covering the years 411 to 362 BC, therefore extensively dealing with Agesilaus' rule. Xenophon furthermore composed a panegyric biography of his friend, perhaps to clean his memory from the criticisms voiced against him. Another historical tradition—much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece. Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its political independence until its forced integration into the Achaean League in 192 BC. The city nevertheless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysander
Lysander (; grc-gre, Λύσανδρος ; died 395 BC) was a Spartan military and political leader. He destroyed the Athenian fleet at the Battle of Aegospotami in 405 BC, forcing Athens to capitulate and bringing the Peloponnesian War to an end. He then played a key role in Sparta's domination of Greece for the next decade until his death at the Battle of Haliartus. Lysander's vision for Sparta differed from most Spartans; he wanted to overthrow the Athenian Empire and replace it with Spartan hegemony. Early life Little is known of Lysander's early life. His year of birth is estimated at 454 BC. Some ancient authors record that his mother was a helot or slave. Lysander's father was Aristocritus, who was a member of the Spartan Heracleidae; that is, he claimed descent from Heracles but was not a member of a royal family. According to Plutarch, Lysander grew up in poverty and showed himself obedient, conformed to norms, and had a "manly spirit".Plutarch, Lives. Life of Lysander. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paphlagonia
Paphlagonia (; el, Παφλαγονία, Paphlagonía, modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; tr, Paflagonya) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus to the east, and separated from Phrygia (later, Galatia) by a prolongation to the east of the Bithynian Olympus. According to Strabo, the river Parthenius formed the western limit of the region, and it was bounded on the east by the Halys River. ''Paphlagonia'' was said to be named after Paphlagon, a son of the mythical Phineus.Eustath. ad Horn. II. ii. 851, ad Dion. Per. 787; Steph. B. t.v.; Const. Porph. de Them. i. 7. Geography The greater part of Paphlagonia is a rugged mountainous country, but it contains fertile valleys and produces a great abundance of hazelnuts and fruit – particularly plums, cherries and pears. The mountains are clothed with dense forests, notable for the quantity of boxwood that they furnish. Hence, its coasts were occupied by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
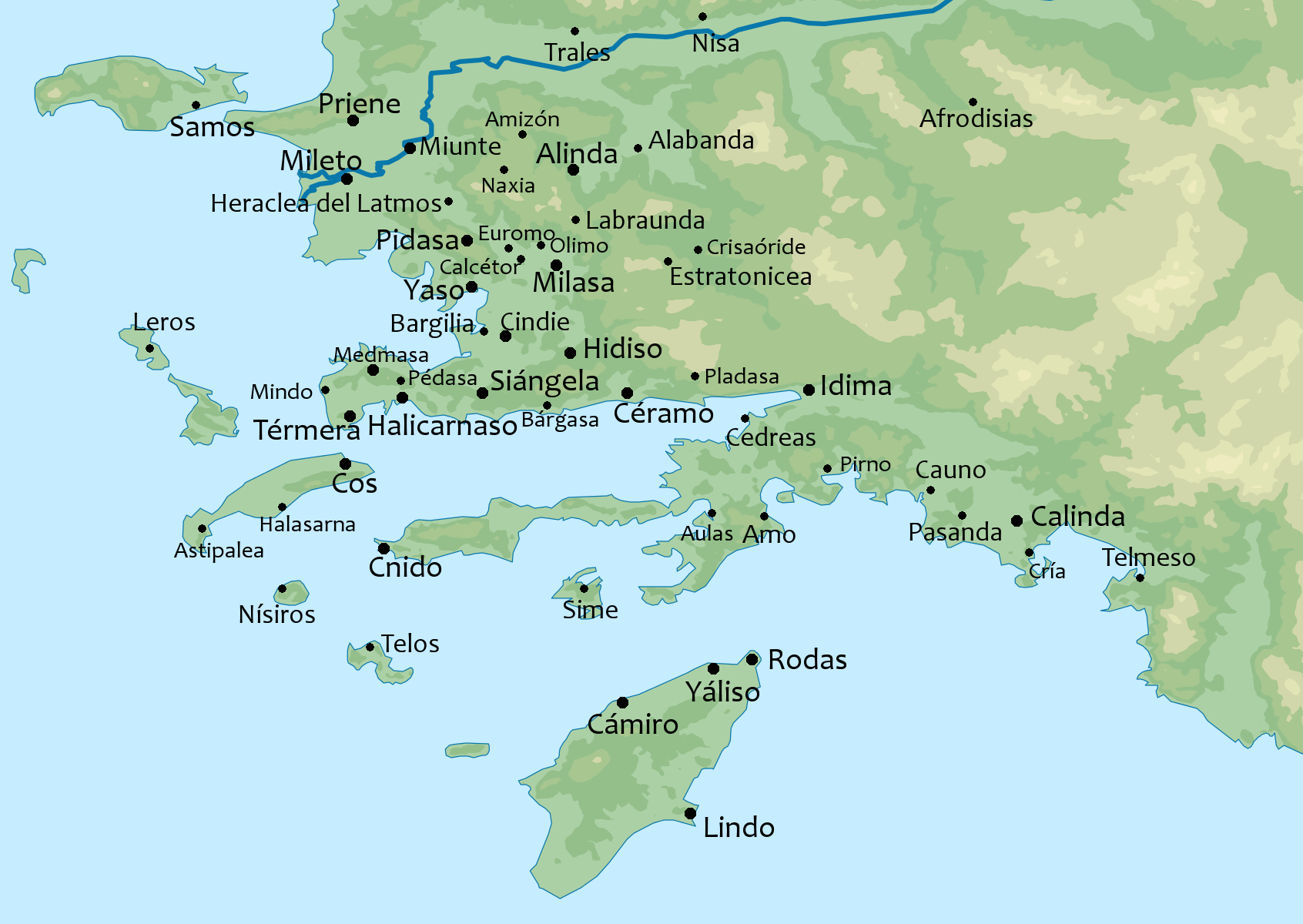
Halicarnassus
Halicarnassus (; grc, Ἁλικαρνᾱσσός ''Halikarnāssós'' or ''Alikarnāssós''; tr, Halikarnas; Carian: 𐊠𐊣𐊫𐊰 𐊴𐊠𐊥𐊵𐊫𐊰 ''alos k̂arnos'') was an ancient Greek city in Caria, in Anatolia. It was located in southwest Caria, on an advantageous site on the Gulf of Gökova, which is now in Bodrum, Turkey.} The city was famous for the Mausoleum of Halicarnassus, also known simply as the Tomb of Mausolus, whose name provided the origin of the word "mausoleum". The mausoleum, built from 353 to 350 BC, ranked as one of the seven wonders of the ancient world. Halicarnassus' history was special on two interlinked issues. Halicarnassus retained a monarchical system of government at a time when most other Greek city states had long since rid themselves of their kings. And secondly, while their Ionian neighbours rebelled against Persian rule, Halicarnassus remained loyal to the Persians and formed part of the Persian Empire until Alexander the Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephesus
Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἔφεσος, Éphesos; tr, Efes; may ultimately derive from hit, 𒀀𒉺𒊭, Apaša) was a city in ancient Greece on the coast of Ionia, southwest of present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built in the 10th century BC on the site of Apasa, the former Arzawan capital, by Attica, Attic and Ionians, Ionian Greek colonists. During the Classical Greece, Classical Greek era, it was one of twelve cities that were members of the Ionian League. The city came under the control of the Roman Republic in 129 BC. The city was famous in its day for the nearby Temple of Artemis (completed around 550 BC), which has been designated one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Its many monumental buildings included the Library of Celsus and a theatre capable of holding 24,000 spectators. Ephesus was recipient city of one of the Pauline epistles; one of the seven churches of Asia addressed in the Book of Revelation; the Gospel of John may have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psyché (play)
''Psyché'' is a five-act '' tragicomédie et ballet'', originally written as a prose text by Molière and versified in collaboration with Pierre Corneille and Philippe Quinault, with music composed by Jean-Baptiste Lully in 1671 and by Marc-Antoine Charpentier in 1684 (music lost). The plot is based on the story of ''Cupid and Psyche'' in ''The Golden Ass'', written in the 2nd century by Apuleius. It was first performed on 17 January 1671 before the royal court of Louis XIV at the Théâtre des Tuileries, with ballets by Pierre Beauchamps, Anthoine des Brosses, and Nicolas Delorge, and spectacular scenery and special effects designed by Carlo Vigarani.Gaines 2002, p. 394; Powell 2008, pp. 123–124. History Molière's play was one of many sumptuous spectacles produced in celebration of the peace of Aix-la-Chapelle. The treaty was signed in 1668 but the festivities continued well into 1671. More specifically, the play was a product of Louis XIV's desire to re-use the Salle des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolas Boileau
Nicolas or Nicolás may refer to: People Given name * Nicolas (given name) Mononym * Nicolas (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian footballer * Nicolas (footballer, born 2000), Brazilian footballer Surname Nicolas * Dafydd Nicolas (c.1705–1774), Welsh poet * Jean Nicolas (1913–1978), French international football player * Nicholas Harris Nicolas (1799–1848), English antiquary * Paul Nicolas (1899–1959), French international football player * Robert Nicolas (1595–1667), English politician Nicolás * Adolfo Nicolás (1936–2020), Superior General of the Society of Jesus * Eduardo Nicolás (born 1972), Spanish former professional tennis player Other uses * Nicolas (wine retailer), a French chain of wine retailers * ''Le Petit Nicolas'', a series of children's books by René Goscinny See also * San Nicolás (other) * Nicholas (other) * Nicola (other) * Nikola Nikola () is a given name which, like Nicholas, is a version of the Greek ''Nikolaos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1666 Plays
This is the first year to be designated as an ''Annus mirabilis'', in John Dryden's 1667 poem so titled, celebrating England's failure to be beaten either by the Dutch or by fire. It is the only year to contain each Roman numeral once in descending order (1000(M)+500(D)+100(C)+50(L)+10(X)+5(V)+1(I) = 1666). Events January–March * January 17 – The Chair of Saint Peter (''Cathedra Petri'', designed by Bernini) is set above the altar in St. Peter's Basilica in Rome. * February 1 – The joint English and Scottish royal court returns to London, as the Great Plague of London subsides. * March 11 – The tower of St. Peter's Church in Riga, collapses, burying eight people in the rubble. April–June * April 20 – In colonial British North America, " Articles of Peace and Amity" are signed between the governments of the Province of Maryland and 12 Eastern Algonquian tribes — the Piscataways, Anacostancks, Doegs, Mattawomans, Portob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plays By Pierre Corneille
Play most commonly refers to: * Play (activity), an activity done for enjoyment * Play (theatre), a work of drama Play may refer also to: Computers and technology * Google Play, a digital content service * Play Framework, a Java framework * Play Mobile, a Polish internet provider * Xperia Play, an Android phone * Rakuten.co.uk (formerly Play.com), an online retailer * Backlash (engineering), or ''play'', non-reversible part of movement * Petroleum play, oil fields with same geological circumstances * Play symbol, in media control devices Film * ''Play'' (2005 film), Chilean film directed by Alicia Scherson * ''Play'', a 2009 short film directed by David Kaplan * ''Play'' (2011 film), a Swedish film directed by Ruben Östlund * ''Rush'' (2012 film), an Indian film earlier titled ''Play'' and also known as ''Raftaar 24 x 7'' * ''The Play'' (film), a 2013 Bengali film Literature and publications * ''Play'' (play), written by Samuel Beckett * ''Play'' (''The New York Times'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |