|
Agushevi Konatsi
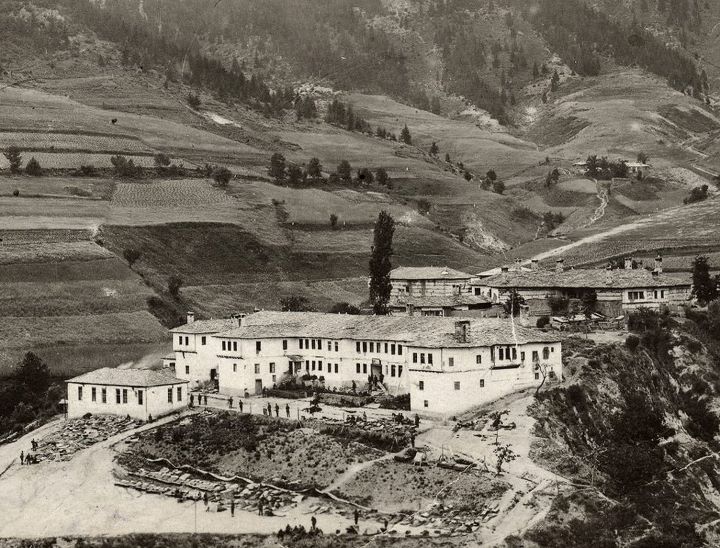
Agushevi konatsi ( bg, Агушеви конаци, "The Agush Agha's Konaks"), built during the 19th century, is a winter estate of the Ottoman feudal who belongend to the Pomaks in the Mogilitsa village in Bulgaria. It is formed of three consecutive identical large residential edifices with courtyards. It was declared a national monument of art and culture under Government Order No PMC 388 on 30 December 1964. It was named after the title of its owner, Agush Aga. Location Agushevi konatsi is located in the Mogilitsa village on the Rhodope Mountains of southern Bulgaria. It is at a distance of to the south of the town of Smolyan. History The feudal estate was built from 1820 to 1840 (1840-42 is also mentioned) by Aguş Ağa a son of Hacı Osman, an Ottoman feudal of Pomaks origin, who ruled the Agaluk An Agaluk ( tr, Ağalık) was a feudal unit of the Ottoman Empire governed by an ''agha'' (tax collector landlord). In Bosnian history, an agaluk may often refer to land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smolyan
Smolyan ( bg, Смолян) List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, is a town and ski resort in the south of Bulgaria near the border with Greece. It is the administrative and industrial centre of the homonymous Smolyan Province. The town is built along the valley of Cherna ("Black") and Byala River, Byala ("White") rivers in the central Rhodope Mountains which makes him the longest city in Bulgaria. It is also located at foot of the mountain's highest peak Golyam Perelik - 2191m. Smolyan is just 10-15 minutes drive from the popular ski resorts Pamporovo and Chepelare. As of June 2022 it has a population of 30 689 inhabitants. Name The name of the town comes from the local Slavic tribe of the Smolyani, the name of whom is probably cognate to the Slavic word ''smola'' ("resin"). History According to archaeological evidence, the area around Smolyan was first settled in the 2nd millennium BC, 2nd-1st millennium BC. In the Middle Ages it acquired its name from the Slavic peoples, Sla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of , and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Neolithic Karanovo culture, which dates back to 6,500 BC. In the 6th to 3rd century BC the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, tribal invasions in the region resumed. Around the 6th century, these territories were settled by the early Slavs. The Bulgars, led by Asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agha (Ottoman Empire)
Agha ( tr, ağa; ota, آغا; fa, آقا, āghā; "chief, master, lord") is an honorific title for a civilian or officer, or often part of such title. In the Ottoman times, some court functionaries and leaders of organizations like bazaar or the janissary units were entitled to the ''agha'' title. In rural communities, this term is used for people who own considerable lands and are influential in their community. Regardless of a rural community, this title is also used for any male that is influential or respected. Etymology The word ''agha'' entered English from Turkish, and the Turkish word comes from the Old Turkic language, Old Turkic ''aqa'', meaning "elder brother". It is an equivalent of Mongolian language, Mongolian word ''aqa'' or ''aka''. Other uses "Agha" is nowadays used as a common Persian language, Persian honorific title for men, the equivalent of "mister" in English language, English.Khani, S., and R. Yousefi. "The study of address terms and their translatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konak (residence)
Konak ( tr, konak) is a name for a house in Turkey and on the territories of the former Ottoman Empire, especially one used as an official residence. See also * Konak of Durrës *Princess Ljubica's Residence *Residence of Prince Miloš *Museum of Vuk and Dositej *Agushevi konatsi Agushevi konatsi ( bg, Агушеви конаци, "The Agush Agha's Konaks"), built during the 19th century, is a winter estate of the Ottoman feudal who belongend to the Pomaks in the Mogilitsa village in Bulgaria. It is formed of three con ... References Merriam-Webster Unabridged — Konak entry House types Architecture in the Ottoman Empire Architecture in Turkey Turkish words and phrases {{Ottoman-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomaks
Pomaks ( bg, Помаци, Pomatsi; el, Πομάκοι, Pomáki; tr, Pomaklar) are Bulgarian-speaking Muslims inhabiting northwestern Turkey, Bulgaria and northeastern Greece. The c. 220,000 strong ethno-confessional minority in Bulgaria is recognized officially as Bulgarian Muslims by the government. The term has also been used as a wider designation, including also the Slavic Muslim populations of North Macedonia and Albania. Most Pomaks today live in Turkey where they have settled as muhacirs as a result of escaping previous ethnic cleansing in Bulgaria. Bulgaria recognizes their language as a Bulgarian dialect whereas in Greece and Turkey they self-declare their language as the Pomak language. The community in Greece is commonly fluent in Greek, and in Turkey, Turkish, while the communities in these two countries, especially in Turkey, are increasingly adopting Turkish as their first language as a result of education and family links with the Turkish people. They are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mogilitsa
Mogilitsa ( bg, Могилица; also ''Mogilitza'', ''Mogilica'', meaning "hillock") is a village in the Rhodope Mountains in southernmost Bulgaria, part of Smolyan municipality, Smolyan Province. As of September 2005, it has a population of 483. Mogilitsa lies at , 1,041 m above mean sea level, near the border with Greece and the upper course of the river Arda, 35 kilometres southeast of Smolyan. Mogilitsa is famous for ''Agushevi konatsi'' (Агушеви конаци), the 19th-century winter estate of a rich Ottoman feudal lord, Agush Agha (title) who belongend to the Pomaks, and his three son's. Built in 1825-1872 by local Bulgarian masters, the castle-like complex consists of three buildings with a separate yard surrounded by a common wall with a richly-decorated tower in the southeastern corner. The estate has a total of 221 windows, 86 doors and 24 chimneys and is situated near the banks of the Arda. Paşmaklı Smolyan was the main city of Ahiçelebi, Smolyan Province, u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
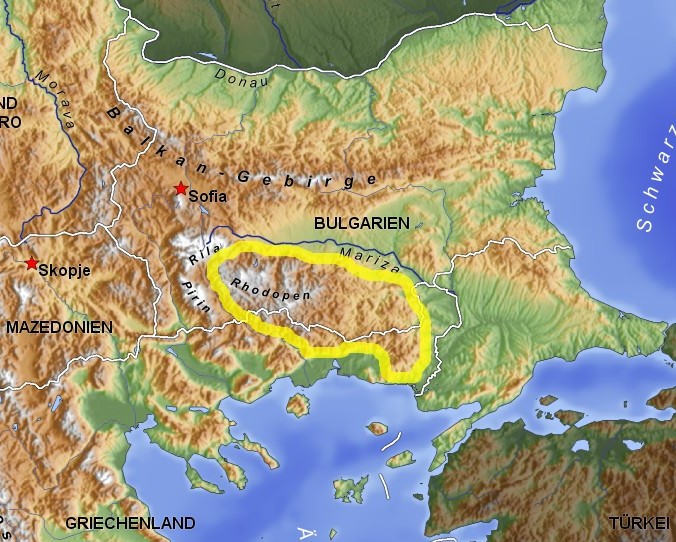
Rhodope Mountains
The Rhodopes (; bg, Родопи, ; el, Ροδόπη, ''Rodopi''; tr, Rodoplar) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at . The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge. A significant part of Bulgaria's hydropower resources are located in the western areas of the range. There are a number of hydro-cascades and dams used for electricity production, irrigation, and as tourist destinations. In Greece, there are also the hydroelectric power plants of Thisavros and Platanovrysi. The Rhodopes have a rich cultural heritage including a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaluk
An Agaluk ( tr, Ağalık) was a feudal unit of the Ottoman Empire governed by an ''agha'' (tax collector landlord). In Bosnian history, an agaluk may often refer to land ''owned'' by an ''aga''. See also *Subdivisions of the Ottoman Empire *Kadiluk *Pashaluk *Sanjak * Timar A timar was a land grant by the sultans of the Ottoman Empire between the fourteenth and sixteenth centuries, with an annual tax revenue of less than 20,000 akçes. The revenues produced from the land acted as compensation for military service. A ..., land granted by the Ottoman sultans between the fourteenth and sixteenth centuries References Subdivisions of the Ottoman Empire Types of administrative division Feudalism in the Ottoman Empire {{Ottoman-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salon (gathering)
A salon is a gathering of people held by an inspiring host. During the gathering they amuse one another and increase their knowledge through conversation. These gatherings often consciously followed Horace's definition of the aims of poetry, "either to please or to educate" (Latin: ''aut delectare aut prodesse''). Salons in the tradition of the French literary and philosophical movements of the 17th and 18th centuries were carried on until as recently as the 1920s in urban settings. Historical background The salon was an Italian invention of the 16th century, which flourished in France throughout the 17th and 18th centuries. The salon continued to flourish in Italy throughout the 19th century. In 16th-century Italy, some brilliant circles formed in the smaller courts which resembled salons, often galvanized by the presence of a beautiful and educated patroness such as Berta Zuckerkandl, Isabella d'Este or Elisabetta Gonzaga. Salons were an important place for the exchange of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castles In Bulgaria
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a palace, which is not fortified; from a fortress, which was not always a residence for royalty or nobility; from a ''pleasance'' which was a walled-in residence for nobility, but not adequately fortified; and from a fortified settlement, which was a public defence – though there are many similarities among these types of construction. Use of the term has varied over time and has also been applied to structures such as hill forts and 19th-20th century homes built to resemble castles. Over the approximately 900 years when genuine castles were built, they took on a great many forms with many different features, although some, such as curtain walls, arrowslits, and portcullises, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tourist Attractions In Smolyan Province
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as being limited to holiday activity only", as people "travelling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure and not less than 24 hours, business and other purposes". Tourism can be domestic (within the traveller's own country) or international, and international tourism has both incoming and outgoing implications on a country's balance of payments. Tourism numbers declined as a result of a strong economic slowdown (the late-2000s recession) between the second half of 2008 and the end of 2009, and in consequence of the outbreak of the 2009 H1N1 influenza virus, but slowly recovered until the COVID-19 pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |