|
Adventure-class Ship
The ''Adventure''-class ship was a class of eight 44-gun sailing two-decker warships of the Royal Navy, classed as a fifth rate like a frigate, but carrying two complete decks of guns, a lower battery of 18-pounders and an upper battery of 12-pounders. This enabled the vessel to deliver a broadside of 318 pounds. The class was designed in 1782 by Edward Hunt, Surveyor of the Navy, as a successor to the Roebuck class ship, ''Roebuck'' class design of Sir Thomas Slade. The design saw a slight increase in breadth over the ''Roebuck'' class, but was otherwise very similar. Like the ''Roebuck'' class, the ''Adventure'' class were not counted by the Admiralty as frigates; although sea officers sometimes casually described them and other small two-deckers as frigates, the Admiralty officially never referred to them as such. By 1750, the Admiralty strictly defined frigates as ships of 28 guns or more, carrying all their main battery (24, 26 or even 28 guns) on the upper deck, with no gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full-rigged Ship
A full-rigged ship or fully rigged ship is a sailing vessel's sail plan with three or more masts, all of them square-rigged. A full-rigged ship is said to have a ship rig or be ship-rigged. Such vessels also have each mast stepped in three segments: lower mast, top mast, and topgallant mast. Other large, multi-masted sailing vessels may be regarded as ships while lacking one of the elements of a full-rigged ship, e.g. having one or more masts support only a fore-and-aft sail or having a mast that only has two segments. Masts The masts of a full-rigged ship, from bow to stern, are: * Foremast, which is the second tallest mast * Mainmast, the tallest * Mizzenmast, the third tallest * Jiggermast, which may not be present but will be fourth tallest if so If the masts are of wood, each mast is in three or more pieces. They are (in order, from bottom up): * The lowest piece is called the ''mast'' or the ''lower''. * Topmast * Topgallant mast * Royal mast, if fitted On steel-m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Sheerness (1787)
Seven ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS ''Sheerness'', after the town of Sheerness in Kent, once home to one of the navy's dockyards: * was a 2-gun smack launched in 1673 and sunk as a foundation in 1695. * was a 32-gun fifth rate launched in 1691, rebuilt in 1731 and sold in 1744. * was a 24-gun sixth rate launched in 1743 and sold in 1768. * was a store lighter launched in 1759 and broken up in 1811. * was a 44-gun fifth rate launched in 1787 and wrecked in 1805. Because ''Sheerness'' served in the navy's Egyptian campaign (8 March to 2 September 1801), her officers and crew qualified for the clasp "Egypt" to the Naval General Service Medal, which the Admiralty Admiralty most often refers to: *Admiralty, Hong Kong * Admiralty (United Kingdom), military department in command of the Royal Navy from 1707 to 1964 *The rank of admiral * Admiralty law Admiralty can also refer to: Buildings *Admiralty, Tr ... issued in 1847 to all surviving claimants. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Gorgon (1785)
HMS ''Gorgon'' was a 44-gun fifth-rate two-decker ship of the of 911 tons, launched at Blackwall Yard in 1785 and completed as a troopship. She was subsequently converted to a storeship. She also served as a guardship and a hospital ship at various times before being broken up in 1817. Troopship ''Gorgon'' was fitted as a troopship at Portsmouth at a cost of £5,210, the work being completed on 15 December 1787. Lieutenant Charles Craven commissioned her in October 1787. She then was paid off one year later. One year after that, she was fitted for foreign service at an additional cost of £5,200 and recommissioned under Lieutenant William Harvey in October 1789. New South Wales Under Commander John Parker (c1749–1794), she went to New South Wales on 15 March 1791, along with the Third Fleet, arriving on 21 September 1791. She carried six months provisions for 900 people in the starving colony. She also carried about 30 convicts, and Philip Gidley King, who was returning to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deptford Dockyard
Deptford Dockyard was an important naval dockyard and base at Deptford on the River Thames, operated by the Royal Navy from the sixteenth to the nineteenth centuries. It built and maintained warships for 350 years, and many significant events and ships have been associated with it. Founded by Henry VIII in 1513, the dockyard was the most significant royal dockyard of the Tudor period and remained one of the principal naval yards for three hundred years. Important new technological and organisational developments were trialled here, and Deptford came to be associated with the great mariners of the time, including Francis Drake and Walter Raleigh. The yard expanded rapidly throughout the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, encompassing a large area and serving for a time as the headquarters of naval administration, and the associated Victualling Yard became the Victualling Board's main depot. Tsar Peter the Great visited the yard officially incognito in 1698 to learn shipbuildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
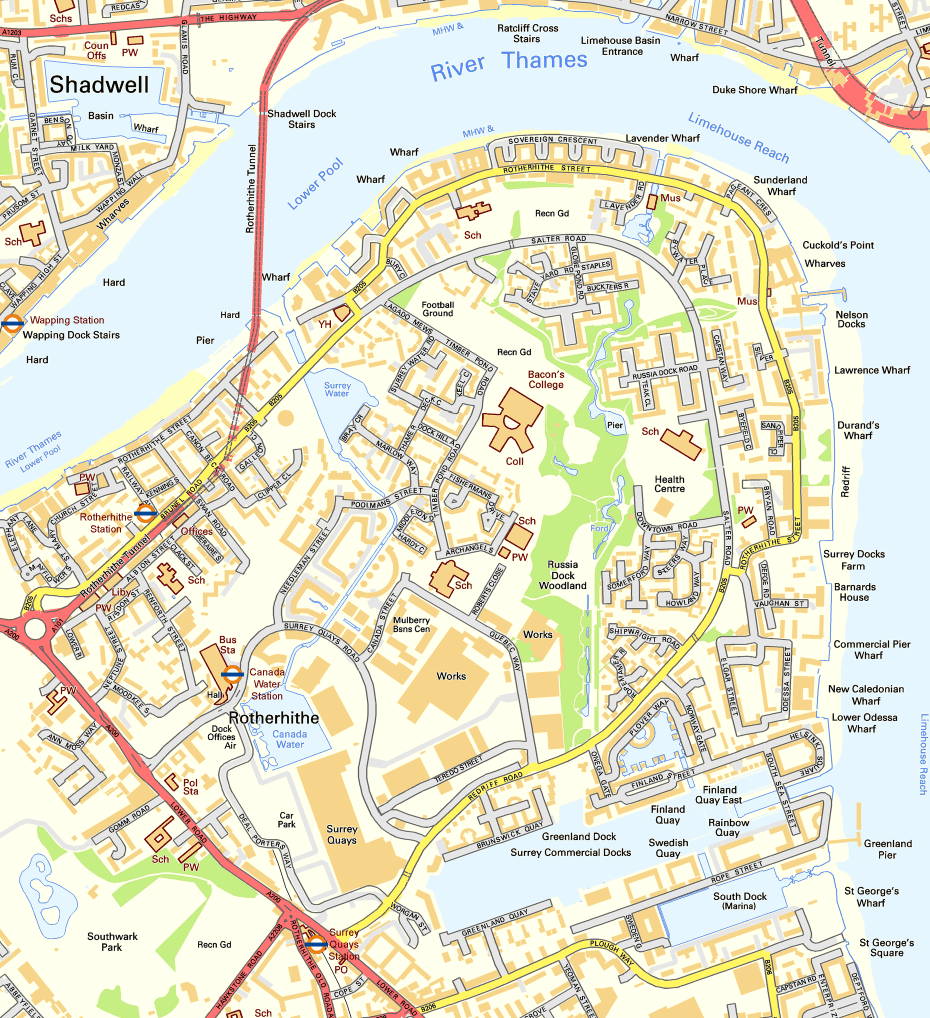
Rotherhithe
Rotherhithe () is a district of south-east London, England, and part of the London Borough of Southwark. It is on a peninsula on the south bank of the Thames, facing Wapping, Shadwell and Limehouse on the north bank, as well as the Isle of Dogs to the east of the Thames and is a part of the London Docklands, Docklands area. It borders Bermondsey to the west and Deptford to the south east. Rotherhithe has a long history as a port, with Elizabethan era, Elizabethan shipyards and working docks until the 1970s. In the 1980s, the area along the river was redeveloped as housing through a mix of warehouse conversions and new-build developments. Following the arrival of the Jubilee line in 1999 (giving quick connections to the West End of London, West End and to Canary Wharf) and the London Overground in 2010 (providing a quick route to the City of London), the rest of Rotherhithe is now a gentrification, gentrifying residential and commuter area, with urban regeneration progressing arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Randall (shipbuilder)
John Randall (1755–1802) was an English shipbuilder. Life The son of John Randall, shipbuilder of Rotherhithe, he had a liberal education, and on the death of his father, around 1776, continued the shipbuilding business under his own management. He also worked on mathematics, and naval construction. In addition to many ships which he built for the mercantile marine and for the East India Company, Randall built over 50 naval vessels. They included 74-gun ships and large frigates, among them being HMS ''Audacious'', HMS ''Ramillies'', and HMS ''Culloden'', noted in the French Revolutionary Wars. He took a prominent part in founding the Society of Naval Architects. On the Peace of Amiens, Randall lowered his rates of pay from the wartime level, and his men went out on strike. The Admiralty permitted him to take on workmen from the Deptford dockyard, and offered a military force to protect them, which was turned down. The Deptford men were prevented from working in his yard; an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Expedition (1784)
Six vessels of the Royal Navy have been named HMS ''Expedition'': * was a 20-gun French ship captured in 1618 and last listed in 1652 * was a 30-gun ship launched in 1637 and sold in 1667 * was a 70-gun ship of the line launched in 1679. She was renamed ''Prince Frederick'' in 1715 and sold in 1784 * was a 44-gun frigate launched in 1747 and broken up in 1764 * was a 14-gun cutter Cutter may refer to: Tools * Bolt cutter * Box cutter, aka Stanley knife, a form of utility knife * Cigar cutter * Cookie cutter * Glass cutter * Meat cutter * Milling cutter * Paper cutter * Side cutter * Cutter, a type of hydraulic rescue to ... launched in 1778 and listed until 1801 * was a 44-gun frigate launched in 1784. She became a 26-gun troopship in 1798 and was broken up in 1817 References * {{DEFAULTSORT:Expedition, HMS Royal Navy ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woolwich Dockyard
Woolwich Dockyard (formally H.M. Dockyard, Woolwich, also known as The King's Yard, Woolwich) was an English Royal Navy Dockyard, naval dockyard along the river Thames at Woolwich in north-west Kent, where many ships were built from the early 16th century until the late 19th century. William Camden called it 'the Mother Dock of all England'. By virtue of the size and quantity of vessels built there, Woolwich Dockyard is described as having been 'among the most important shipyards of seventeenth-century Europe'. During the Age of Sail, the yard continued to be used for shipbuilding and repair work more or less consistently; in the 1830s a specialist factory within the dockyard oversaw the introduction of Steamship, steam power for ships of the Royal Navy. At its largest extent it filled a 56-acre site north of Woolwich Church Street, between Warspite Road and New Ferry Approach; 19th-century naval vessels were fast outgrowing the yard, however, and it eventually closed in 1869 (th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackwall Yard
Blackwall Yard is a small body of water that used to be a shipyard on the River Thames in Blackwall, engaged in ship building and later ship repairs for over 350 years. The yard closed in 1987. History East India Company Blackwall was a shipbuilding area since the Middle Ages. In 1607, the Honorable East India Company (HEIC) decided to build its own ships and leased a yard in Deptford. Initially, this change of policy proved profitable as the first ships cost the Company about £10 per ton instead of the £45 per ton that it had been paying to have ships built for it. However, the situation changed as the Deptford yard came to be expensive to run. In 1614 the East India Company outgrew Deptford and ordered William Burrell to begin work on a new yard for repair, construction and loading of out-going ships. The site Burrell selected was at Blackwall, which was further down river and had deeper water, allowing laden ships to moor closer to the dock. The new yard was fully ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Adventure (1784)
Twelve ships of the Royal Navy have been named ''Adventure''. A thirteenth was planned but never completed: * was a 26-gun galley launched in 1594 and broken up 1645. * was a 32-gun ship launched in 1646, rebuilt in 1691 and captured by the French in 1709. * was a 40-gun fifth rate launched in 1709 and broken up in 1741. * was a fourth-rate ship of the line launched in 1741, rebuilt as a 32-gun fifth rate in 1758, and sold in 1770. * was a 12-gun cutter purchased in 1763 and sold in 1768. * was a survey ship, originally a collier named ''Marquis of Rockingham''. She was purchased in 1771 and renamed ''Rayleigh'', then renamed ''Adventure'' later that year. She accompanied on James Cook's second voyage to the Pacific (1772–1775). She returned to mercantile service after Cook's expedition; she was sunk in the Saint Lawrence River in 1811. * was a 44-gun fifth rate launched in 1784 and broken up in 1816. * HMS ''Adventure'' was a 10-gun transport launched in 1809 as . S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itchenor
West Itchenor is a village and civil parish, on the Manhood Peninsula, in the Chichester District of West Sussex, England. It lies north of the B2179 Chichester to West Wittering road 4.5 miles (7.3 km) southwest of Chichester. The village lies on the shores of Chichester Harbour. The parish covers an area of 413 hectares (1020 acres). According to the Office for National Statistics, based on the 2011 Census estimates, 289 people lived in 140 households, of whom 122 were economically active. 99.7% of residents were White and 76.5% identified as Christian. Since the desertion of East Itchenor in the 15th century, the village has been simply referred to as Itchenor. West Itchenor was an ancient parish of the county of Sussex. Until 1894 it formed part of Manhood Hundred, an ancient division of Chichester Rape. From 1894 to 1933 it was part of Westhampnett Rural District. From 1933 to 1974 it was part of Chichester Rural District, and since 1974 it has been a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Chichester (1785)
HMS ''Chichester'' was a two-deck, fifth-rate ship of the Royal Navy. One of the Adventure-class ships designed by Edward Hunt, she was built to carry 44 guns but for her entire career she served as a troopship, never carrying more than 22. In 1803, she was part of the squadron under Samuel Hood that captured the French held islands of St Lucia and Tobago, and the Dutch colonies of Demerara, Essequibo and Berbice. Design, construction and armament Edward Hunt designed his Adventure class as a marginally broader contender to Thomas Slade's successful 44-gun Roebuck class. The two-deck ships were intended to be 896 bm, with a battery 22 × carronades on the lower deck and 20 × carronades on the upper deckWinfield (2007) p. 183 but most of the class, including ''Chichester'', were built and commissioned as transport or store ships, carrying either 20 or 22 guns and, from 1793, those serving as warships, swapped the carronades for long guns; 20 × on the lower deck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

