|
Actinobacillus Pleuropneumoniae
''Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae'' (previously ''Haemophilus pleuropneumoniae''), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, respiratory pathogen found in pigs. It was first reported in 1957, and was formally declared to be the causative agent of porcine pleuropneumonia in 1964. It was reclassified in 1983 after DNA studies showed it was more closely related to ''A. lignieresii''. Microbiology ''Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae'' is a nonmotile, Gram-negative, encapsulated coccobacillus bacterium found in the family Pasteurellaceae. It exhibits β-hemolysis activity, thus explaining its growth on chocolate or blood agar, but must be supplemented with NAD ('V factor') to facilitate growth for one of its biological variants (biovar 1). As a facultative anaerobic pathogen, ''A. pleuropneumoniae'' may need CO2 to grow. Depending on the biovar, the bacteria may or may not be positive for urease; both biovars are positive for porphyrin. Porcine pleuropneumonia ''Actinobacillus pleuro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane. Gram-negative bacteria are found in virtually all environments on Earth that support life. The gram-negative bacteria include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', as well as many pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and ''Yersinia pestis''. They are a significant medical challenge as their outer membrane protects them from many antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and lysozyme, an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. Additionally, the outer leaflet of this membrane comprises a complex lipo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and plants, as opposed to a tissue extract or dead organism. This is not to be confused with experiments done ''in vitro'' ("within the glass"), i.e., in a laboratory environment using test tubes, Petri dishes, etc. Examples of investigations ''in vivo'' include: the pathogenesis of disease by comparing the effects of bacterial infection with the effects of purified bacterial toxins; the development of non-antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and new drugs generally; and new surgical procedures. Consequently, animal testing and clinical trials are major elements of ''in vivo'' research. ''In vivo'' testing is often employed over ''in vitro'' because it is better suited for observing the overall effects of an experiment on a living subject. In dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemolysin
Hemolysins or haemolysins are lipids and proteins that cause lysis of red blood cells by disrupting the cell membrane. Although the lytic activity of some microbe-derived hemolysins on red blood cells may be of great importance for nutrient acquisition, many hemolysins produced by pathogens do not cause significant destruction of red blood cells during infection. However, hemolysins are often capable of lysing red blood cells ''in vitro''. While most hemolysins are protein compounds, some are lipid biosurfactants. Properties Many bacteria produce hemolysins that can be detected in the laboratory. It is now believed that many clinically relevant fungi also produce hemolysins. Hemolysins can be identified by their ability to lyse red blood cells ''in vitro''. Not only are the erythrocytes affected by hemolysins, but there are also some effects among other blood cells, such as leucocytes (white blood cells). ''Escherichia coli'' hemolysin is potentially cytotoxic to monocytes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytotoxin
Cytotoxicity is the quality of being toxic to cells. Examples of toxic agents are an immune cell or some types of venom, e.g. from the puff adder (''Bitis arietans'') or brown recluse spider (''Loxosceles reclusa''). Cell physiology Treating cells with the cytotoxic compound can result in a variety of cell fates. The cells may undergo necrosis, in which they lose membrane integrity and die rapidly as a result of cell lysis. The cells can stop actively growing and dividing (a decrease in cell viability), or the cells can activate a genetic program of controlled cell death (apoptosis). Cells undergoing necrosis typically exhibit rapid swelling, lose membrane integrity, shut down metabolism, and release their contents into the environment. Cells that undergo rapid necrosis in vitro do not have sufficient time or energy to activate apoptotic machinery and will not express apoptotic markers. Apoptosis is characterized by well defined cytological and molecular events including a change i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fimbria (bacteriology)
A pilus (Latin for 'hair'; plural: ''pili'') is a hair-like appendage found on the surface of many bacteria and archaea. The terms ''pilus'' and '' fimbria'' (Latin for 'fringe'; plural: ''fimbriae'') can be used interchangeably, although some researchers reserve the term ''pilus'' for the appendage required for bacterial conjugation. All conjugative pili are primarily composed of pilin – fibrous proteins, which are oligomeric. Dozens of these structures can exist on the bacterial and archaeal surface. Some bacteria, viruses or bacteriophages attach to receptors on pili at the start of their reproductive cycle. Pili are antigenic. They are also fragile and constantly replaced, sometimes with pili of different composition, resulting in altered antigenicity. Specific host responses to old pili structures are not effective on the new structure. Recombination genes of pili code for variable (V) and constant (C) regions of the pili (similar to immunoglobulin diversity). As the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithelial Cells
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epithelia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
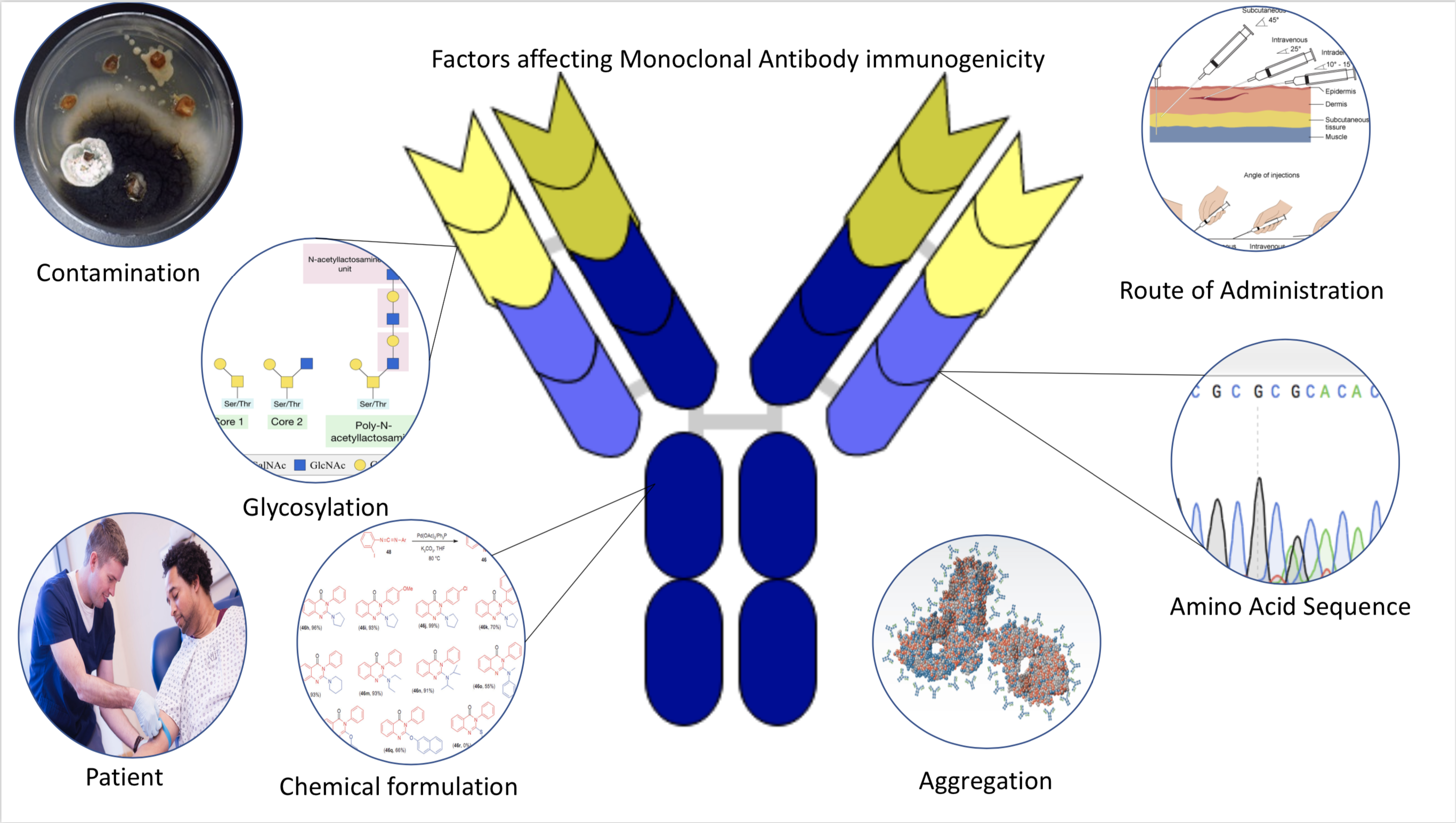
Immunogenicity
Immunogenicity is the ability of a foreign substance, such as an antigen, to provoke an immune response in the body of a human or other animal. It may be wanted or unwanted: * Wanted immunogenicity typically relates to vaccines, where the injection of an antigen (the vaccine) provokes an immune response against the pathogen, protecting the organism from future exposure. Immunogenicity is a central aspect of vaccine development. * Unwanted immunogenicity is an immune response by an organism against a therapeutic antigen. This reaction leads to production of anti-drug-antibodies (ADAs), inactivating the therapeutic effects of the treatment and potentially inducing adverse effects. A challenge in biotherapy is predicting the immunogenic potential of novel protein therapeutics. For example, immunogenicity data from high-income countries are not always transferable to low-income and middle-income countries. Another challenge is considering how the immunogenicity of vaccines changes with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with water (hydrolysis) using amylase enzymes as catalyst, which produces constituent sugars (monosaccharides, or oligosaccharides). They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Examples include storage polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen and galactogen and structural polysaccharides such as cellulose and chitin. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure, these macromolecules can have distinct properties from their monosaccharide building blocks. They may be amorphous or even insoluble in water. When all the monosaccharides in a polysaccharide are the same type, the polysaccharide is called a homopolysaccharide or homoglycan, but when more t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotype
A serotype or serovar is a distinct variation within a species of bacteria or virus or among immune cells of different individuals. These microorganisms, viruses, or cells are classified together based on their surface antigens, allowing the epidemiologic classification of organisms to the subspecies level. A group of serovars with common antigens is called a serogroup or sometimes ''serocomplex''. Serotyping often plays an essential role in determining species and subspecies. The ''Salmonella'' genus of bacteria, for example, has been determined to have over 2600 serotypes. ''Vibrio cholerae'', the species of bacteria that causes cholera, has over 200 serotypes, based on cell antigens. Only two of them have been observed to produce the potent enterotoxin that results in cholera: O1 and O139. Serotypes were discovered by the American microbiologist Rebecca Lancefield in 1933. Role in organ transplantation The immune system is capable of discerning a cell as being 'self' or 'n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
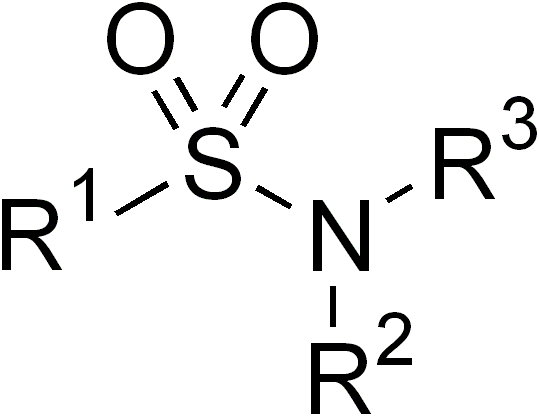
Sulfonamide (medicine)
Sulfonamide is a functional group (a part of a molecule) that is the basis of several groups of drugs, which are called sulphonamides, sulfa drugs or sulpha drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic (nonantibiotic) antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame. The sulfonylureas and thiazide diuretics are newer drug groups based upon the antibacterial sulfonamides. Allergies to sulfonamides are common. The overall incidence of adverse drug reactions to sulfa antibiotics is approximately 3%, close to penicillin; hence medications containing sulfonamides are prescribed carefully. Sulfonamide drugs were the first broadly effective antibacterials to be used systemically, and paved the way for the antibiotic revolution in medicine. Function In bacteria, antibacterial sulfonamides act as competitive inhibitors of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase (DHP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tylosin
Tylosin is a macrolide antibiotic and bacteriostatic feed additive used in veterinary medicine. It has a broad spectrum of activity against Gram-positive organisms and a limited range of Gram-negative organisms. It is found naturally as a fermentation product of '' Streptomyces fradiae''. Tylosin is used in veterinary medicine to treat bacterial infections in a wide range of species and has a high margin of safety. It has also been used as a growth promotant in some species, and as a treatment for colitis in companion animals. Mode of action Like other macrolides, tylosin has a bacteriostatic effect on susceptible organisms, caused by inhibition of protein synthesis through binding to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome. Spectrum of activity Tylosin has a wide spectrum of activity against Gram-positive bacteria including ''Staphylococcus'', ''Streptococcus'', ''Corynebacterium'', and ''Erysipelothrix''. It has a much narrower Gram-negative spectrum of activity, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' moulds, principally '' P. chrysogenum'' and '' P. rubens''. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using deep tank fermentation and then purified. A number of natural penicillins have been discovered, but only two purified compounds are in clinical use: penicillin G (intramuscular or intravenous use) and penicillin V (given by mouth). Penicillins were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are still widely used today for different bacterial infections, though many types of bacteria have developed resistance following extensive use. 10% of the population claims penicillin allergies but because the frequency of positive skin test results decreases by 10% with each year of avoidance, 90% of these patients can tolerate penicillin. Additionally, those with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |