|
Admetella Brevis
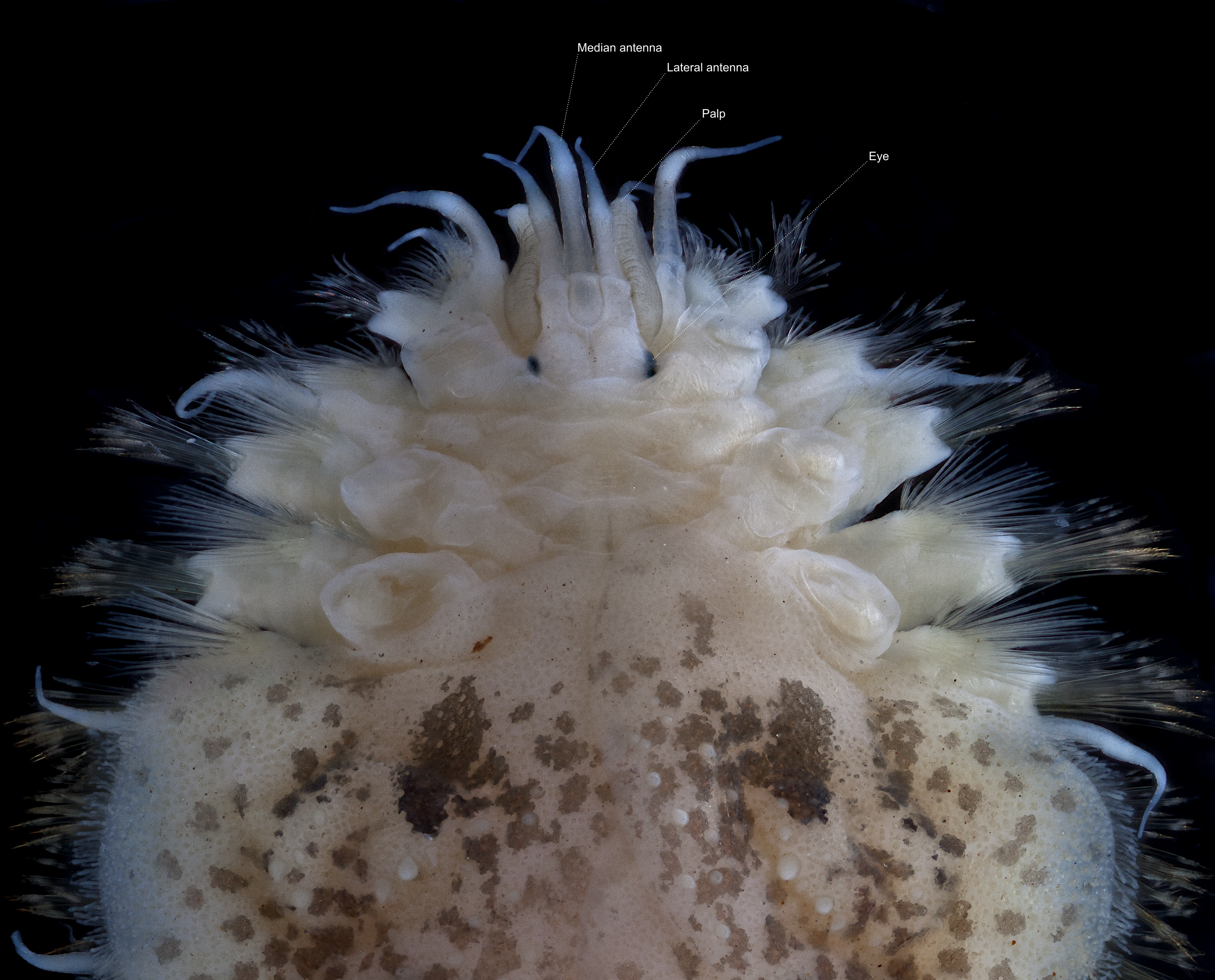
''Admetella brevis'' is a scale worm known from the Hjort Trench in the south-west Pacific Ocean at a depth of 5760m. Description ''Admetella brevis'' has 50 segments and 20 pairs of elytra, with light beige body pigmentation. The lateral antennae are inserted ventrally (beneath prostomium and median antenna), with auxiliary appendages at base of lateral antennae present. Bidentate neurochaetae A chaeta or cheta (from Greek χαίτη “crest, mane, flowing hair"; plural: chaetae) is a chitinous bristle or seta found in annelid worms, (although the term is also frequently used to describe similar structures in other invertebrates such ... are absent. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q2447565 Phyllodocida Animals described in 1978 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynoidae
Polynoidae is a family of marine Polychaete worms known as "scale worms" due to the scale-like elytra on the dorsal surface. Almost 900 species are currently recognised belonging to 9 subfamilies and 167 genera. They are active hunters, but generally dwell in protected environments such as under stones. The group is widely distributed from shallow intertidal waters to hadal trenches. They are the most diverse group of polychaetes in terms of genus number and second most diverse in terms of species number which is almost 8% of all segmented worm species. Description Most Polynoidae species are short and flattened, but can reach as much as 20 cm in length and 10 cm width in ''Eulagisca gigantea'' and ''Eulagisca uschakovi''. Individuals are usually covered almost entirely by elytra, which can be shed and regenerated in many species. The elytra of some species are faintly bioluminescent, and leave glowing traces around the mouthparts of their predators, making those preda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hjort Trench
The Hjort Trench is a linear topographic depression south of Macquarie Island in the southwest Pacific Ocean. Geologically, the depression is considered to be the seafloor expression of an ocean-ocean subduction zone, where the Australian plate is thrusting beneath the Pacific Plate. As the southernmost portion of the Macquarie Ridge Complex, the Hjort Trench lies in an area of diagonal convergence produced by the transform fault evolution of the Emerald Fracture Zone. Frequent seismic events, most less than deep, characterize the transpression along this plate boundary.Lodolo, E. and F. Coren (1994). "The Westernmost Pacific Antarctic plate boundary in the vicinity of the Macquarie triple junction." (In C.A. Ricci, ed. Terra Antarctica, vol.1). pp. 158–161 The trench is named in honour of the Norwegian oceanographer Johan Hjort. Geomorphology The deepest point of Hjort Trench is approximately below sea level. To the east, the Hjort ridge follows the general curve of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
Elytron (Annelida)
In annelids, elytra (; from Greek Greek may refer to: Greece Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group. *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family. **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ... ἔλυτρον "sheath, cover"; singular: elytron ) are shield-like scales that are attached dorsally, one pair on each of a number of alternating segments and entirely or partly cover the dorsum. Elytra are modified dorsal cirri, and their number, size, location, and ornamentation are important taxonomic characters. The basal part of the elytra is known as the elytrophore; if (as is often the case) elytra are lost their presence is indicated by the elytrophore which is still present and visible. Annelids possessing elytra are also known as "scale worms". Possession of elytra is characteristic of the annelid suborder Aphroditiformia. Gallery File:Eunoe leiotentaculata lower res.jpg, A '' Eunoe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostomium
The prostomium (From Ancient Greek, meaning "before the mouth"; plural: prostomia; sometimes also called the "acron") is the cephalized first body segment in an annelid worm's body at the anterior end. It is in front of (but does not include) the mouth, being usually a small shelf- or lip-like extension over the dorsal side of the mouth. The prostomium together with the peristomium, which includes the mouth and pharynx, make up the annelid head. Description The prostomium is part of the head and holds at least part of the brain and often bears sensory structures such as the eyes, antennae and palps. It may function like a kind of overlip when the animal is feeding. The prostomium bears many important taxonomic characters and its shape and composition are important for annelid systematics. In addition to the eyes, antennae and palps, the prostomium can possess appendages such as tentacles or cirri. Moreover, some polychaete prostomia have a posterior extension or ridge with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostomium
The prostomium (From Ancient Greek, meaning "before the mouth"; plural: prostomia; sometimes also called the "acron") is the cephalized first body segment in an annelid worm's body at the anterior end. It is in front of (but does not include) the mouth, being usually a small shelf- or lip-like extension over the dorsal side of the mouth. The prostomium together with the peristomium, which includes the mouth and pharynx, make up the annelid head. Description The prostomium is part of the head and holds at least part of the brain and often bears sensory structures such as the eyes, antennae and palps. It may function like a kind of overlip when the animal is feeding. The prostomium bears many important taxonomic characters and its shape and composition are important for annelid systematics. In addition to the eyes, antennae and palps, the prostomium can possess appendages such as tentacles or cirri. Moreover, some polychaete prostomia have a posterior extension or ridge with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaeta
A chaeta or cheta (from Greek χαίτη “crest, mane, flowing hair"; plural: chaetae) is a chitinous bristle or seta found in annelid worms, (although the term is also frequently used to describe similar structures in other invertebrates such as arthropods). Polychaete annelids, ('polychaeta' literally meaning "many bristles") are named for their chaetae. In Polychaeta, chaetae are found as bundles on the parapodia, paired appendages on the side of the body. The chaetae are epidermal extracellular structures, and clearly visible in most polychaetes. They are probably the best studied structures in these animals. Use in taxonomy and identification The ultrastructure of chaetae is fundamentally similar for all taxa but there is vast diversity in chaetal morphology. Moreover, chaetae bear precise characters for determination of species and taxonomic assessment. The shape, absolute and relative size, number, position, ornamentation and type are important taxonomic characters a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phyllodocida
Phyllodocida is an order of polychaete worms in the subclass Aciculata. These worms are mostly marine, though some are found in brackish water. Most are active benthic creatures, moving over the surface or burrowing in sediments, or living in cracks and crevices in bedrock. A few construct tubes in which they live and some are pelagic, swimming through the water column. There are estimated to be more than 4,600 accepted species in the order. Characteristics Phyllodocida are segmented worms and range in size from a few millimetres long to over a metre. Each segment bears a pair of paddle-like parapodia. The prostomium generally has one or two pairs of eyes, a dorsal pair of antennae, a ventral pair of sensory palps and a pair of organs on the neck. The peristomium is a ring, often hidden dorsally by the prostomium and the first segment. There is a muscular proboscis with one or more pairs of jaws. The next few segments tend to differ from those further back in having enlarged do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)