|
Aeolis Mensae
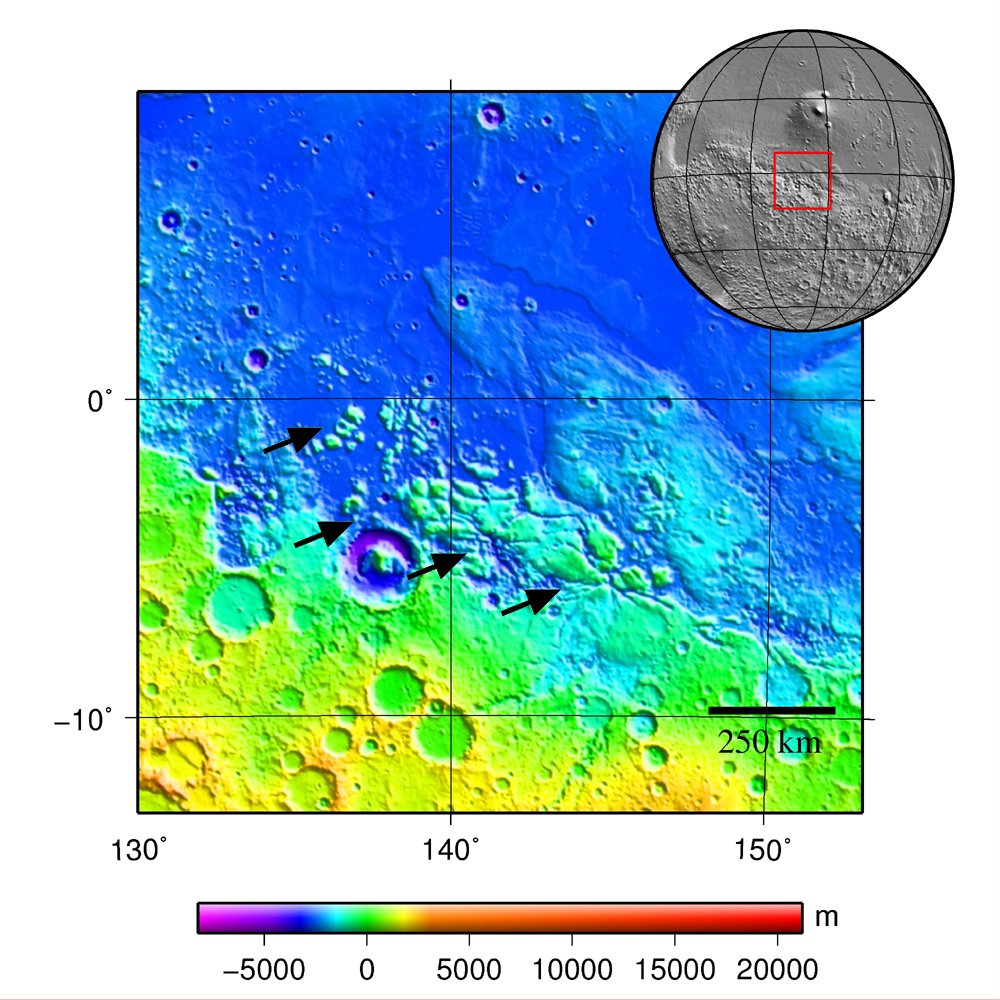
Aeolis Mensae is a tableland feature in the northwest Aeolis quadrangle of Mars. Its location is centered at 2.9° south latitude and 219.6° west longitude, in the transition zone between the Martian highlands and lowlands. It is long and was named after a classical albedo feature (Aeolis). The constituent mensae can be as long as and as tall as . It is notable for being the origin of an abnormal concentration of methane detected by ''Curiosity'' in 2019, although its geology has attracted scientific attention since at least a decade before this event. Aeolis Mensae is also the first region in Mars where submarine cyclic steps, an erosion feature that gives evidence of an ancient ocean, were identified. Observation history It was named in 1976, and examined in detail by Mars Express's HRSC camera in 2007. The ''Curiosity'' rover landed in the neighboring Gale Crater in 2012, and since then the area has received limited but continued attention from both ESA's HRSC an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
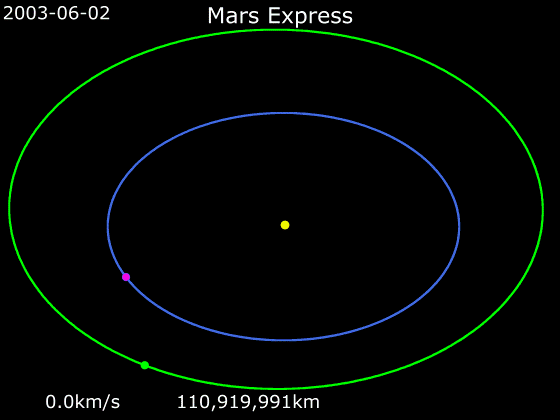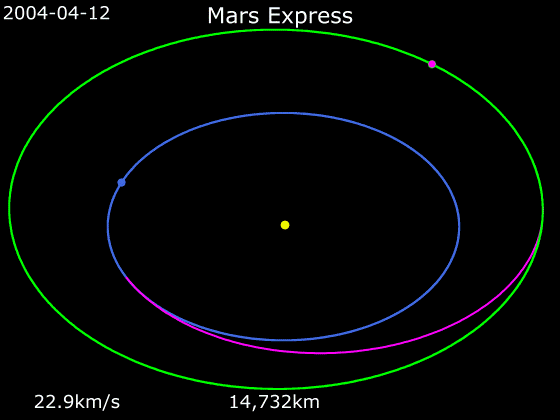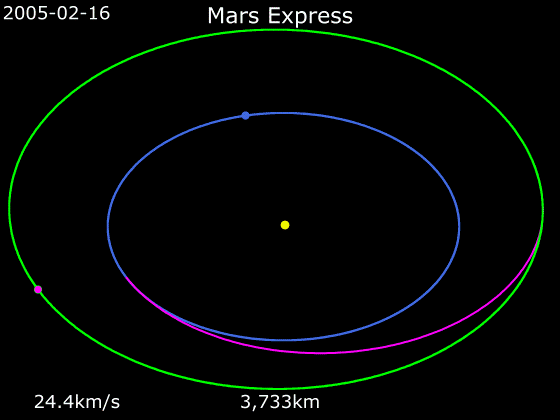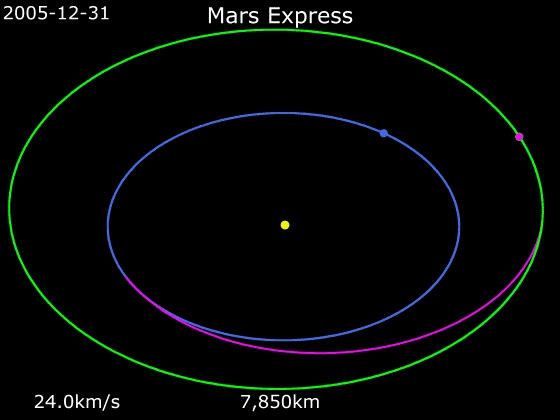
Mars Express
''Mars Express'' is a space exploration mission being conducted by the European Space Agency (ESA). The ''Mars Express'' mission is exploring the planet Mars, and is the first planetary mission attempted by the agency. "Express" originally referred to the speed and efficiency with which the spacecraft was designed and built. However, "Express" also describes the spacecraft's relatively short interplanetary voyage, a result of being launched when the orbits of Earth and Mars brought them closer than they had been in about 60,000 years. ''Mars Express'' consists of two parts, the ''Mars Express Orbiter'' and ''Beagle 2'', a lander designed to perform exobiology and geochemistry research. Although the lander failed to fully deploy after it landed on the Martian surface, the orbiter has been successfully performing scientific measurements since early 2004, namely, high-resolution imaging and mineralogical mapping of the surface, radar sounding of the subsurface structure down to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOLA Aeolis Mensae
Mola can refer to: Places * La Mola, Formentera, Balearic Islands, Spain * Lake Mola, a lake near Ilirska Bistrica, Inner Carniola region, Slovenia * Mola di Bari, or simply Mola, a city in Apulia, Southern Italy Mountains *Mola de Colldejou, a mountain chain in Catalonia, Spain *Mola dels Quatre Termes, a mountain in Catalonia, Spain * Mola del Guerxet, a mountain in Catalonia, Spain *Mola Gran, a mountain in the Valencian Community, Spain *Mola de Llaberia, a mountain in Catalonia, Spain Museums * Museum of the Living Artist (MoLA), a new exhibition of works by San Diego artists * Museum of London Archaeology (MOLA), an archaeological organisation and charity (formerly part of the Museum of London) * Museum of Living Art (MOLA), an exhibition at Fort Worth Zoo, USA People * Mola Ram (1743–1833), Indian painter * Mola Sylla (born 1956), Senegalese musician * Carlos Loret de Mola (born 1976), Mexican journalist * Carlos Loret de Mola Mediz (1921–1986), Mexican politician a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elysium Planitia
Elysium Planitia, located in the Elysium and Aeolis quadrangles, is a broad plain that straddles the equator of Mars, centered at . It lies to the south of the volcanic province of Elysium, the second largest volcanic region on the planet, after Tharsis. Elysium contains the major volcanoes Elysium Mons, Albor Tholus and Hecates Tholus. Another more ancient shield volcano, Apollinaris Mons, is situated just to the south of eastern Elysium Planitia. Within the plains, Cerberus Fossae is the only Mars location with recent volcanic eruptions. Lava flows dated no older than 0.2 million years from the present have been found, and evidence has been found that volcanic activity may have occurred as recently as 53,000 years ago. Such activity could have provided the environment, in terms of energy and chemicals, needed to support life forms. The largest craters in Elysium Planitia are Eddie, Lockyer, and Tombaugh. The planitia also has river valleys—one of which, Athabasca Val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V-shaped Valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between Hill, hills or Mountain, mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over a very long period. Some valleys are formed through erosion by glacier, glacial ice. These glaciers may remain present in valleys in high mountains or polar areas. At lower latitudes and altitudes, these glaciation, glacially formed valleys may have been created or enlarged during ice ages but now are ice-free and occupied by streams or rivers. In desert areas, valleys may be entirely dry or carry a watercourse only rarely. In karst, areas of limestone bedrock, dry valleys may also result from drainage now taking place cave, underground rather than at the surface. Rift valleys arise principally from tectonics, earth movements, rather than erosion. Many different types of valleys are described by geographers, using terms th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U-shaped Valley
U-shaped valleys, also called trough valleys or glacial troughs, are formed by the process of glaciation. They are characteristic of mountain glaciation in particular. They have a characteristic U shape in cross-section, with steep, straight sides and a flat or rounded bottom (by contrast, valleys carved by rivers tend to be V-shaped in cross-section). Glaciated valleys are formed when a glacier travels across and down a slope, carving the valley by the action of scouring. When the ice recedes or thaws, the valley remains, often littered with small boulders that were transported within the ice, called glacial till or glacial erratic. Examples of U-shaped valleys are found in mountainous regions throughout the world including the Andes, Alps, Caucasus Mountains, Himalaya, Rocky Mountains, New Zealand and the Scandinavian Mountains. They are found also in other major European mountains including the Carpathian Mountains, the Pyrenees, the Rila and Pirin mountains in Bulgaria, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesperian
The Hesperian is a system (stratigraphy), geologic system and geologic timescale, time period on the planet Mars characterized by widespread Volcanology of Mars, volcanic activity and catastrophic flooding that carved immense outflow channels across the surface. The Hesperian is an intermediate and transitional period of Martian history. During the Hesperian, Mars changed from the wetter and perhaps warmer world of the Noachian (Mars), Noachian to the dry, cold, and dusty planet seen today. The absolute age of the Hesperian Period is uncertain. The beginning of the period followed the end of the Late Heavy Bombardment and probably corresponds to the start of the lunar Late Imbrian period, around 3700 million years ago (Myr, Mya). The end of the Hesperian Period is much more uncertain and could range anywhere from 3200 to 2000 Mya, with 3000 Mya being frequently cited. The Hesperian Period is roughly coincident with the Earth's early Archean Eon. With the decline of heavy impacts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noachian
The Noachian is a geologic system and early time period on the planet Mars characterized by high rates of meteorite and asteroid impacts and the possible presence of abundant surface water. The absolute age of the Noachian period is uncertain but probably corresponds to the lunar Pre-Nectarian to Early Imbrian periods of 4100 to 3700 million years ago, during the interval known as the Late Heavy Bombardment. Many of the large impact basins on the Moon and Mars formed at this time. The Noachian Period is roughly equivalent to the Earth's Hadean and early Archean eons when the first life forms likely arose. Noachian-aged terrains on Mars are prime spacecraft landing sites to search for fossil evidence of life. During the Noachian, the atmosphere of Mars was denser than it is today, and the climate possibly warm enough to allow rainfall. Large lakes and rivers were present in the southern hemisphere, and an ocean may have covered the low-lying northern plains. Extensive volc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fretted Terrain
Fretted terrain is a type of surface feature common to certain areas of Mars and was discovered in Mariner 9 images. It lies between two different types of terrain. The surface of Mars can be divided into two parts: low, young, uncratered plains that cover most of the northern hemisphere, and high-standing, old, heavily cratered areas that cover the southern and a small part of the northern hemisphere. Between these two zones is a region called the Martian dichotomy and parts of it contain fretted terrain. This terrain contains a complicated mix of cliffs, mesas, buttes, and straight-walled and sinuous canyons. It contains smooth, flat lowlands along with steep cliffs. The scarps or cliffs are usually 1 to 2 km high. Channels in the area have wide, flat floors and steep walls. Fretted terrain shows up in northern Arabia, between latitudes 30°N and 50°N and longitudes 270°W and 360°W, and in Aeolis Mensae, between 10 N and 10 S latitude and 240 W and 210 W longitude.I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacial Groove
Glacial striations or striae are scratches or gouges cut into bedrock by glacial abrasion. These scratches and gouges were first recognized as the result of a moving glacier in the late 18th century when Swiss alpinists first associated them with moving glaciers. They also noted that if they were visible today that the glaciers must also be receding. Glacial striations are usually multiple, straight, and parallel, representing the movement of the glacier using rock fragments and sand grains, embedded in the base of the glacier, as cutting tools. Large amounts of coarse gravel and boulders carried along underneath the glacier provide the abrasive power to cut trough-like ''glacial grooves''. Finer sediments also in the base of the moving glacier further scour and polish the bedrock surface, forming a ''glacial pavement''. Ice itself is not a hard enough material to change the shape of rock but because the ice has rock embedded in the basal surface it can effectively abrade the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeolis Mensae Yardangs
Aeolis (; grc, Αἰολίς, Aiolís), or Aeolia (; grc, Αἰολία, Aiolía, link=no), was an area that comprised the west and northwestern region of Asia Minor (modern-day Turkey), mostly along the coast, and also several offshore islands (particularly Lesbos), where the Aeolian Greek city-states were located. Aeolis incorporated the southern parts of Mysia, and is bounded by it to the north, Ionia to the south, and Lydia to the east. Geography Aeolis was an ancient district on the western coast of Asia Minor. It extended along the Aegean Sea from the entrance of the Hellespont (now the Dardanelles) south to the Hermus River (now the Gediz River). It was named for the Aeolians, some of whom migrated there from Greece before 1000 BC. Aeolis was, however, an ethnological and linguistic enclave rather than a geographical unit. The district often was considered part of the larger northwest region of Mysia. History According to Homer's ''Odyssey'', Odysseus, after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazonian (Mars)
The Amazonian is a geologic system and time period on the planet Mars characterized by low rates of meteorite and asteroid impacts and by cold, hyperarid conditions broadly similar to those on Mars today.Carr, M.H. (2006), The Surface of Mars. Cambridge Planetary Science Series, Cambridge University Press. The transition from the preceding Hesperian period is somewhat poorly defined. The Amazonian is thought to have begun around 3 billion years ago, although error bars on this date are extremely large (~500 million years). The period is sometimes subdivided into the Early, Middle, and Late Amazonian. The Amazonian continues to the present day. The Amazonian period has been dominated by impact crater formation and Aeolian processes with ongoing isolated volcanism occurring in the Tharsis and Cerberus Fossae, including signs of activity as recently as a tens of thousands of years ago in the latter and within the past few million years on Olympus Mons, implying they may still be a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methane On Mars
The reported presence of methane in the atmosphere of Mars is of interest to many geologists and astrobiologists, as methane may indicate the presence of microbial life on Mars, or a geochemical process such as volcanism or hydrothermal activity. Since 2004, trace amounts of methane (range from 60 ppbv to under detection limit (< 0.05 ppbv)) have been reported in various missions and observational studies. The source of methane on Mars and the explanation for the enormous discrepancy in the observed methane concentrations are still unknown and are under study. Whenever methane is detected, it is rapidly removed from the atmosphere by an efficient, yet unknown process. History of detections  [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |