|
Aeroflot Flight 315 (1960)
Aeroflot Flight 315 (1960) was a regularly scheduled passenger flight operated by Aeroflot from Vnukovo International Airport in Moscow to Lviv Airport in Lviv, Ukraine. On 26 February 1960, the An-10 operating this flight crashed short of the airport runway while on final approach. 24 passengers and eight crew members were killed, one passenger survived. The Air Accident Investigation Commission concluded the cause of the accident was a combination of design flaw and icing. Accident Flight 315 departed Vnukovo Airport at 14:38 Moscow time, and was cleared to climb to 7,000 meters. At 16:35 as the airliner approached Lviv the crew received clearance to descend to 4,000 meters. Weather was reported as a cloud base of 150-200 meters in icing conditions with visibility at three km. The descent was normal and the pilot reported reaching the marker beacon at an altitude of 200 meters, the flight was then cleared to land. When the aircraft penetrated the cloud base the crew switch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loss Of Control (aeronautics)
In aeronautics, loss of control (LOC) is the unintended departure of an aircraft from controlled flight, and is a significant factor in several Aviation accidents and incidents, aviation accidents worldwide and the leading cause of jet fatalities worldwide. Loss of control may be the result of mechanical failure, external disturbances, aircraft upset conditions, or inappropriate crew actions or responses. Causes Aircraft experiencing a loss of control depart from normal flight and can reach attitudes or situations from which it is impossible for them to be recovered. Due to the certification and design processes, it is extremely rare for aircraft to experience a loss of control without extreme mishandling or a technical defect. A NASA study on aircraft loss of control causal factors and mitigation challenges developed a preliminary list of causal factors that contribute to loss of control compiled through interviews, reviews of accident reports and team analysis of available dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Principal Axes
An aircraft in flight is free to rotate in three dimensions: '' yaw'', nose left or right about an axis running up and down; ''pitch'', nose up or down about an axis running from wing to wing; and ''roll'', rotation about an axis running from nose to tail. The axes are alternatively designated as ''vertical'', ''lateral'' (or ''transverse''), and ''longitudinal'' respectively. These axes move with the vehicle and rotate relative to the Earth along with the craft. These definitions were analogously applied to spacecraft when the first manned spacecraft were designed in the late 1950s. These rotations are produced by torques (or moments) about the principal axes. On an aircraft, these are intentionally produced by means of moving control surfaces, which vary the distribution of the net aerodynamic force about the vehicle's center of gravity. Elevators (moving flaps on the horizontal tail) produce pitch, a rudder on the vertical tail produces yaw, and ailerons (flaps on the win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviation Accidents And Incidents In The Soviet Union
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air balloons and airships. Aviation began in the 18th century with the development of the hot air balloon, an apparatus capable of atmospheric displacement through buoyancy. Some of the most significant advancements in aviation technology came with the controlled gliding flying of Otto Lilienthal in 1896; then a large step in significance came with the construction of the first powered airplane by the Wright brothers in the early 1900s. Since that time, aviation has been technologically revolutionized by the introduction of the jet which permitted a major form of transport throughout the world. Etymology The word ''aviation'' was coined by the French writer and former naval officer Gabriel La Landelle in 1863. He derived the term from the v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviation Accidents And Incidents In 1960
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air balloons and airships. Aviation began in the 18th century with the development of the hot air balloon, an apparatus capable of atmospheric displacement through buoyancy. Some of the most significant advancements in aviation technology came with the controlled gliding flying of Otto Lilienthal in 1896; then a large step in significance came with the construction of the first powered airplane by the Wright brothers in the early 1900s. Since that time, aviation has been technologically revolutionized by the introduction of the jet which permitted a major form of transport throughout the world. Etymology The word ''aviation'' was coined by the French writer and former naval officer Gabriel La Landelle in 1863. He derived the term from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
November 1960 Events In Europe
November is the eleventh and penultimate month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian Calendars, the fourth and last of four months to have a length of 30 days and the fifth and last of five months to have a length of fewer than 31 days. November was the ninth month of the calendar of Romulus . November retained its name (from the Latin ''novem'' meaning "nine") when January and February were added to the Roman calendar. November is a month of late spring in the Southern Hemisphere and late autumn in the Northern Hemisphere. Therefore, November in the Southern Hemisphere is the seasonal equivalent of May in the Northern Hemisphere and vice versa. In Ancient Rome, Ludi Plebeii was held from November 4–17, Epulum Jovis was held on November 13 and Brumalia celebrations began on November 24. These dates do not correspond to the modern Gregorian calendar. November was referred to as Blōtmōnaþ by the Anglo-Saxons. Brumaire and Frimaire were the months on which November fell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeroflot Accidents And Incidents In The 1960s
Following is a list of accidents and incidents Aeroflot experienced in the 1960s. The deadliest event the Soviet Union's flag carrier went through in the decade occurred in , when an Ilyushin Il-18V crashed upside down shortly after takeoff from Koltsovo Airport in Sverdlovsk, then located in the Russian SSR, killing all 107 occupants on board, prompting the temporary grounding of the type within the airline's fleet. In terms of fatalities, the accident ranks as the fifth worst involving an Il-18, . Another aircraft of the type was involved in the second deadliest accident the airline experienced in the decade, this time in , when 87 people were killed when the aircraft struck a hillside on approach to Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk. The decade was also marked by the only deadly accident experienced by a Tupolev Tu-114, which entered commercial service on the Moscow–Khabarovsk route in . The number of recorded fatalities aboard Aeroflot aircraft during the decade rose to 1801; likewise, 175 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeroflot Accidents And Incidents
Founded in 1923, Aeroflot, the flag carrier and largest airline of Russia (and formerly the Soviet Union) (formerly the world's largest airline), has had a high number of fatal crashes, with a total of 8,231 passengers dying in Aeroflot crashes according to the Aircraft Crashes Record Office, mostly during the Soviet-era, about five times more than any other airline. From 1946 to 1989, the carrier was involved in 721 incidents. From 1995 to 2017, the carrier was involved in 10 incidents. In 2013, AirlineRatings.com reported that five of the ten aircraft models involved in the highest numbers of fatal accidents were old Soviet models. Following is a list of accidents and incidents Aeroflot experienced from 1932 to the present. 1930s 1940s 1950s 1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s * On 21 September 2001, Ilyushin Il-86 (RA-86074) landed gear-up at Dubai Airport due to pilot error; all 322 passengers and crew survived, but the aircraft was written off. The aircraft was ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
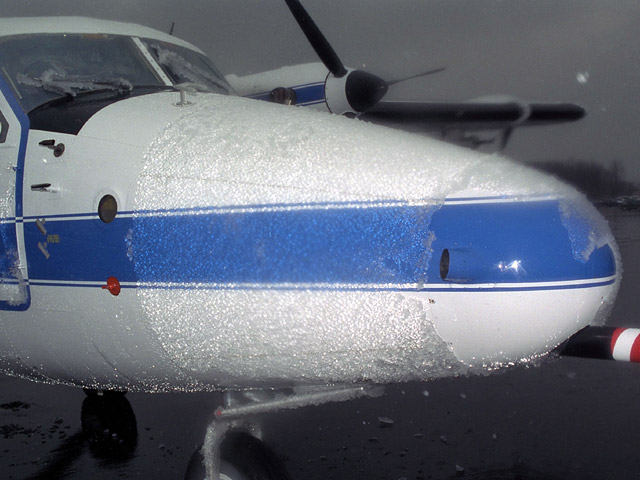
Ice Protection Systems
In aeronautics, ice protection systems keep atmospheric moisture from accumulating on aircraft surfaces, such as wings, propellers, rotor blades, engine intakes, and environmental control intakes. Ice buildup can change the shape of airfoils and flight control surfaces, degrading control and handling characteristics as well as performance. An anti-icing, de-icing, or ice protection system either prevents formation of ice, or enables the aircraft to shed the ice before it becomes dangerous. Effects of icing Aircraft icing increases weight and drag, decreases lift, and can decrease thrust. Ice reduces engine power by blocking air intakes. When ice builds up by freezing upon impact or freezing as runoff, it changes the aerodynamics of the surface by modifying the shape and the smoothness of the surface which increases drag, and decreases wing lift or propeller thrust. Both a decrease in lift on the wing due to an altered airfoil shape, and the increase in weight from the ice loa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Of Attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a reference line on a body (often the chord line of an airfoil) and the vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is moving. Angle of attack is the angle between the body's reference line and the oncoming flow. This article focuses on the most common application, the angle of attack of a wing or airfoil moving through air. In aerodynamics, angle of attack specifies the angle between the chord line of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft and the vector representing the relative motion between the aircraft and the atmosphere. Since a wing can have twist, a chord line of the whole wing may not be definable, so an alternate reference line is simply defined. Often, the chord line of the root of the wing is chosen as the reference line. Another choice is to use a horizontal line on the fuselage as the reference line (and also as the longitudinal axis). Some aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tailplane
A tailplane, also known as a horizontal stabiliser, is a small lifting surface located on the tail (empennage) behind the main lifting surfaces of a fixed-wing aircraft as well as other non-fixed-wing aircraft such as helicopters and gyroplanes. Not all fixed-wing aircraft have tailplanes. Canards, tailless and flying wing aircraft have no separate tailplane, while in V-tail aircraft the vertical stabiliser, rudder, and the tail-plane and elevator are combined to form two diagonal surfaces in a V layout. The function of the tailplane is to provide stability and control. In particular, the tailplane helps adjust for changes in position of the centre of pressure or centre of gravity caused by changes in speed and attitude, fuel consumption, or dropping cargo or payload. Tailplane types The tailplane comprises the tail-mounted fixed horizontal stabiliser and movable elevator. Besides its planform, it is characterised by: *Number of tailplanes - from 0 ( tailless or canard) t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeroflot Flight 315 (1959)
Aeroflot Flight 315 was a regularly scheduled passenger flight operated by Aeroflot from Vnukovo International Airport in Moscow to Lviv Airport in Lviv, Ukraine. On 16 November 1959, the Antonov An-10 operating this flight crashed short of the airport runway while on final approach. All 32 passengers and eight crew members were killed. The Air Accident Investigation Commission concluded the cause of the accident was a combination of design flaw and icing. Accident Flight 315 departed Vnukovo Airport at 16:48 Moscow time, and was cleared to climb to 7,000 meters. As the airliner approached Lviv the weather was reported as temperature -1 degree C, humidity 97% with visibility at three km and the possibility of icing conditions. The descent was normal and the pilot reported reaching the outer marker at an altitude of 200 meters. Before reaching the inner marker the aircraft descended out of the clouds and the crew switched to visual flight rules (VFR). At 19:06 while descending ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flap (aeronautics)
A flap is a high-lift device used to reduce the stall (flight), stalling speed of an aircraft wing at a given weight. Flaps are usually mounted on the wing trailing edges of a fixed-wing aircraft. Flaps are used to reduce the take-off distance and the landing distance. Flaps also cause an increase in Drag (physics), drag so they are retracted when not needed. The flaps installed on most aircraft are partial-span flaps; spanwise from near the wing root to the inboard end of the ailerons. When partial-span flaps are extended they alter the spanwise lift distribution on the wing by causing the inboard half of the wing to supply an increased proportion of the lift, and the outboard half to supply a reduced proportion of the lift. Reducing the proportion of the lift supplied by the outboard half of the wing is accompanied by a reduction in the angle of attack on the outboard half. This is beneficial because it increases the margin above the Stall (fluid dynamics), stall of the outboa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |