|
Africville, Nova Scotia
Africville was a small community of predominantly African Nova Scotians located in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. It developed on the southern shore of Bedford Basin and existed from the early 1800s to the 1960s. From 1970 to the present, a protest has occupied space on the grounds. The government has recognized it as a commemorative site and established a museum here. The community has become an important symbol of Black Canadian identity, as an example of the "urban renewal" trend of the 1960s that razed similarly racialized neighbourhoods across Canada, and the struggle against racism. Africville was founded by Black Nova Scotians from a variety of origins. Many of the first settlers were formerly enslaved African Americans from the Thirteen Colonies, Black Loyalists who were freed by the Crown during the American Revolutionary War and War of 1812. (Black people settled in Africville along Albemarle Street, where they had a school established in 1785 that served the Black comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornwallis Street Baptist Church
New Horizons Baptist Church is a Baptist church in Halifax, Nova Scotia that was established by Black Refugees in 1832. When the chapel was completed, black citizens of Halifax were reported to be proud because it was evidence that former slaves could establish their own institutions in Nova Scotia. Under the direction of Richard Preston, the church laid the foundation for social action to address the plight of Black Nova Scotians. History Preston and others established a network of socially active Black baptist churches throughout Nova Scotia, with the Halifax church being referred to as the "Mother Church." Five of these churches were established in Halifax: Preston (1842), Beechville (1844), Hammonds Plains (1845), and another in Africville (1849) and Dartmouth. From meetings held at the church, they also established the African Friendly Society, the African Abolition Society, and the African United Baptist Association of Nova Scotia (AUBA). In the fight to end slavery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halifax Explosion
On the morning of 6 December 1917, the French cargo ship collided with the Norwegian vessel in the waters of Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. The ''Mont-Blanc'', laden with high explosives, caught fire and exploded, devastating the Richmond district of Halifax. 1,782 people were killed, largely in Halifax and Dartmouth, by the blast, debris, fires, or collapsed buildings, and an estimated 9,000 others were injured. The blast was the largest human-made explosion at the time, releasing the equivalent energy of roughly . ''Mont-Blanc'' was under orders from the French government to carry her cargo from New York City via Halifax to Bordeaux, France. At roughly 8:45 am, she collided at low speed, approximately one knot (), with the unladen ''Imo'', chartered by the Commission for Relief in Belgium to pick up a cargo of relief supplies in New York. On the ''Mont-Blanc'', the impact damaged benzol barrels stored on deck, leaking vapours which were ignited by sparks from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian National Railways
The Canadian National Railway Company (french: Compagnie des chemins de fer nationaux du Canada) is a Canadian Class I railroad, Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern United States, Midwestern and Southern United States. CN is Canada's largest railway, in terms of both revenue and the physical size of its rail network, spanning Canada from the Atlantic coast in Nova Scotia to the Pacific coast in British Columbia across approximately of track. In the late 20th century, CN gained extensive capacity in the United States by taking over such railroads as the Illinois Central. CN is a public company with 22,600 employees, and it has a market cap of approximately CA$90 billion. CN was government-owned, having been a Crown corporations of Canada, Canadian Crown corporation from its founding in 1919 until being privatized in 1995. , Bill Gates is the largest single shareholder of CN stock, owning a 14.2% interest throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halifax And Southwestern Railway
The Halifax and South Western Railway was a historic Canadian railway operating in the province of Nova Scotia. The legal name of this railway was the Halifax & South Western Railway, as is defined in various Acts of the Nova Scotia Legislature, such as 1902 c.1, Act respecting the Halifax & South Western Railway Co.. However, Halifax & Southwestern Railway is also sometimes also used. The H&SW was created in spring 1901 when William Mackenzie and Donald Mann approached the provincial government with plans to finish the abortive plans for a railway from Halifax to Yarmouth along the province's South Shore. For many years, the line had significant curvature throughout its length, a result of the rugged local topography, which earned it the moniker, "Hellish Slow & Wobbly". Predecessors The H&SW was not the first railway to build on the South Shore of Nova Scotia, as various charters for railway companies had preceded it. The Nova Scotia Central Railway (NSCR) had opened its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richmond, Nova Scotia
Richmond was a Canadian urban neighbourhood comprising part of the North End of the Halifax Peninsula in Nova Scotia's Halifax Regional Municipality. History Formerly a separately incorporated part of Halifax County, the village of Richmond grew north of North Street, the traditional dividing line with the City of Halifax's original North End. Located on the western shore of The Narrows of Halifax Harbour, Richmond soon industrialized after the Nova Scotia Railway built along the shore to serve the navy dockyard and various shipping piers and warehouses. Richmond was amalgamated into the City of Halifax during the late 19th century and its traditional boundary was blurred as the area became absorbed into the expanding North End. Richmond was devastated on December 6, 1917 when the Halifax Explosion levelled much of its structures and waterfront. The rising slope of Fort Needham protected some areas from the immediate effects of the shock wave. The Halifax Relief Commission, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercolonial Railway
The Intercolonial Railway of Canada , also referred to as the Intercolonial Railway (ICR), was a historic Canadian railway that operated from 1872 to 1918, when it became part of Canadian National Railways. As the railway was also completely owned and controlled by the Government of Canada, the Intercolonial was also one of Canada's first Crown corporations. Origins The idea of a railway connecting Britain's North American colonies arose as soon as the railway age began in the 1830s. In the decades following the War of 1812 and ever-mindful of the issue of security, the colonies of Upper and Lower Canada (later the Province of Canada after 1840) wished to improve land-based transportation with the Atlantic coast colonies of Nova Scotia and New Brunswick, and to a lesser extent Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland. A railway connection from the Province of Canada to the British colonies on the coast would serve a vital military purpose during the winter months when the waters o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
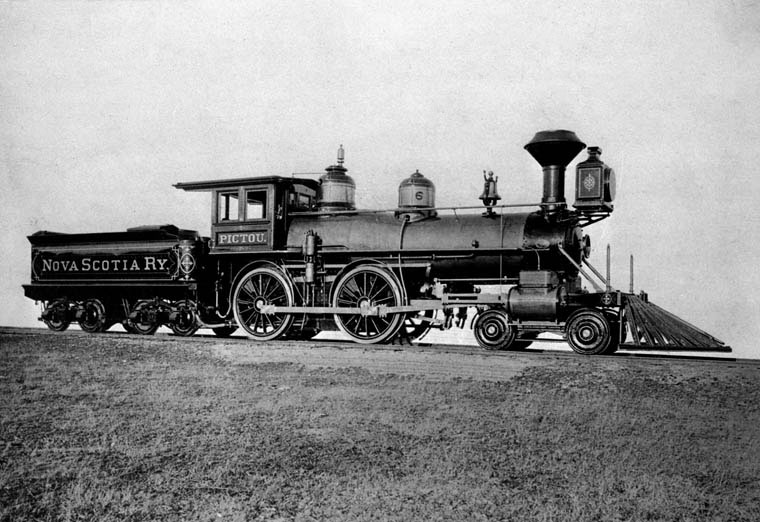
Nova Scotia Railway
The Nova Scotia Railway is a historic Canadian railway. It was composed of two lines, one connecting Richmond (immediately north of Halifax) with Windsor, the other connecting Richmond with Pictou Landing via Truro. The railway was incorporated March 31, 1853 and received a charter to build railway lines from Halifax to Pictou by way of Truro, as well as from Halifax to Victoria Beach, Nova Scotia on the Annapolis Basin opposite Digby by way of Windsor. The company also received a charter to build from Truro to the border with New Brunswick. The railway was a key project of the visionary Nova Scotian leader Joseph Howe who felt a government built railway led by Nova Scotia was necessary after the failure of the Intercolonial Railway talks and several fruitless private proposals. The railway line to Windsor (known as the Windsor Branch) was opened in June 1858 and the line to Truro (known as the Eastern Line) was opened in December 1858. No further work was undertaken on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septimus Clarke
Septimus D. Clarke (1787–1859) was a farmer and leader within the Black community in Nova Scotia. Clarke was one of thousands of Black refugees who escaped slavery in the United States during the War of 1812 and migrated to the British colony of Nova Scotia. Little is known of his life before November 1816, by which time he, his wife, and four children had established a farm of about . In 1819, having cleared and planted all the land he had been granted, Clarke petitioned Governor Dalhousie for an additional , as the family required more trees for fuel. Dalhousie appears to have been swayed by the request, suggesting a grant of , although Surveyor General Charles Morris scaled the grant back further to . His was the first successful request for additional land by a Black immigrant, and encouraged others to apply for similar grants. Clarke was active in a number of organizations within the Black community. In 1854 he cofounded the African United Baptist Association of Nova Scoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dartmouth, Nova Scotia
Dartmouth ( ) is an urban community and former city located in the Halifax Regional Municipality of Nova Scotia, Canada. Dartmouth is located on the eastern shore of Halifax Harbour. Dartmouth has been nicknamed the City of Lakes, after the large number of lakes located within its boundaries. On April 1, 1996, the provincial government amalgamated all the municipalities within the boundaries of Halifax County into a single-tier regional government named the Halifax Regional Municipality (HRM). Dartmouth and its neighbouring city of Halifax, the town of Bedford and the Municipality of the County of Halifax were dissolved. The city of Dartmouth forms part of the urban core of the larger regional municipality and is officially designated as part of the "capital district" by the Halifax Regional Municipality. At the time that the City of Dartmouth was dissolved, the provincial government altered its status to a separate community to Halifax; however, its status as part of the metrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammonds Plains, Nova Scotia
Hammonds Plains is a community within the urban area of Municipality of Halifax, in Nova Scotia, Canada. History Hammonds Plains was established as a settlement area for United Empire Loyalists in 1786 along a road running from Birch Cove on Bedford Basin to St. Margaret's Bay. Landowners voted to name the road after the popular outgoing Lt. Governor Andrew Snape Hamond. Further settlers arrived with disbanded soldiers from the Napoleonic Wars and Black Refugees from the War of 1812. The settlement was also the eastern end of the Old Annapolis Road intended to create a settled corridor and transportation link between Halifax and Annapolis Royal. While the Annapolis Road never developed, settlement opened up the a modest amount of viable farmland and more significantly developed many saw mills. Geography The Government of Nova Scotia defines Hammonds Plains as adjacent to Bedford-and- Lucasville to the east; Upper Sackville-and- Middle Sackville to the north; Stillwater Lak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beechville, Nova Scotia
Beechville (pop. 2,100) is a Black Nova Scotian settlement and suburban community within the Halifax Regional Municipality of Nova Scotia, Canada, on the St. Margaret's Bay Road ( Trunk 3). The Beechville Lakeside Timberlea (BLT) trail starts here near Lovett Lake, following the line of the old Halifax and Southwestern Railway. Ridgecliff Middle School, located in Beechville Estates, serves the communities of Beechville, Lakeside and Timberlea. History In 1816, the first Black refugees from the War of 1812 arrived in Beechville (aka Beech Hill). The early settlers of the community were refugee Blacks fleeing from the southern American colonies. They were given a grant of five thousand acres (20 km²) close to the Northwest Arm in an area to be known as Refugee Hill. In 1821 ninety-six adults resettled in Trinidad. The Beechville community spiritual leadership was under the care of Baptist Pastor, Rev. John Burton from England. Rev. Burton preached in Beechville as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
